PPT Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID809250
Linear programming, also abbreviated as LP, is a simple method that is used to depict complicated real-world relationships by using a linear function. The elements in the mathematical model so obtained have a linear relationship with each other. Linear programming is used to perform linear optimization so as to achieve the best outcome.
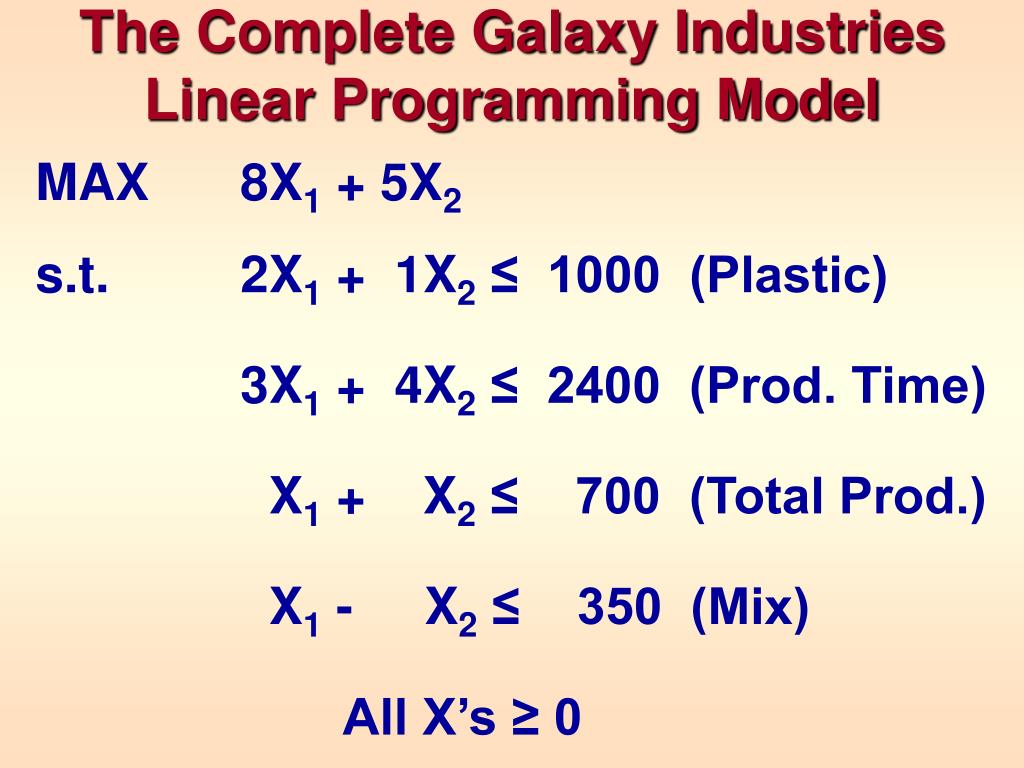
Linear Programming Model
1.2 Concepts in Linear Programming The term linear programming arises from the fact that the objective function is a linear combination of decision variables and parameters that one seeks to maximize or minimize. For example, classic problems seek to maximize profits and flow and to minimize cost or time. The

Module Outline Introduction The Linear Programming Model Examples
A linear program is in canonical form if it is of the form: Max z= cTx subject to: Ax b x 0: A linear program in canonical form can be replaced by a linear program in standard form by just replacing Ax bby Ax+ Is= b, s 0 where sis a vector of slack variables and Iis the m m identity matrix. Similarly, a linear program in standard form can be.

Linear Programming Models (The Graphical Method) YouTube
3: Linear Programming. As we approach day to day life we often need to quantify the things around us, giving structure and numeric value to various situations. This ability to add structure enables us to make choices based..
