PPT STRUKTUR DAN FUNGSI SEL PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3304420
Introduction. Microorganisms have long provided powerful systems for understanding basic principles of chromosome organization, dynamics and function, beginning with the replicon hypothesis [].Over the past decade, increasingly sophisticated imaging analysis and insights from physical perspectives have been added to the more traditional tools provided by biochemistry, genetics and molecular.

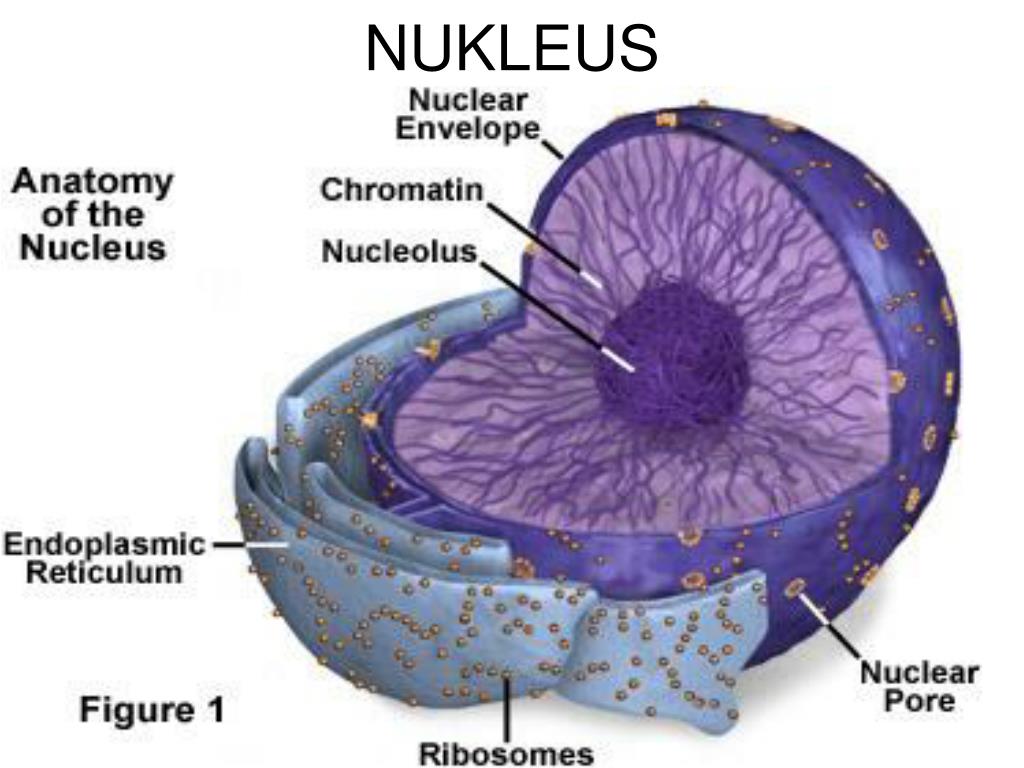
The Nucleus and DNA Replication Anatomy and Physiology I
Bacteria need to find the middle of the cell and prevent the formation of a division septum that bisects the chromosome. The nucleoid occlusion system, mediated by Noc inBacillus subtilis and SlmA.
