
Life cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi in the gut of the insect vector. After
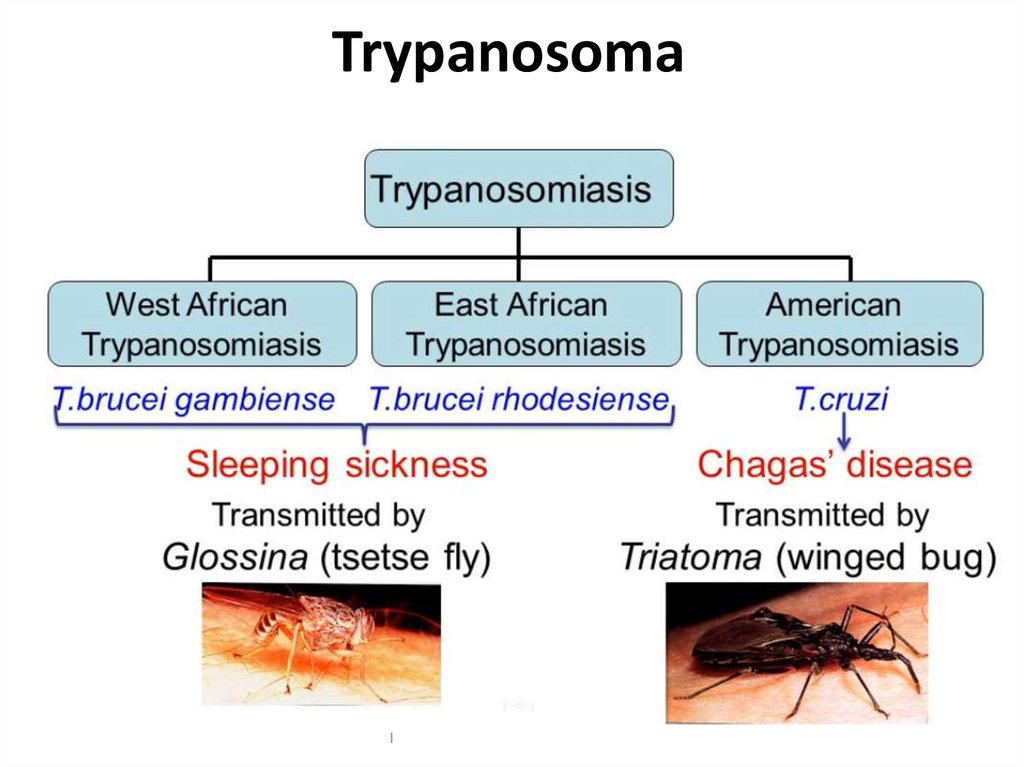
Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) is a parasitic infection that almost invariably progresses to death unless treated. Human African trypanosomiasis caused devastating epidemics during the 20th century. Thanks to sustained and coordinated efforts over the past 15 years, the number of reported cases has fallen to an historically low level. Fewer than 3000 cases were reported in.

The parasite cycle of Trypanosoma brucei. The major mammalian
Introduction African trypanosomiasis is a human and animal infectious disease caused by several species of protozoan parasites of the genus Trypanosoma [1, 2]. These single-celled, eukaryotic.

Ilustración representando el ciclo de vida de Trypanosoma cruzi, el
Search strategy and selection criteria. We searched PubMed for the terms 'Trypanosoma brucei', 'Trypanosoma brucei gambiense', 'Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense', 'Human African trypanosomiasis' to identify papers published between Jan 1, 1990 and Dec 31, 2018 on Human African trypanosomiasis cases in non-endemic countries.Additionally, we reviewed relevant articles cited in.
Trypanosomiasis презентация онлайн
Trypanosomiasis is a parasitic infection that spreads through the bites of tsetse flies in equatorial Africa. Early symptoms include swollen bumps around the bite, a fever, and muscle and joint pain. Advanced symptoms cause confusion and trouble walking, and make it difficult to stay awake. Healthcare providers can cure trypanosomiasis with.

