
Surya Husadha Hospital
Author Summary Dengue is one of the most common viral diseases transmitted by infected mosquitoes. It may range from asymptomatic or self-limiting dengue fever (DF) to severe dengue characterized by plasma leakage (dengue hemorrhagic fever, DHF) and dengue shock syndrome (DSS). Death from dengue infection occurs mostly in DSS, and the mortality of DSS is reportedly 50 times higher compared to.

Dengue knowledge gaps, unmet needs, and research priorities The Lancet Infectious Diseases
All clinically diagnosed dengue cases at CH1 received an ICD-10 code for DHF, whereas at CH2, all patients with a clinical diagnosis of dengue received an ICD-10 code for viral hemorrhagic fever. Modified ICD codes were recorded at discharge by the hospitals to distinguish between DHF severity grades, with DHF grades 3 and 4 classified as.
Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever dengue shock syndrome Pediatric Oncall Journal
Dengue is a febrile illness caused by infection with one of four dengue viruses (DENV) transmitted by Aedes aegypti or Aedes albopictus mosquitoes during the taking of a blood meal [ 1-3 ]. Infection may be asymptomatic or present with a broad range of clinical manifestations including a mild febrile illness to a life-threatening shock syndrome.

Could peak proteinuria determine whether patient with dengue fever develop dengue hemorrhagic