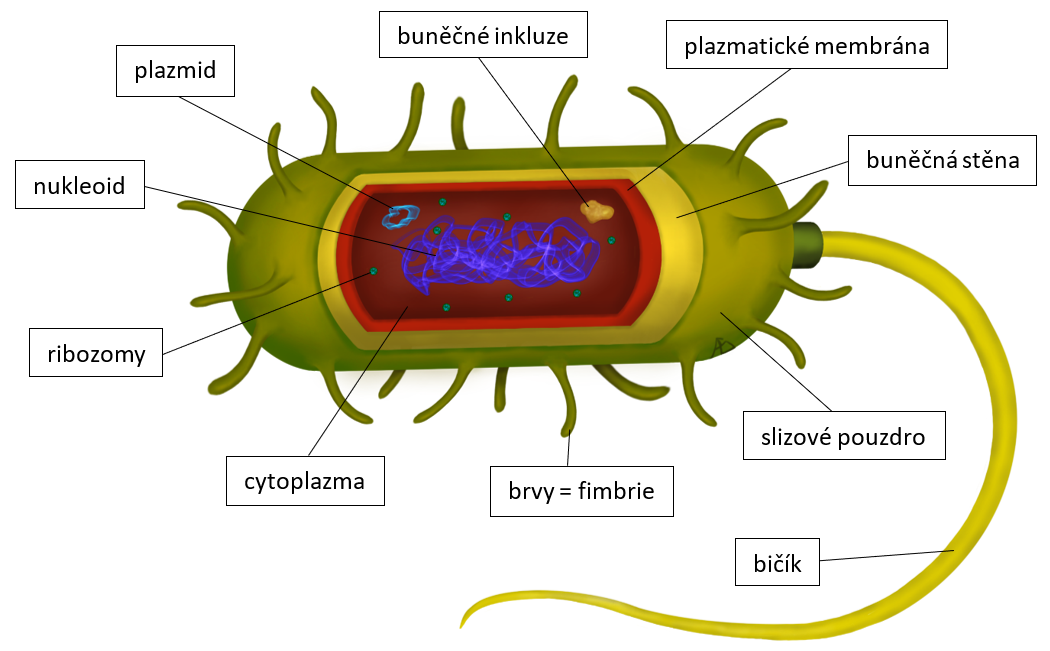
Biologie Buněčná biologie Prokaryotická buňka
Nukleoid. a prokaryotické buňky, uprostřed prokaryotické je kruhovitý nukleoid. Nukleoid ( nukleoplazmatická oblast, centrální oblast, genofor, atp.) je dvoušroubovicová kruhová molekula DNA, která je charakteristická pro prokaryotické buňky bakterií a archeí. Někdy se označuje jako prokaryotický chromozom.

Nukleoid Adalah Wilayah Sel Yang Berisi Materi DNA Primer PDF
Nukleoid je deo citoplazme u prokariotskoj ćeliji u kome se nalazi jedan cirkularni ili linearan molekul DNK ().Naziv nukleoid (sličan jedru) dobija po tome što sadrži DNK i na elektronskim mikrografijama ćelije zauzima