Trypanosoma Under Microscope
Among the trypanosomatids, Trypanosoma is a genus of particular medical and veterinary concern [ 6, 7 ]. The Salivaria group of trypanosomes, so named for being transmitted in the infected saliva of a tsetse fly vector ( Glossina spp.), is represented by Trypanosoma brucei, T. congolense and T. vivax. The former is the most well-studied of the.

Role of mitochondria in life of Trypanosoma brucei AgriHunt A Hunt
This writing method is a study of the literature in Google scholar and Pubmed, with a search using the keyword trypanosoma in humans, emerging parasites, southeast. Keywords: asia. Based on the.

Trypanosoma Spp
Author summary Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease, is a genetically complex protozoan parasite. T. cruzi strains have been classified into seven Discrete Typing Units (DTUs), TcI-TcVI and Tcbat, which have been associated with different geographic distribution and transmission cycles. Two major evolutionary models have been proposed to explain the origin of hybrid.

Figure 137. Life Cycle of Trypanosoma brucei. (concluded
Trypanosoma di Sulawesi akan menjadi perhatian penting dalam dunia konservasi sebelum ditemukannya dampak terhadap kesehatan satwa liar maupun manusia. B. Rumusan Masalah Berdasarkan latar belakang di atas dapat dirumuskan masalah sebagai berikut: 1. Jenis-jenis Trypanosoma apakah yang menginfeksi mamalia kecil di Gunung Dako, Sulawesi Tengah?

Trypanosoma (3) S5175 Microbiology MCQs YouTube
1. Introduction. Trypanosoma brucei is a group of unicellular parasitic protozoa that cause a fatal disease in human beings and domestic animals in Sub-Saharan Africa known as African trypanosomiasis (WHO report; Vickerman, 1986). During its transmission from one mammal to another by the insect vector, the tsetse fly, T. brucei changes its morphology, ultrastructural organization and various.

Trypanosoma
Trypanosoma cruzi infection, currently endemic in 21 countries, is a public health problem not only in the Americas but also in countries with Latin American migrants. However, it is estimated that two-thirds of people with Chagas disease currently live in urban areas and that only 10% of them are aware of it. This review summarizes the most important aspects of the diagnosis of human T. cruzi.

