Chicken Pox Kid Care Pediatrics
Laboratory Testing. Laboratory testing is recommended to: Confirm suspected cases of varicella. Confirm varicella as the cause of outbreaks. Confirm varicella in severe cases (hospitalizations or deaths) or unusual cases. Determine susceptibility to varicella. Determine if suspected vaccine-related adverse events were caused by vaccine-strain VZV.

Billing and Coding for Shingles A Painful Skin Condition
ICD-10 codes not covered for indications listed in the CPB: B01.9: Varicella without complication [prevention of chickenpox]. to 200 participants greater than or equal to 70 years of age who had received a dose of ZV greater than or equal to 10 years previously. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody titers (measured by a VZV glycoprotein.

Disseminated varicella zoster virus encephalitis The Lancet
Zoster without complications. B02.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B02.9 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B02.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 B02.9 may differ.

Diagnosis Varicella Alomedika
For more information on varicella-zoster virus specimen collection, storage, and handling, please contact: National VZV Laboratory. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1600 Clifton Road, NE. Atlanta, GA 30333. Tel: 404-639-2178 or 404-754-0114. Email: [email protected].

Varicella (chickenpox) Immunisation Advisory Centre
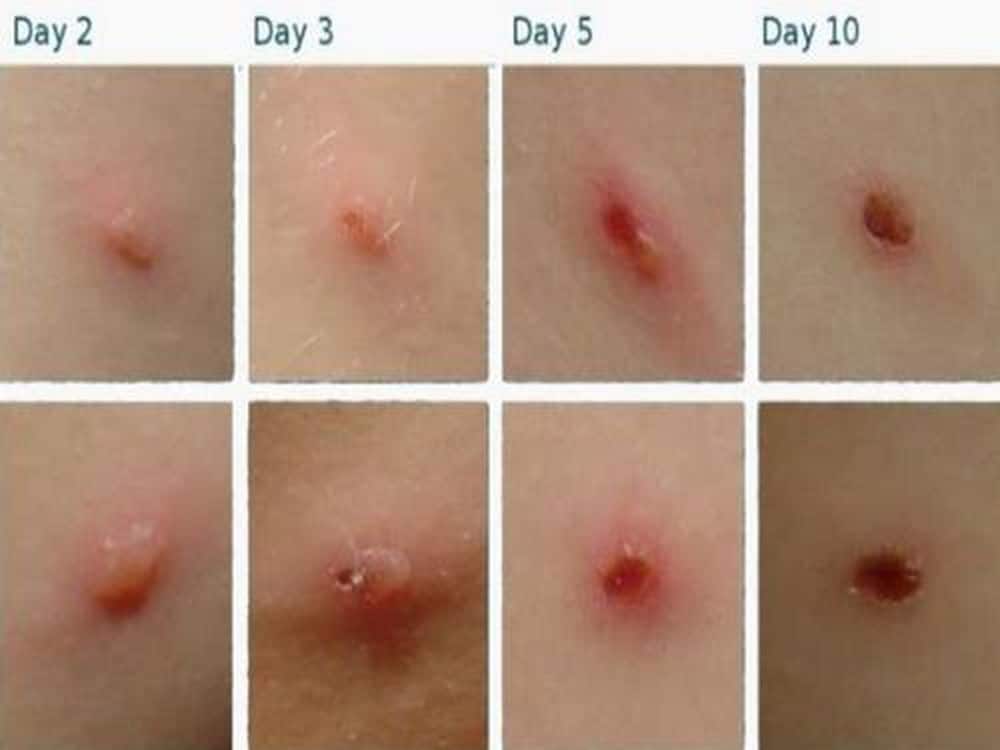
The average incubation period for varicella is 14 to 16 days after exposure to a varicella or a herpes zoster rash, with a range of 10 to 21 days. A mild prodrome of fever and malaise may occur 1 to 2 days before rash onset, particularly in adults. In children, the rash is often the first sign of disease.

Varicella Titer Cpt Code
Shingles is a disease caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. The virus stays dormant in the nerves until your immune system weakens. It then spreads to the skin around the nerves. You can have shingles if you've had varicella (chickenpox). About one-third of people will get shingles at some time.
VaricellaZoster Grade 2 Microbix Biosystems Inc.
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute, highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. Only one serotype of VZV is known, and humans are the only reservoir. Following infection, the virus remains latent in neural ganglia and in about 10-20% of cases it is reactivated it is reactivated to cause herpes zoster, or shingles, generally in persons.