centralni položaj, poput jedra.Osobine nukleoida/kromosoma. Nukleoid prokariotske ćelije, za razliku od jedra eukariotske ćelije, nije lako definisati - nije u pitanju.
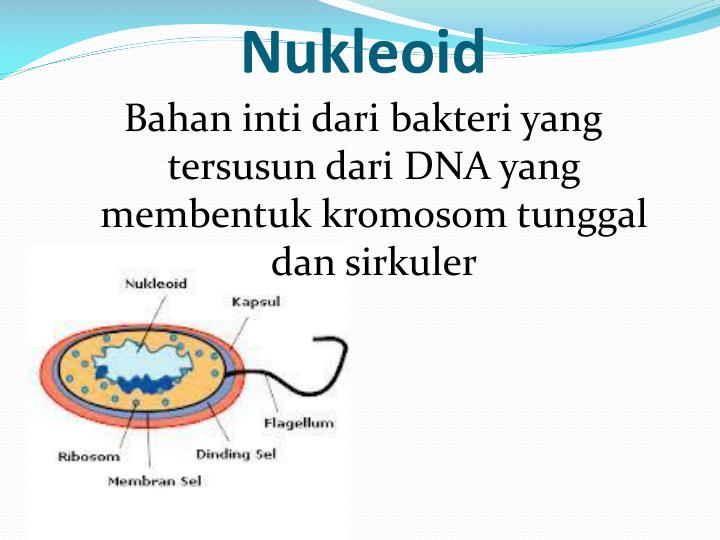
PPT SEL PROKARIOTIK PowerPoint Presentation ID2175295
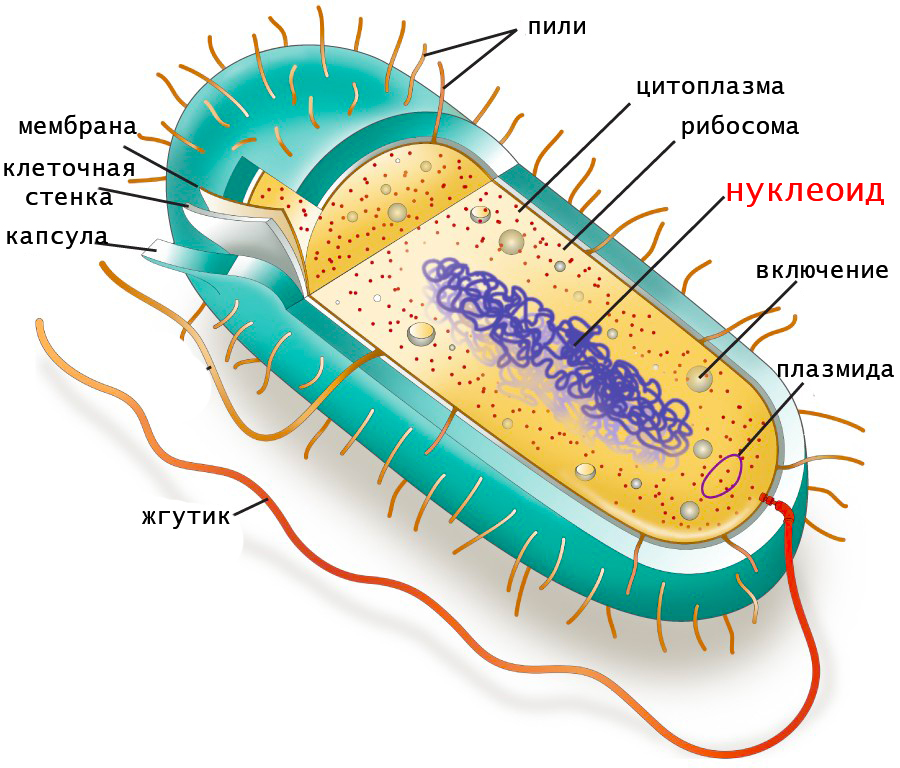
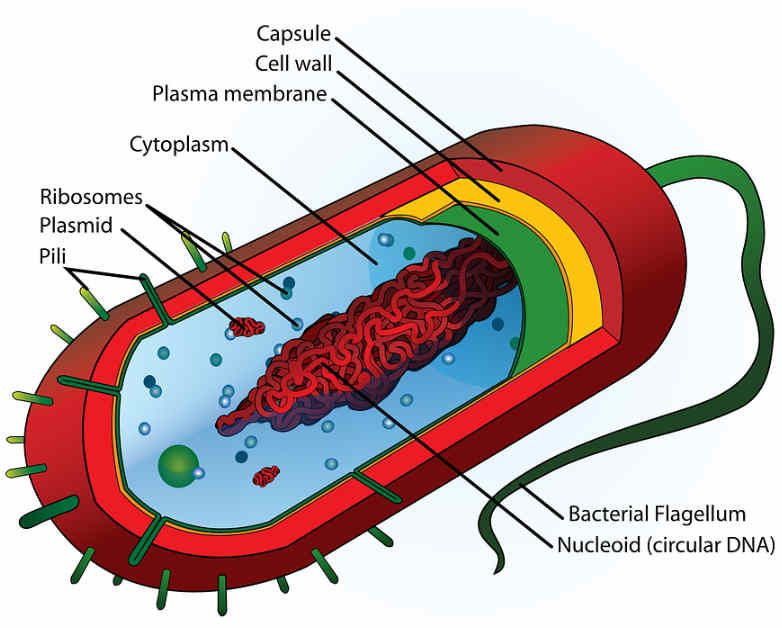
Prokaryote cell showing the nucleoid. In prokaryotes, the nucleoid (meaning nucleus-like and also known as the nuclear region, nuclear body or chromatin body) is an irregularly-shaped region within the cell where the genetic material is localized. The nucleic acid is a circular, double-stranded piece of DNA, and multiple copies may exist.