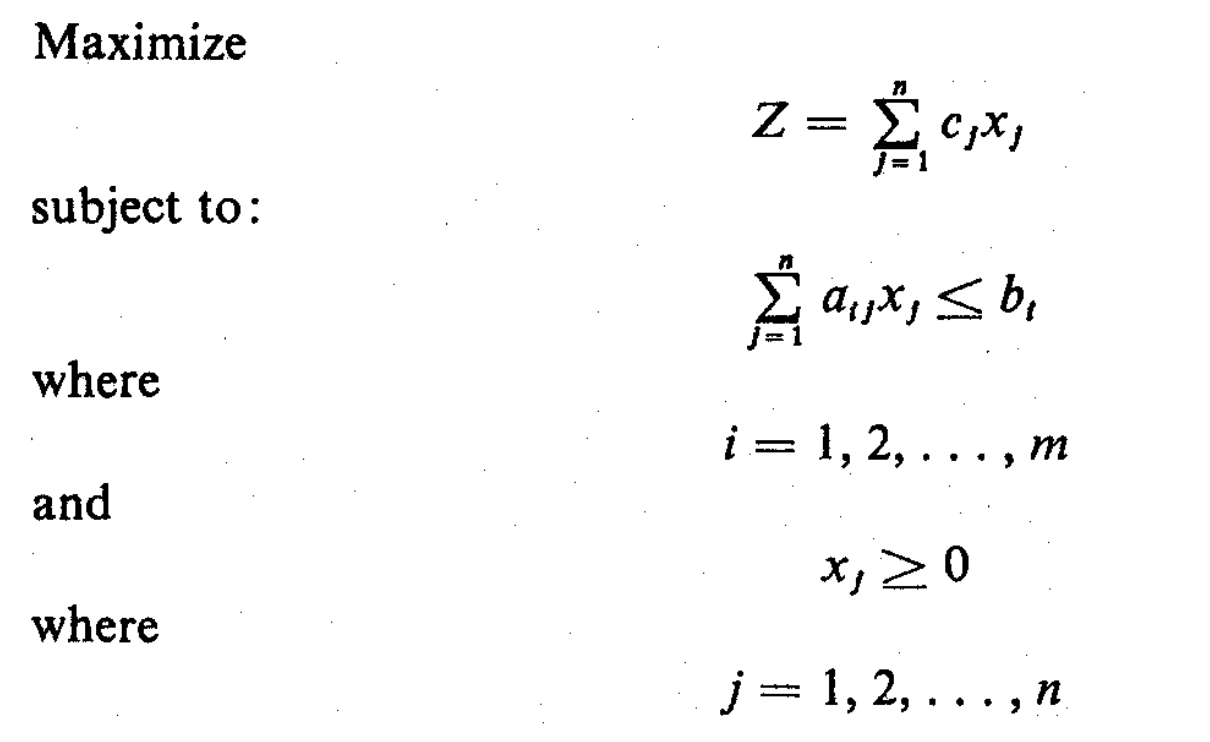
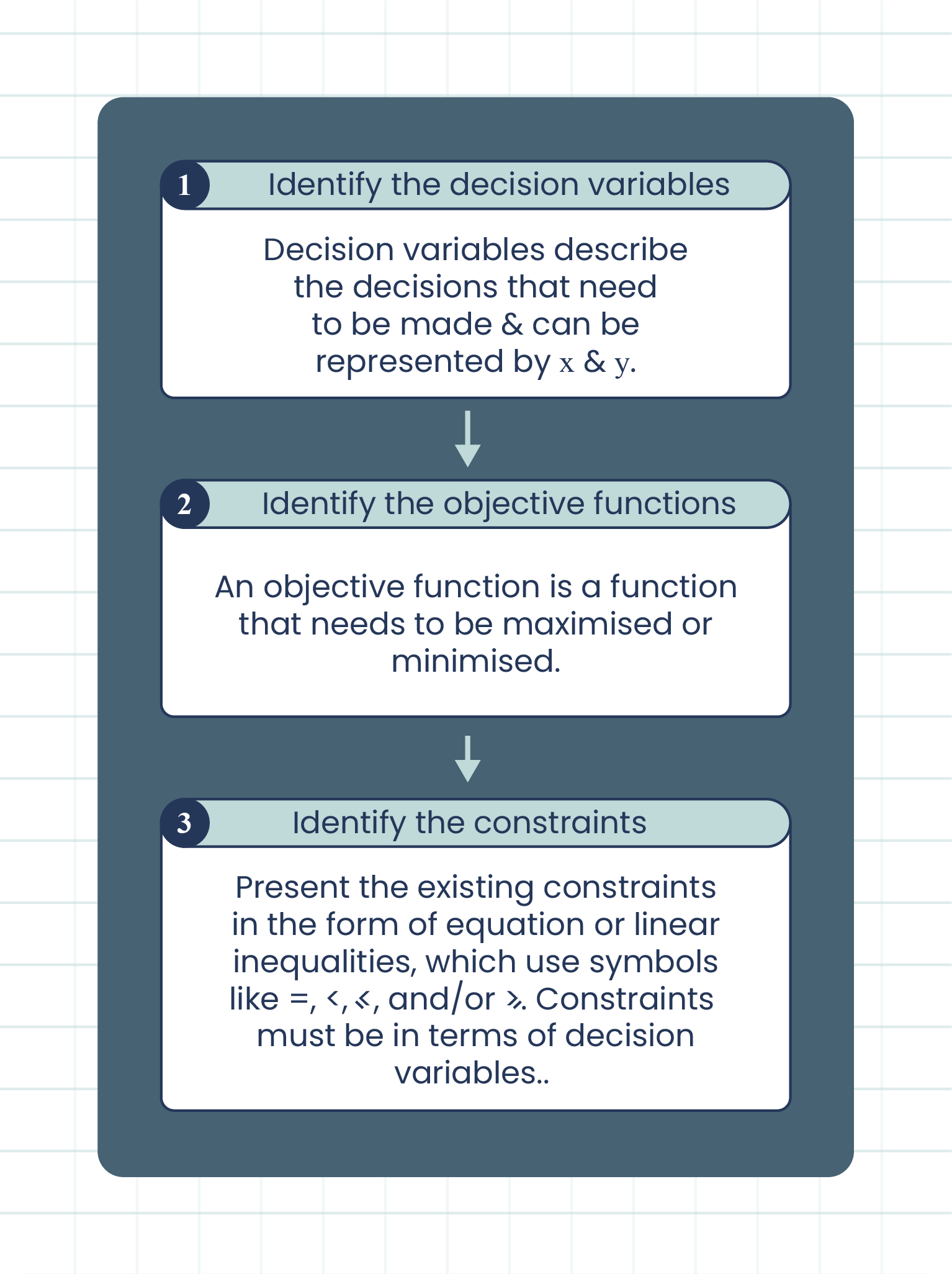