VaricellaZoster Virus Spread Infectious Diseases JAMA JAMA Network
View ICD-10 Tree. Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) » Viral infections characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions (B00-B09) » Varicella [chickenpox] (B01) ICD-10 Subcodes (5) B01.0 - Varicella meningitis. B01.1 - Varicella encephalitis, myelitis and encephalomyelitis. B01.2 - Varicella pneumonia.
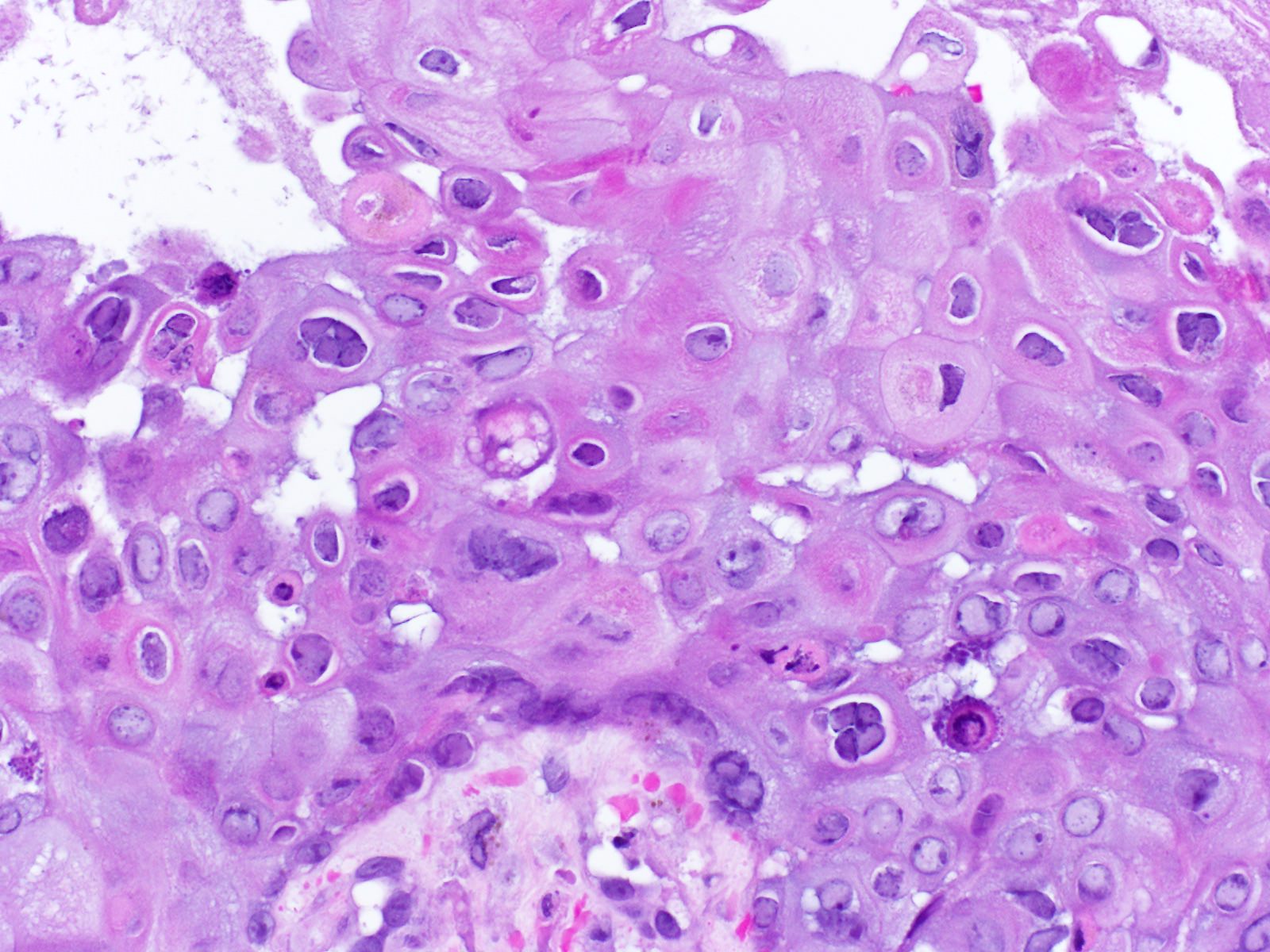
Pathology Outlines Herpes simplex or varicella zoster
Zoster encephalitis. B02.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B02.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B02.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 B02.0 may differ.