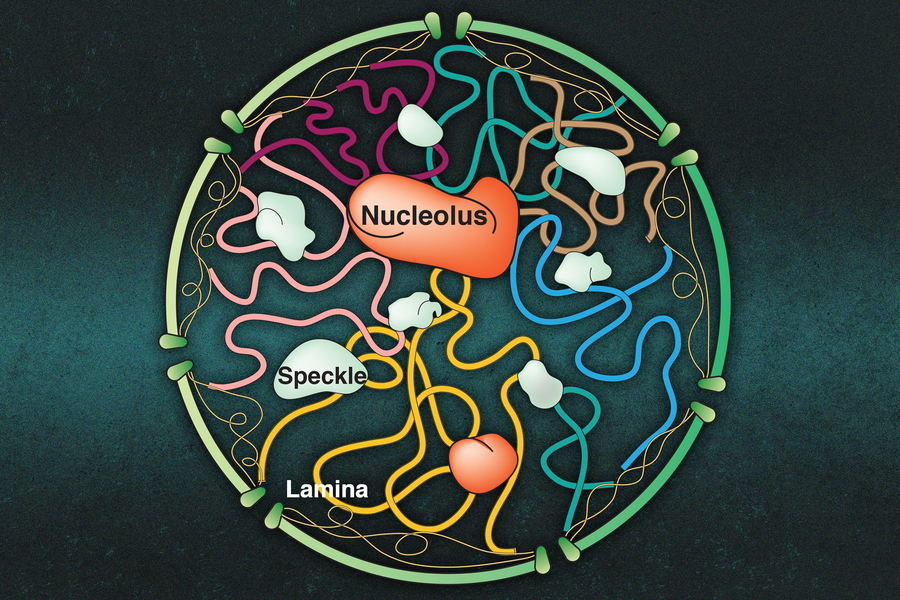
How molecular clusters in the nucleus interact with chromosomes MIT News Massachusetts
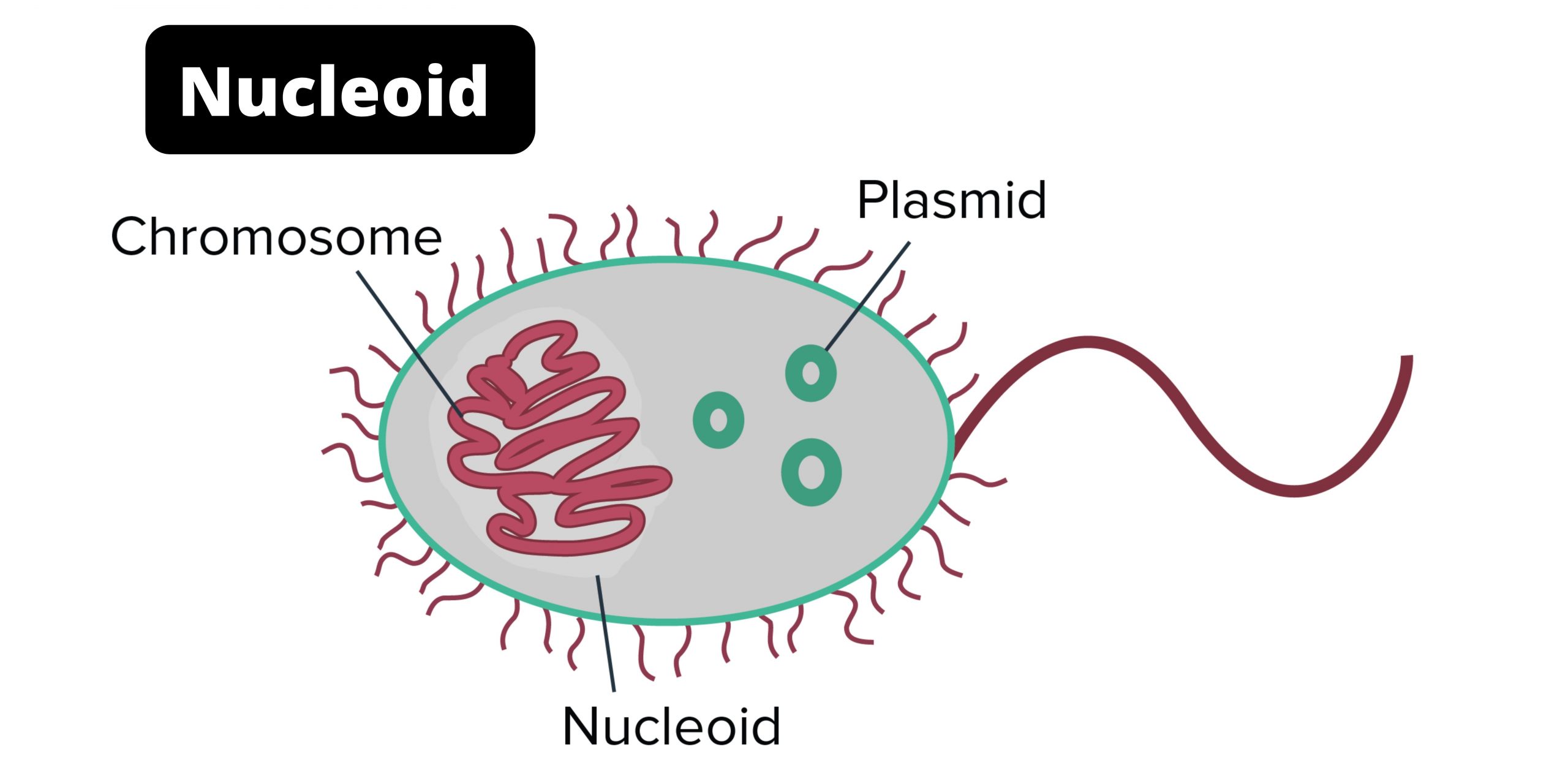
The Nucleoid. The nucleoid (meaning nucleus-like) is an irregularly-shaped region within the cell of a prokaryote that contains all or most of the genetic material. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The genome of prokaryotic organisms generally is a circular, double-stranded piece of DNA, of which multiple copies may exist at any time.

Nucleotide vs Nucleoside Fast Differences and Comparison YouTube
Nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) bind to the bacterial chromosome and alter its dynamics, maintaining nucleoid structure. In this Review, Dillon and Dorman examine the range of proteins in the.

Zellstruktur. Prokaryotische Zelle Mit Nukleoid Vektor Abbildung Illustration von abbildung
The nucleoid, which means nucleus-like, is an irregularly shaped area containing the genetic material of the prokaryotic cell. It is different from the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell in a way that the genetic material is not enclosed in a membrane to separate it from the cytoplasm. Most of the genetic materials found in the nucleoid are the DNAs.
Nucleoid Definition, Functions, Characteristics
The nucleoid is the space within a prokaryotic cell where the genetic information, called the genophore, is found. It is mostly composed of multiple compacted copies of DNA in a continuous thread, with the addition of some RNA and proteins. It is essential for controlling the activity of the cell and reproduction.
Нуклеоид бактерий функции и методы выявления
Nucleoid lacks a protective membrane. A nucleus comprises several chromosomes. Nucleoid usually contains only one chromosome. A nucleus is a spherically shaped organelle. Nucleoid is an irregularly shaped area. Nucleoplasm and nucleolus are present in the nucleus. Nucleoplasm and nucleolus are not found in a nucleoid.