Dengue Virus Infections | 1990 Case Definition. Top of Page. Last Reviewed: April 16, 2021. Source: Office of Public Health Data, Surveillance, and Technology. Access Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS) case definitions; uniform criteria used to define a disease for public health surveillance.

Neurological complications of dengue virus infection The Lancet Neurology
v Foreword Since publication of the new edition of Dengue: Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 20091, the need to provide more training to health-care workers in this area has become increasingly evident.
Dengue shock syndrome Who is at risk? Signs and symptoms of DSS, treatment Health Tips and News
Dengue hemorrhagic fever A91-. A serious condition caused by dengue virus infection. Patients present with an acute febrile illness followed by restlessness, irritability, and bleeding. It may lead to hemorrhagic shock and death. A virulent form of dengue characterized by thrombocytopenia and an increase in vascular permeability (grades i and.
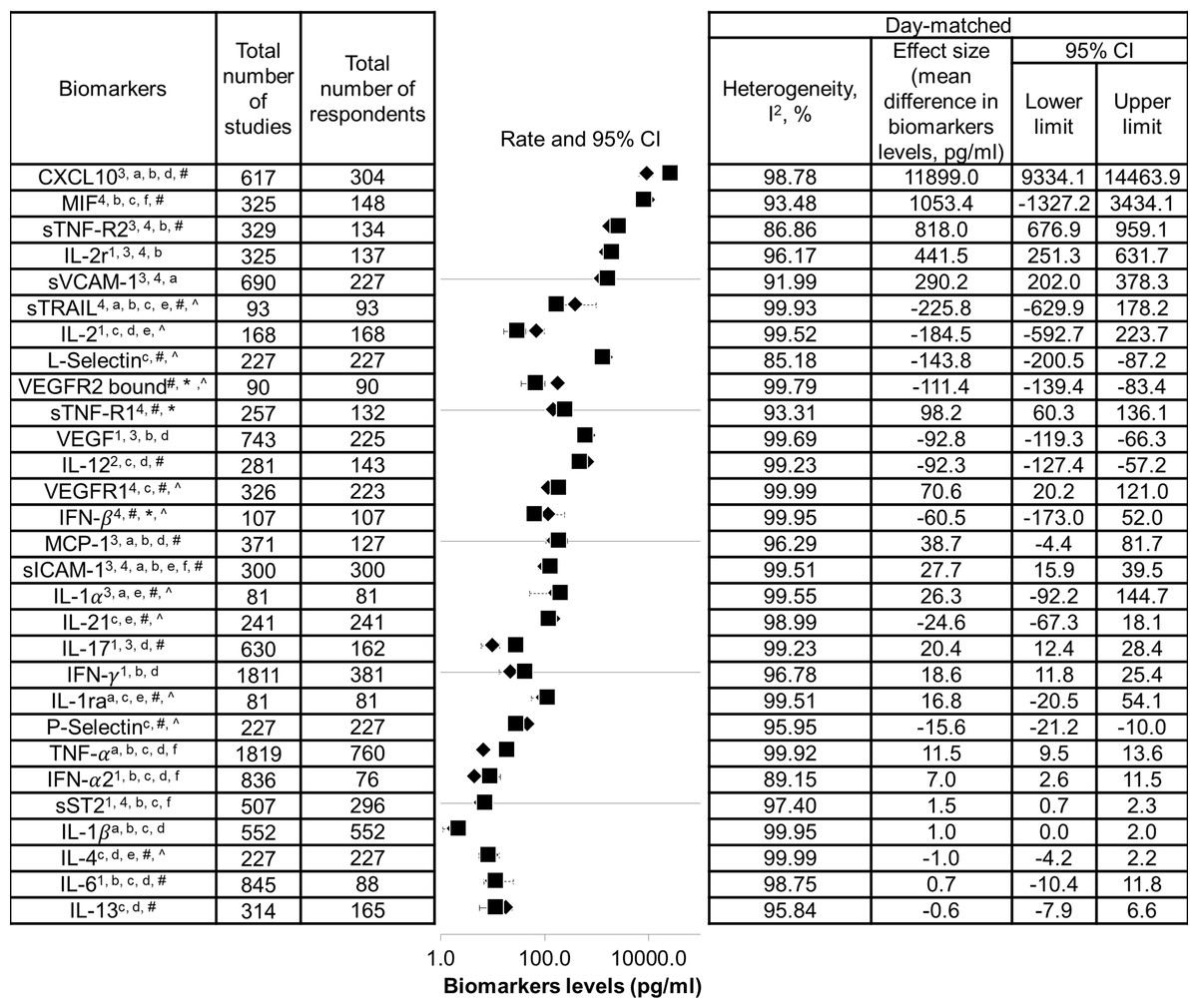
Metaanalysis of biomarkers for severe dengue infections [PeerJ]
Gejala yang Akan Muncul. Pada fase awal, gejala dengue shock syndrome hampir sama dengan demam berdarah dengue, yaitu kemunculan demam yang terjadi setelah 3 hari setelah gigitan nyamuk. Pada demam berdarah, gejala umum yang patut Anda curigai adalah demam tinggi hingga mencapai 40 derajat Celsius. Demam ini akan berlangsung selama 2-7 hari.