Makalah Trypanosoma B. Rhodesiense PDF
Trypanosoma evansi is one of blood protozoans having the most wide distribution region compared to other Trypanosome species. The parasite causes trypanosomiasis known as Surra. The disease may cause mortality to the infected animals. In general T. evansi only attack animal and cannot infect humans due to apolipoprotein 1 (Apo L-1) in human serum.
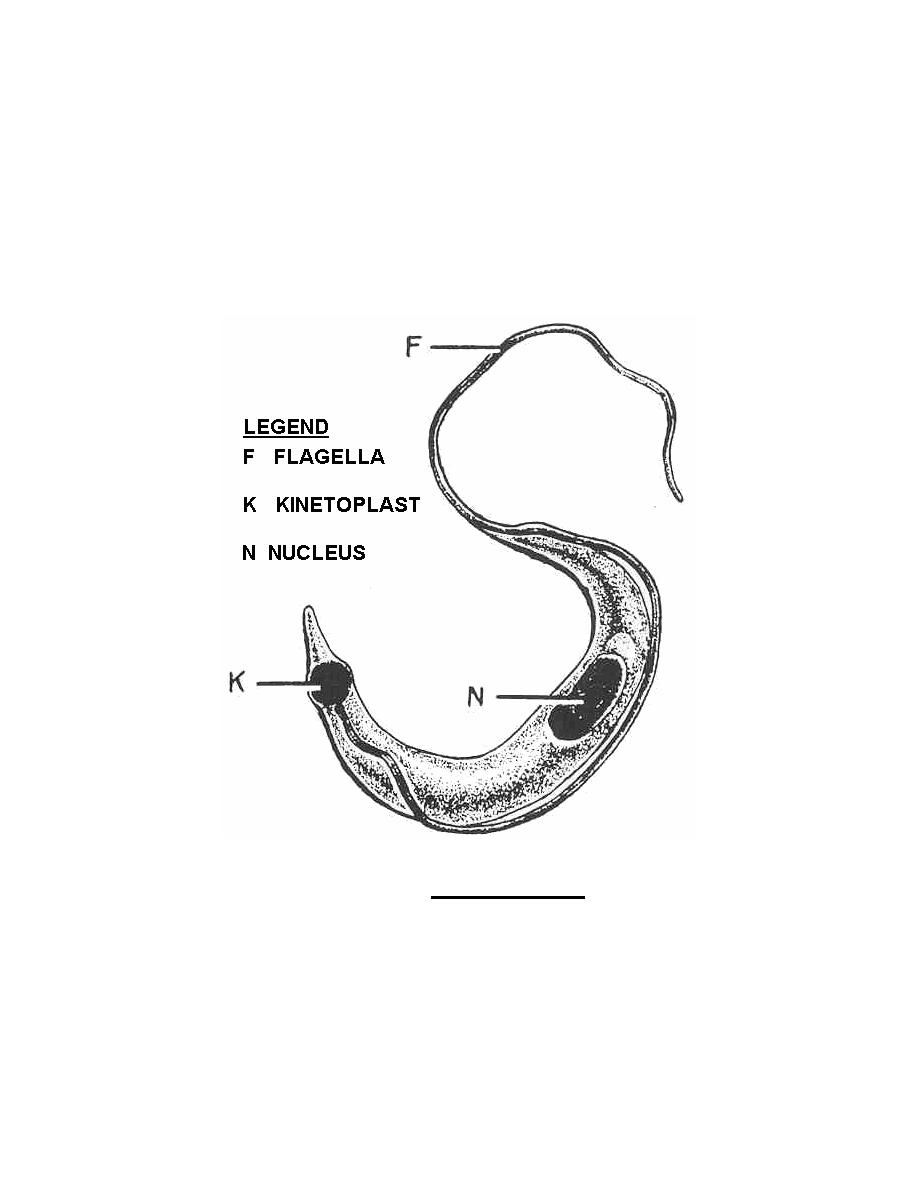
Figure 138. Life cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi. (concluded) Parasitology II
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) also called sleeping sickness, is a parasitic disease classified as one of the world's classical "neglected tropical diseases" representing a major public health threat in sub-Saharan Africa [].Among the parasite species affecting the sub-Saharan Africa countries, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (T.b. gambiense) is the most infectious in West and Central.

2 Trypanosoma cruzi life cycle Görseli, Stok Fotoğraflar ve Vektörler
African trypanosomes are bloodstream protozoan parasites that infect mammals including humans, where they cause sleeping sickness. Long-lasting infection is required to favor parasite transmission between hosts. Therefore, trypanosomes have developed strategies to continuously escape innate and adaptive responses of the immune system, while also preventing premature death of the host. The.
Frontiers Human African Trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) Current
Trypanosoma cruzi is a protozoan parasite that is most frequently transmitted through triatomine bugs. The genome of T. cruzi was fully sequenced in 2005. Triatomine bugs belong to the Rediviidae family and are colloquially known as "kissing bugs" due to sucking blood near the victim's face when feeding. Another common name they are known.