VaricellaZoster Virus Infections in Patients Treated With Fingolimod Risk Assessment and
B02.1 Zoster meningitis. B02.2 Zoster with other nervous system involvement. B02.21 Postherpetic geniculate ganglionitis. B02.22 Postherpetic trigeminal neuralgia. B02.23 Postherpetic polyneuropathy. B02.24 Postherpetic myelitis. B02.29 Other postherpetic nervous system involvement. B02.3 Zoster ocular disease.
VaricellaZoster Grade 2 Microbix Biosystems Inc.
During varicella, VZV establishes a latent infection in sensory ganglia. Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, results from activation of latent VZV from a sensory ganglion. The virus then travels down the associated sensory nerve to the skin, leading to a characteristic dermatomal rash, usually in association with dermatomal pain.

Chickenpox (varicella zoster) Clinical Review
B02.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B02.8 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B02.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 B02.8 may differ. Applicable To.
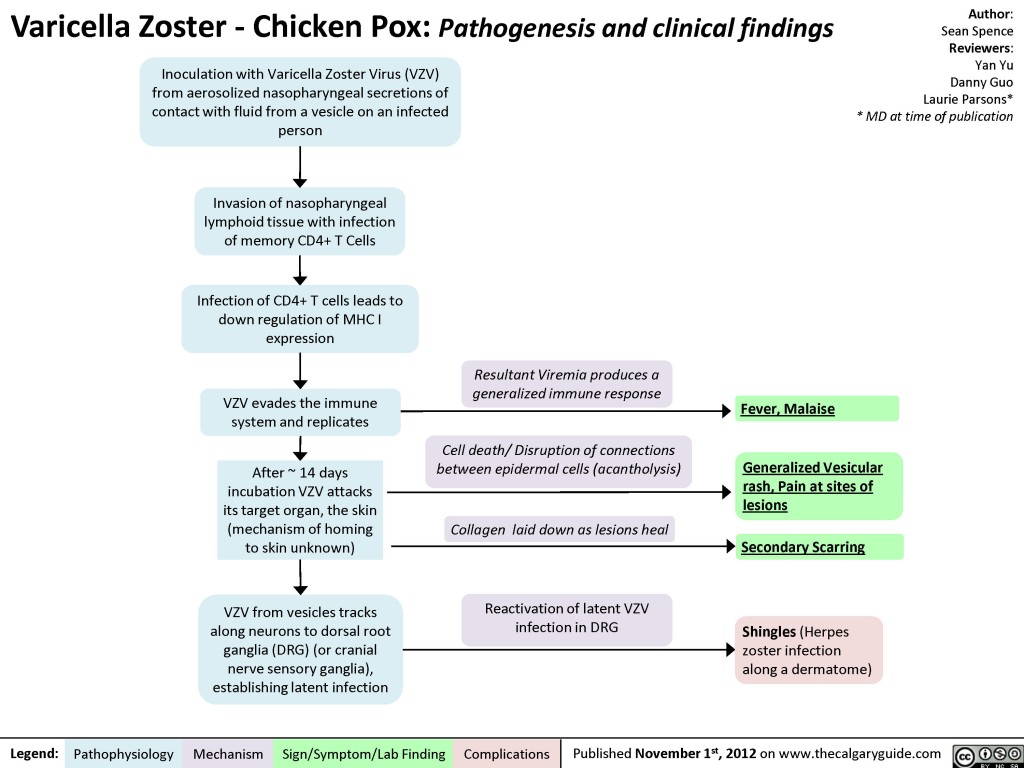
Varicella Zoster (Chicken Pox) Calgary Guide
Varicella without complication. B01.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B01.9 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B01.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 B01.9 may differ.

Herpes Zoster NEJM
Varicella is an acute infectious disease caused by varicella zoster virus (VSV). Primary infection with VZV results in chickenpox. Herpes zoster (shingles) is the result of reactivation of latent VZV.. Condition ICD-10-CM Codes ICD-9-CM Codes 1. Varicella 2. (Possible case) B01 (varicella chickenpox) 052 (chickenpox) B01.0 (varicella.

Decoding the architecture of the varicellazoster virus transcriptome
ICD-10 Codes; Lab Certifications & Accreditations; Lab Data Integrations & Tools Toggle Lab Data Integrations & Tools. Technology & EMR/EHR Integrations; Data Insights & Analysis;. Although most cases of varicella or zoster are clinically unambiguous, serology may be occasionally useful in the differential diagnosis of other blistering.

Varicella zoster virus vasculopathies diverse clinical manifestations, laboratory features
Chickenpox or varicella is a contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The virus is responsible for chickenpox (usually primary infection in non-immune hosts) and herpes zoster or shingles (following reactivation of latent infection). Chickenpox results in a skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which scabs over. It typically starts on the chest, back, and face then.