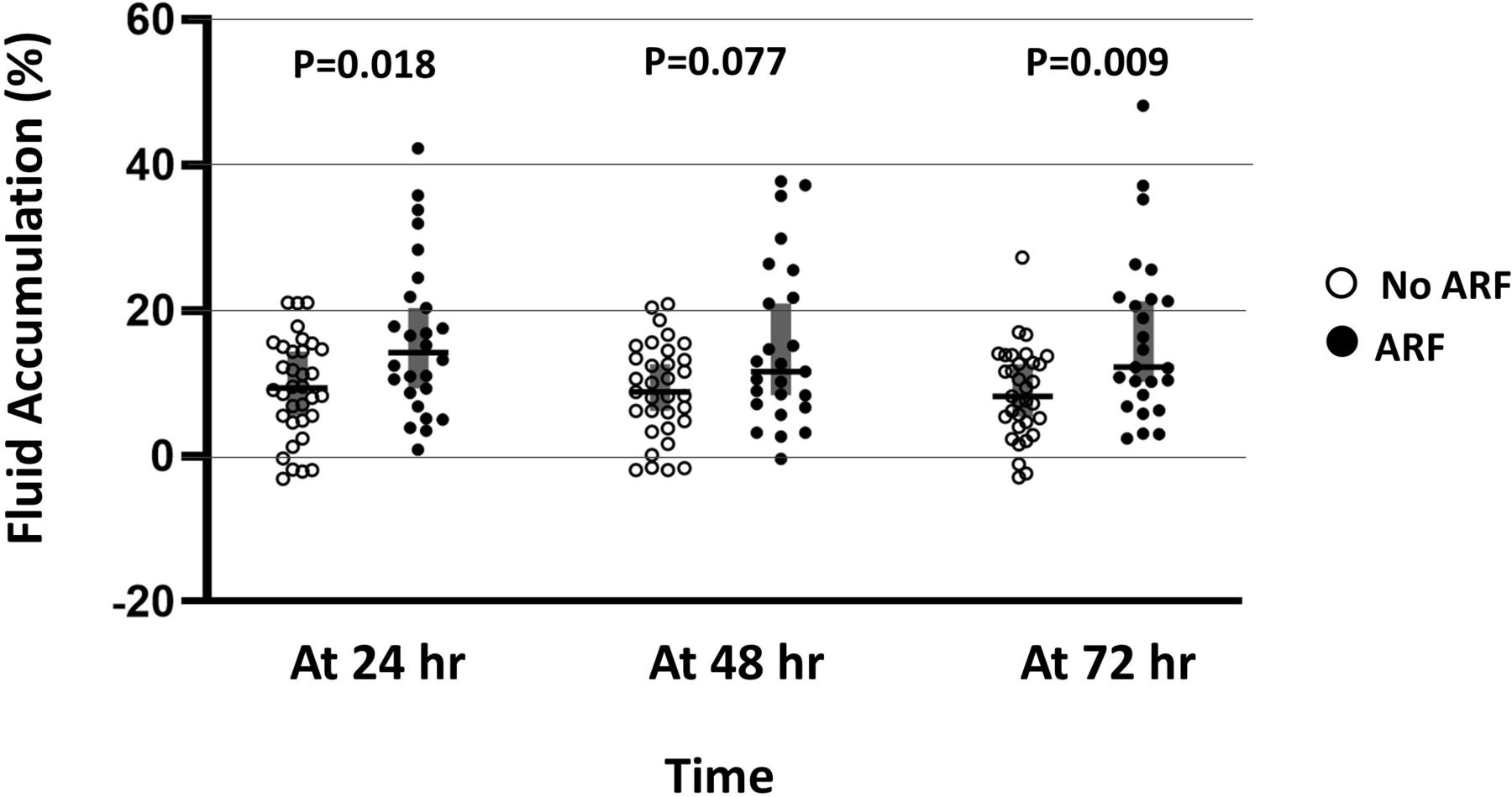
Paediatric dengue shock syndrome and acute respiratory failure a singlecentre retrospective
This is called severe dengue, dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome. Severe dengue happens when your blood vessels become damaged and leaky. And the number of clot-forming cells (platelets) in your bloodstream drops. This can lead to shock, internal bleeding, organ failure and even death. Warning signs of severe dengue fever.

Dengue Duo Test HealthServ Los Baños Medical Center
Abstract. Dengue is a very serious public health problem that can manifest a wide range of symptoms from asymptomatic to fatal conditions, such as dengue shock syndrome (DSS). It is a life-threatening mosquito-borne viral infection widely spread in tropical areas. Dengue virus transmission occurs from an infected Aedes mosquito to humans.
ICD 10 for General Surgery
The current WHO classification used since the 70s classifies dengue into dengue fever (DF), dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF), dengue shock syndrome (DSS). In 2009, a new classification of dengue proposed by WHO Tropical Disease Research (TDR) was published in the WHO TDR 2009 dengue guidelines.