Makalah Trypanosoma Kel 7 PDF
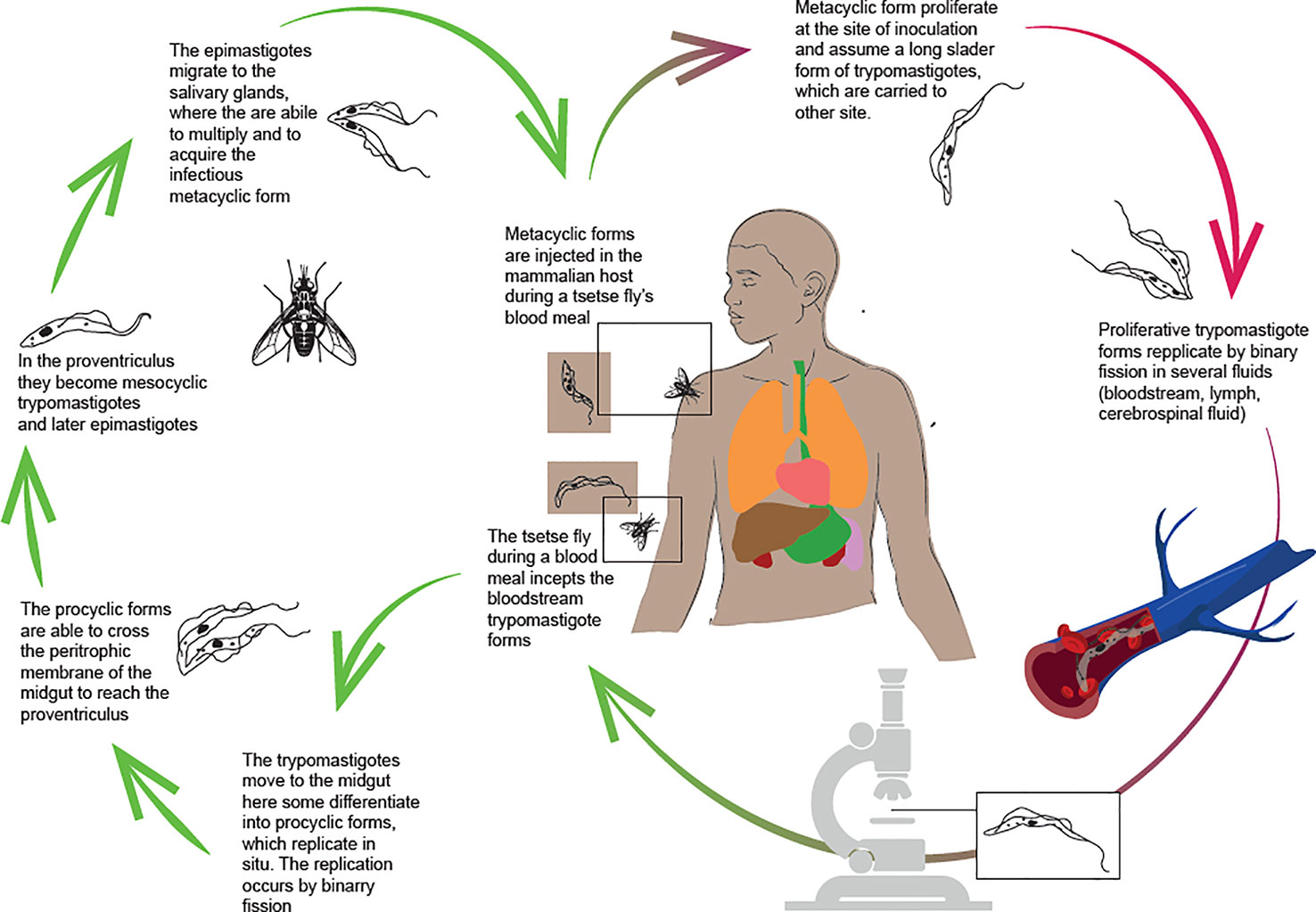
Trypanosoma brucei causes African trypanosomiasis in humans and nagana in domestic animals. This vector-borne parasite, transmitted by the tsetse fly, affects rural areas in sub-Saharan Africa. When injected by the fly, metacyclic-form parasites are introduced into the host dermis and then disseminate into the bloodstream as replicative long slender forms.

Morphology of Trypanosoma evansi with Giemsa staining viewed under a
Trypanosoma brucei is a protozoan parasite that causes human and animal African trypanosomiases (HAT and AAT). In the mammalian host, the parasite lives entirely extracellularly, in both the blood and interstitial spaces in tissues. Although most T. brucei research has focused on the biology of blood- and central nervous system (CNS)-resident parasites, a number of recent studies have.