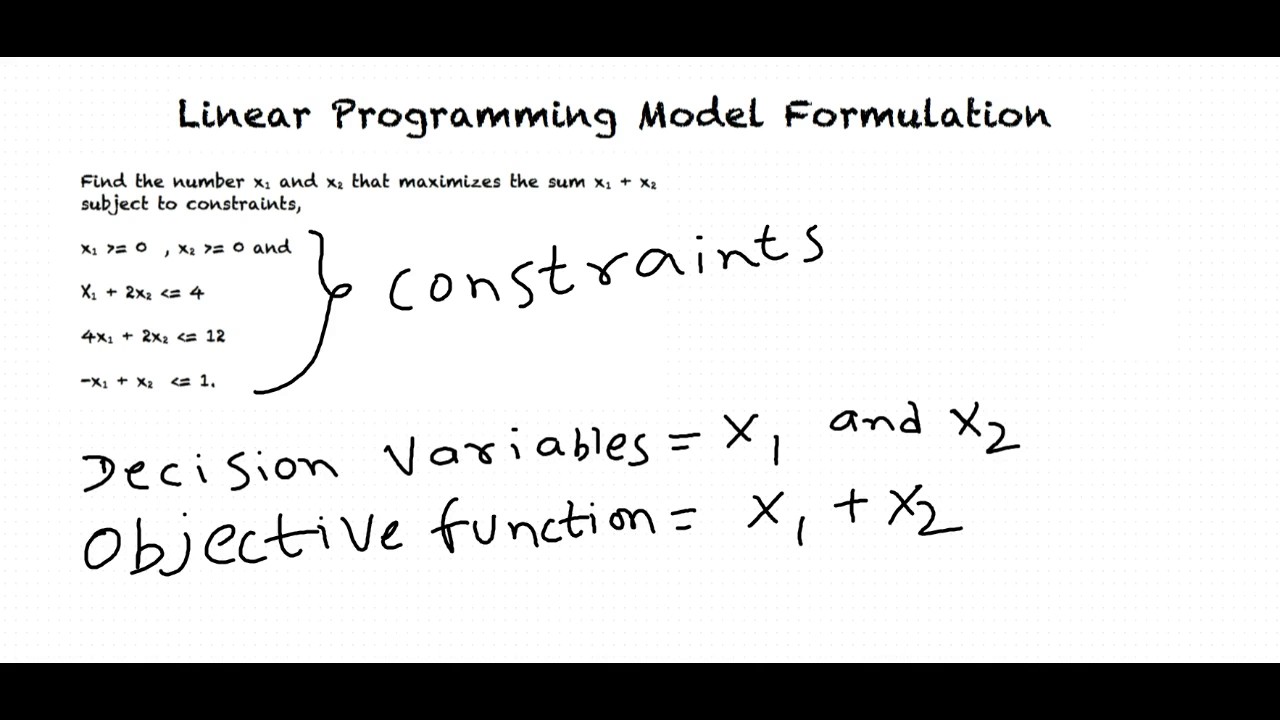
How to formulate a linear programming problem?