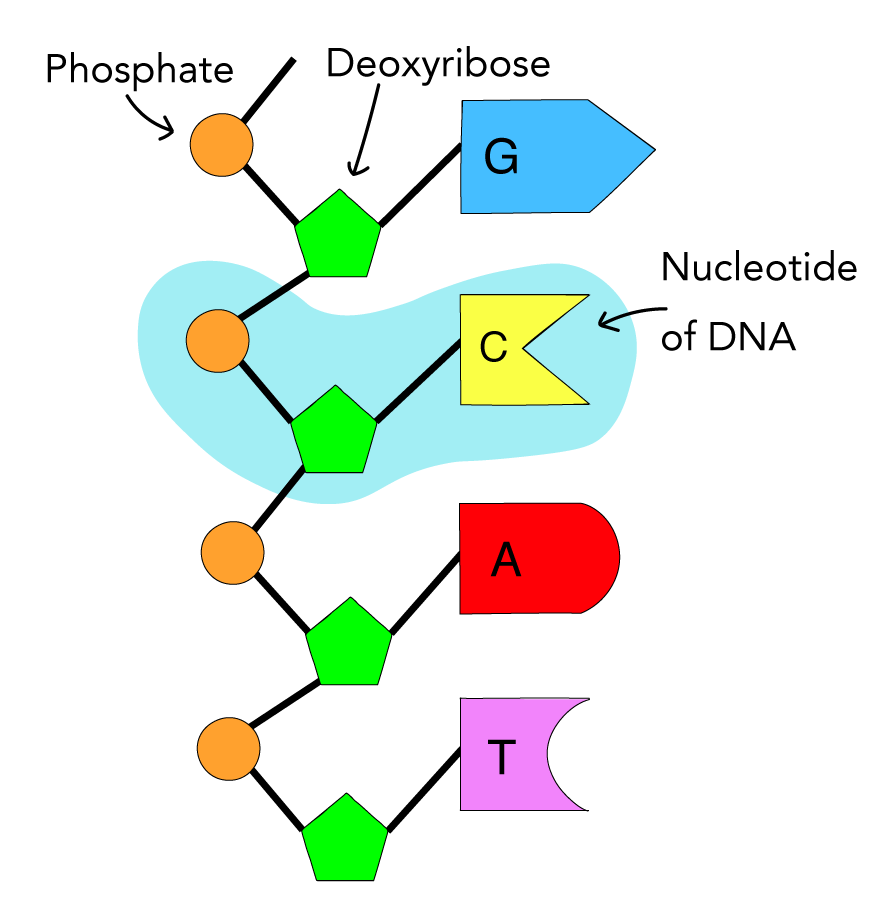
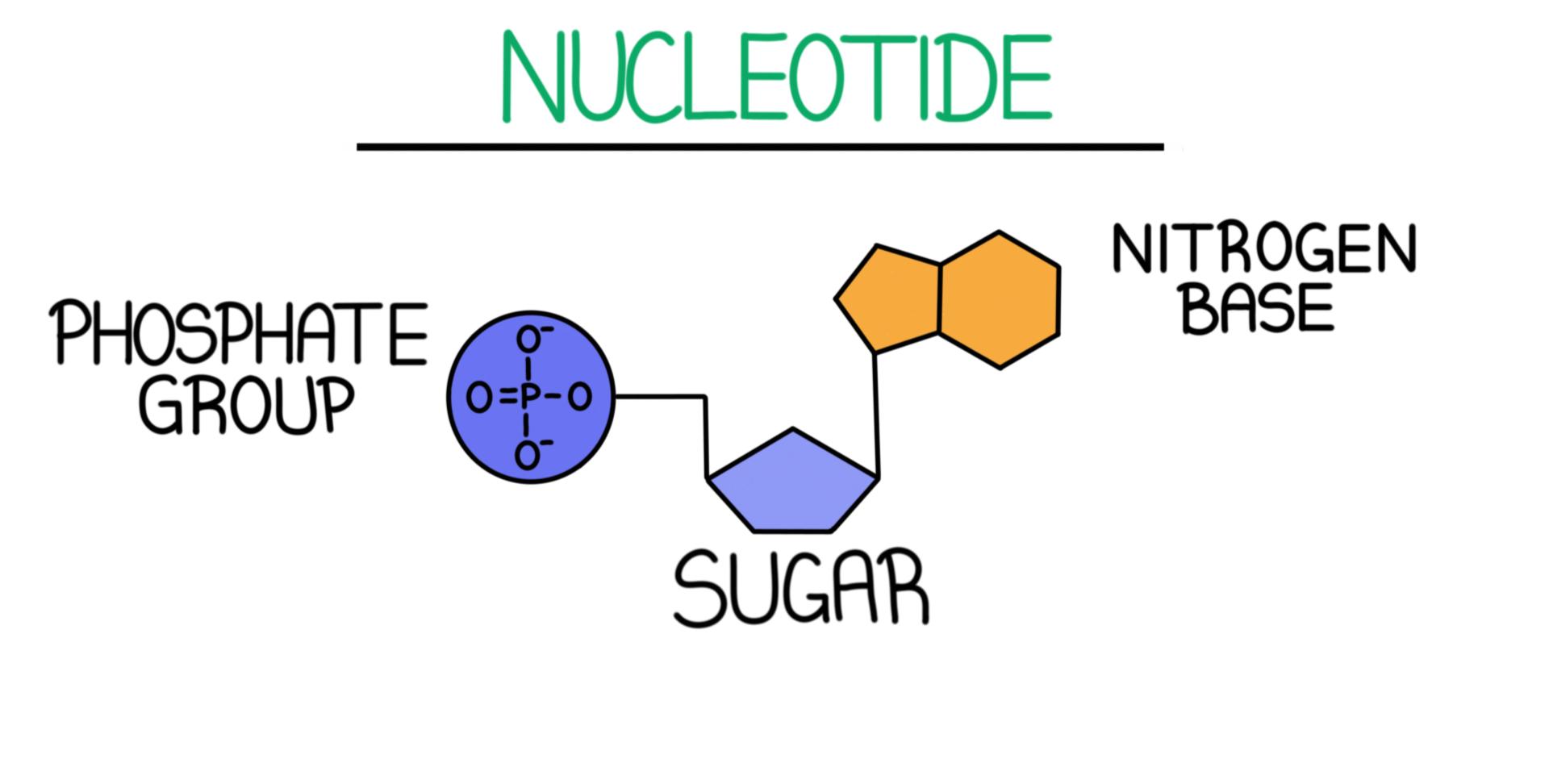
Difference Between Nucleotide and Nucleic Acid Definition, Structure and Composition, Function
mtDNA replication, maintenance, and nucleoid organization. Mara Doimo,. Sjoerd Wanrooij, in The Human Mitochondrial Genome, 2020. 1.4.3 Nucleoid localization. Nucleoids are not randomly distributed in the mitochondrial matrix, but at least a subpopulation interacts with the MIM [193].The first evidence of this interaction dates back to the 1960s, when, with the use of electron microscopy.
About Heredity
Nucleoid. The nucleoid (meaning nucleus -like) is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. [1] [2] [3] The chromosome of a typical prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions, so it needs to be compacted in order to fit.
DNA Structure — Overview & Diagrams Expii
The nucleoid is composed of about 60% DNA, 30% RNA, and 10% protein. The chromosome, composed of DNA, is the predominate molecule in the nucleoid. There is usually one chromosome that is about 1 mm in length, with the typical prokaryotic genome size being on the order of 1.9 to 6.3 x 10 6 base pairs.
Perhatikan gambar sel bakteri dan sel tumbuhan ber...
Nukleoid. Nukleoíd lahko pomeni: [1] območje enotne protoplazme prokariontov, ki ni omejeno z membrano, v katerem leži prstanast kromosom - glej prokariontsko jedro. genetski material virusa v središču viriona. vključek (inkluzija) v celičnem jedru.

Co to jest nukleotyd w biologii?
nucleoid: [noun] the DNA-containing area of a prokaryotic cell (such as a bacterium).

Nucleotides and Bases Generation
Nucleoid Region. The nucleoid region is a membrane-less region in the prokaryotic cell where most, if not all, of the DNA in the cell is located. The nucleoid is located directly in the cytoplasm.