linear programming, mathematical modeling technique in which a linear function is maximized or minimized when subjected to various constraints. This technique has been useful for guiding quantitative decisions in business planning, in industrial engineering, and—to a lesser extent—in the social and physical sciences.
PPT Chapter 2 Linear Programming Models Graphical and Computer Methods PowerPoint
Linear programming is an optimization technique for a system of linear constraints and a linear objective function. An objective function defines the quantity to be optimized, and the goal of linear programming is to find the values of the variables that maximize or minimize the objective function.. A factory manufactures doodads and whirligigs. It costs $2 and takes 3 hours to produce a doodad.

Linear Programming Definition, Formula, Problem, Examples
1.1.3. Lasso¶. The Lasso is a linear model that estimates sparse coefficients. It is useful in some contexts due to its tendency to prefer solutions with fewer non-zero coefficients, effectively reducing the number of features upon which the given solution is dependent.
PPT Introduction to Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5508299
Linear programming, also known as linear optimization, is a method for achieving the best possible outcome in a mathematical model where the requirements are defined by linear relationships. Optimization is the way of life. We all have finite resources and time and we want to make the most of them.

Components of a Linear Programming Model YouTube
4.3: Minimization By The Simplex Method. In this section, we will solve the standard linear programming minimization problems using the simplex method. The procedure to solve these problems involves solving an associated problem called the dual problem. The solution of the dual problem is used to find the solution of the original problem.
PPT Introduction to Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5508299
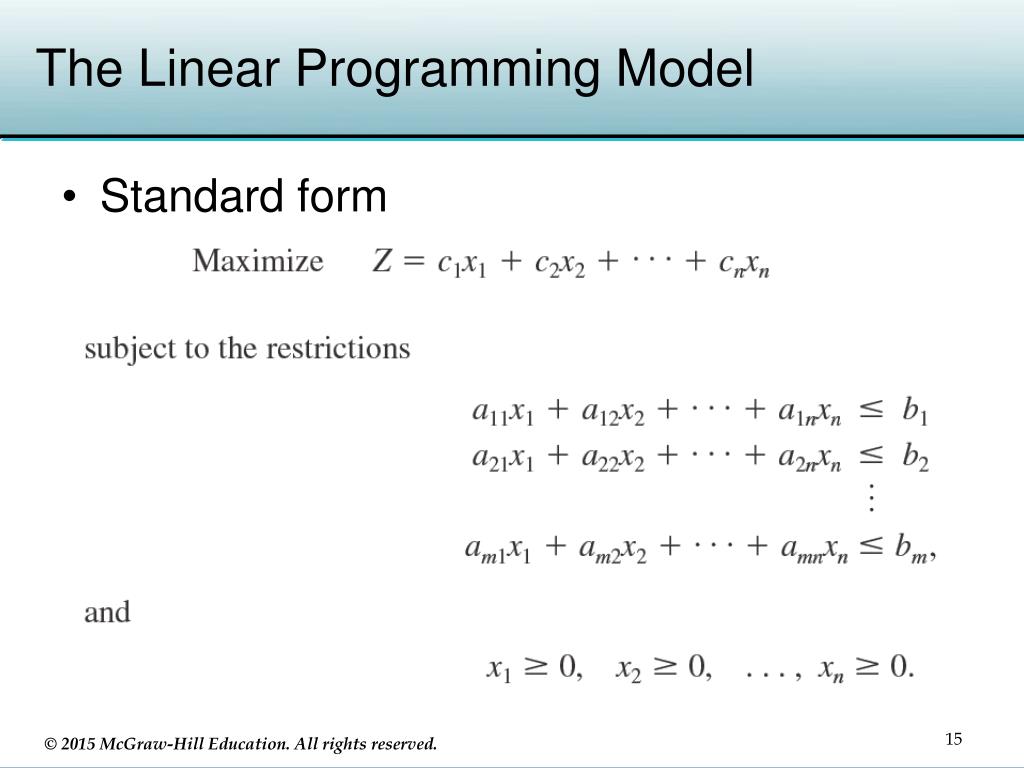
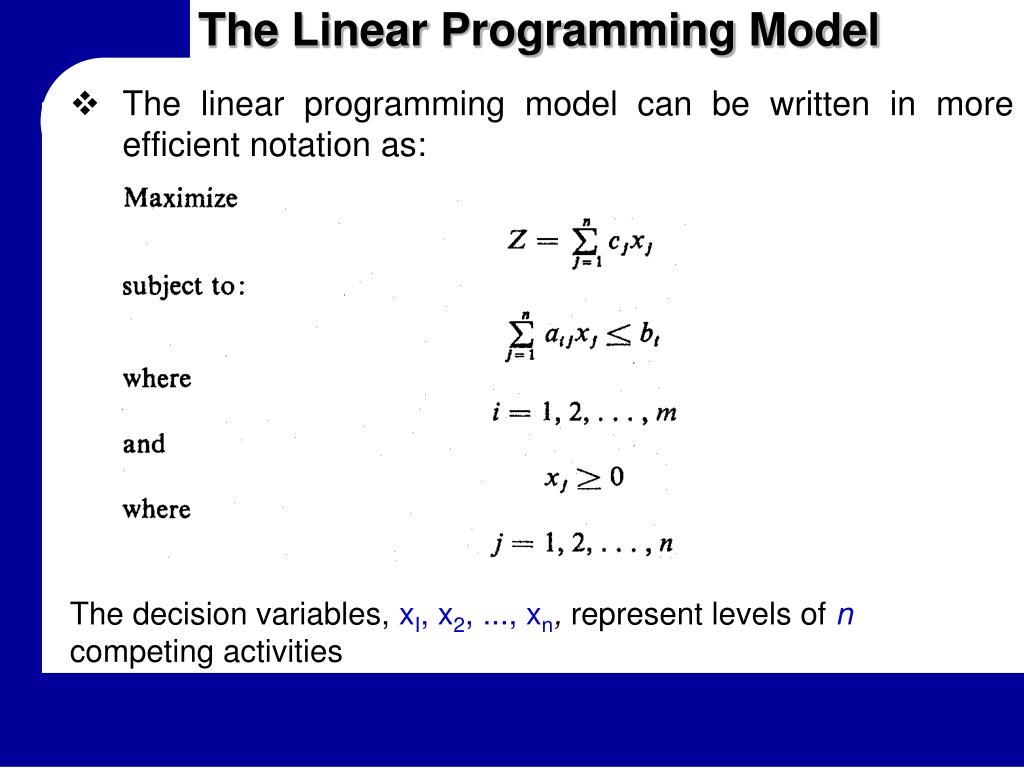
So a linear programming model consists of one objective which is a linear equation that must be maximized or minimized. Then there are a number of linear inequalities or constraints. c T, A and B are constant matrixes. x are the variables (unknowns). All of them are real, continue values. Note the default lower bounds of zero on all variables x.
Linear Programming Model Formulation YouTube
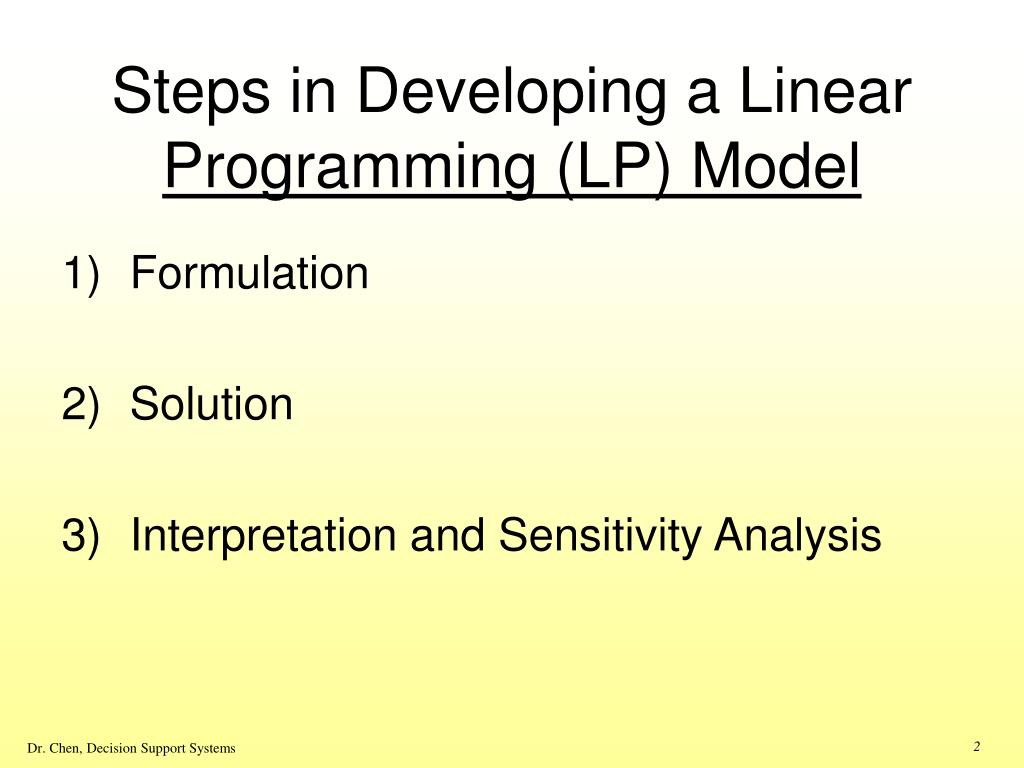
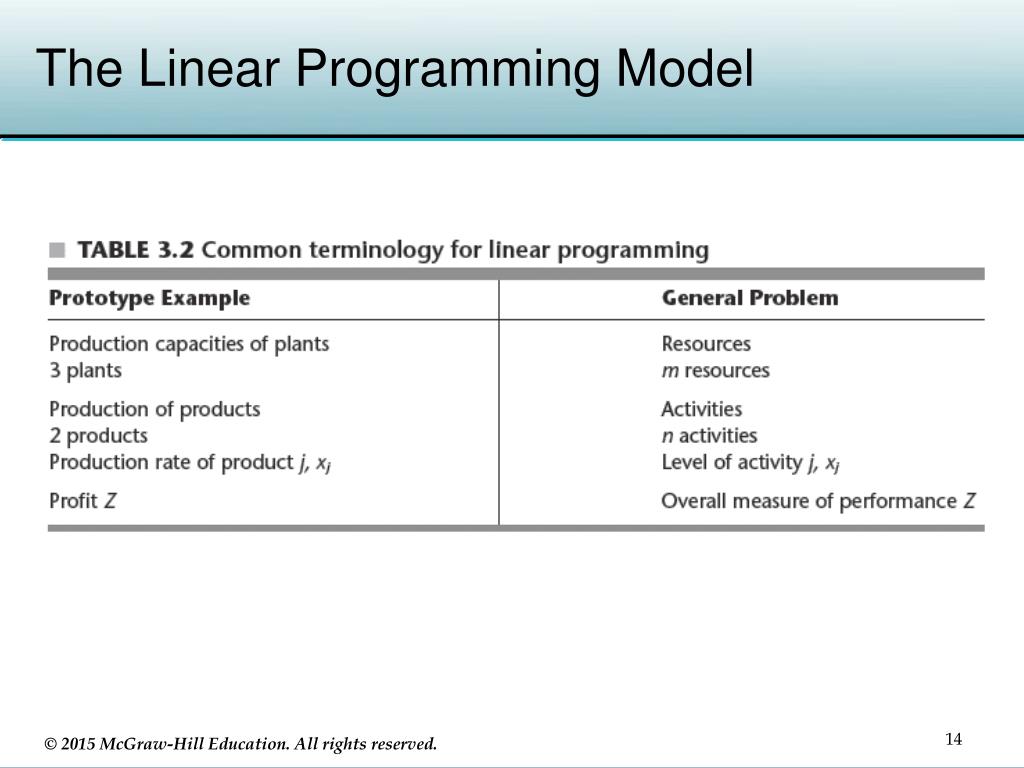
Linear programming uses linear algebraic relationships to represent a firm's decisions, given a business objective, and resource constraints. Steps in application: 1. Identify problem as solvable by linear programming. 2. Formulate a mathematical model of the unstructured problem. 3. Solve the model. 4. Implementation Introduction
PPT Introduction to Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5508299
Linear Programming. In Mathematics, linear programming is a method of optimising operations with some constraints. The main objective of linear programming is to maximize or minimize the numerical value. It consists of linear functions which are subjected to the constraints in the form of linear equations or in the form of inequalities.
PPT Chapter 2 Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5604001
A linear program is in canonical form if it is of the form: Max z = cTx subject to: Ax ≤b x ≥0. A linear program in canonical form can be replaced by a linear program in standard form by just replacing Ax ≤b by Ax + Is = b, s ≥0 where s is a vector of slack variables and I is the m×m identity matrix. Similarly, a linear program in.

To solve a Linear Programming Model with Microsoft Excel YouTube
Lecture 15: Linear Programming. Linear programming (LP) is a method to achieve the optimum outcome under some requirements represented by linear relationships. More precisely, LP can solve the problem of maximizing or minimizing a linear objective function subject to some linear constraints. In general, the standard form of LP consists of.
PPT Introduction to Linear Programming PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5508299
Linear programming can be applied to various fields of study. It is widely used in mathematics and, to a lesser extent, in business, economics, and some engineering problems. Industries that use linear programming models include transportation, energy, telecommunications, and manufacturing.
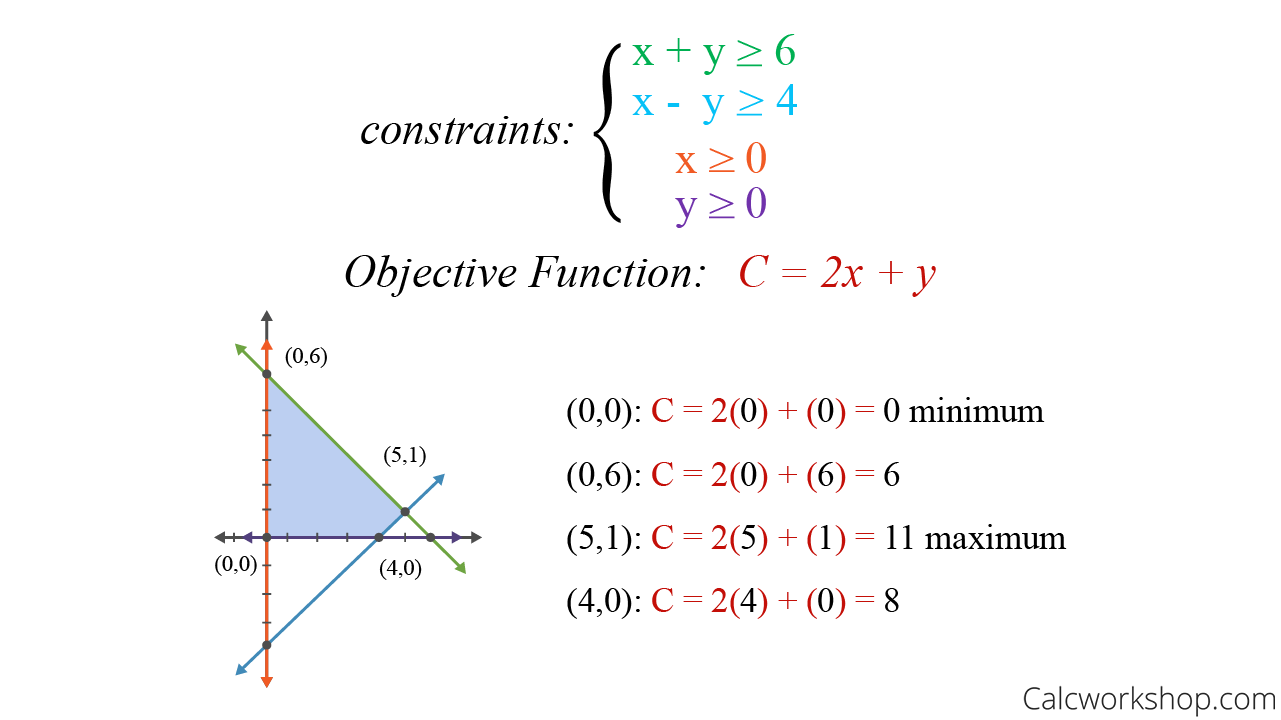
What is Linear Programming? (Explained with 7 Detailed Examples!)
Step 1: Formulate the linear programming problems based on the given constraints. Step 2: Convert all the given inequalities to equations or equalities of the linear programming problems by adding the slack variable to each inequality where ever required. Step 3: Construct the initial simplex table.