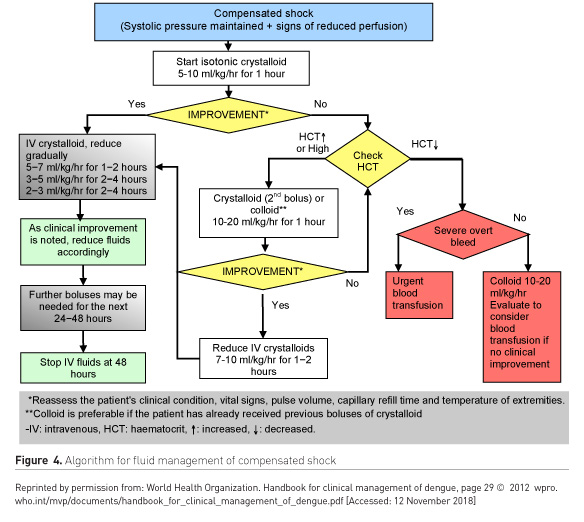
How to manage severe dengue infection
Shock syndrome is a dangerous complication of dengue infection and is associated with high mortality. Severe dengue occurs as a result of secondary infection with a different virus serotype. Increased vascular permeability, together with myocardial dysfunction and dehydration, contribute to the development of shock, with resultant multiorgan.
Dengue Fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a variant presentation of dengue infection that occurs primarily in children 10 years living in areas where dengue is endemic. Dengue hemorrhagic fever, which has also been called Philippine, Thai, or Southeast Asian hemorrhagic fever, frequently requires prior infection with the dengue virus.

Comparison of Three Fluid Solutions for Resuscitation in Dengue Shock Syndrome NEJM
In November 2009, WHO issued a new guideline that classifies symptomatic cases as dengue or severe dengue. Dengue is defined by a combination of ≥2 clinical findings in a febrile person who traveled to or lives in a dengue-endemic area. Clinical findings include nausea, vomiting, rash, aches and pains, a positive tourniquet test, leukopenia, and the following warning signs: abdominal pain or.

Dengue and dengue haemorrhagic fever The Lancet
Dengue hemorrhagic fever. A91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM A91 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A91 - other international versions of ICD-10 A91 may differ.
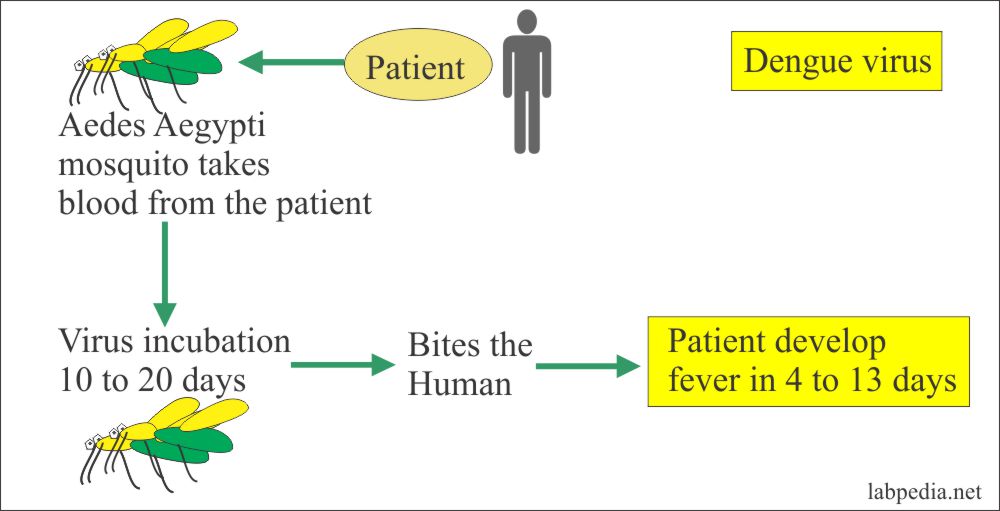
Dengue Fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
than 200 years. In the past 30 years, dengue transmission and the frequency of dengue epidemics have increased greatly in most tropical countries in the American region. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever and Dengue Shock Syndrome Some patients with dengue fever go on to develop dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF), a severe and sometimes fatal form of the.
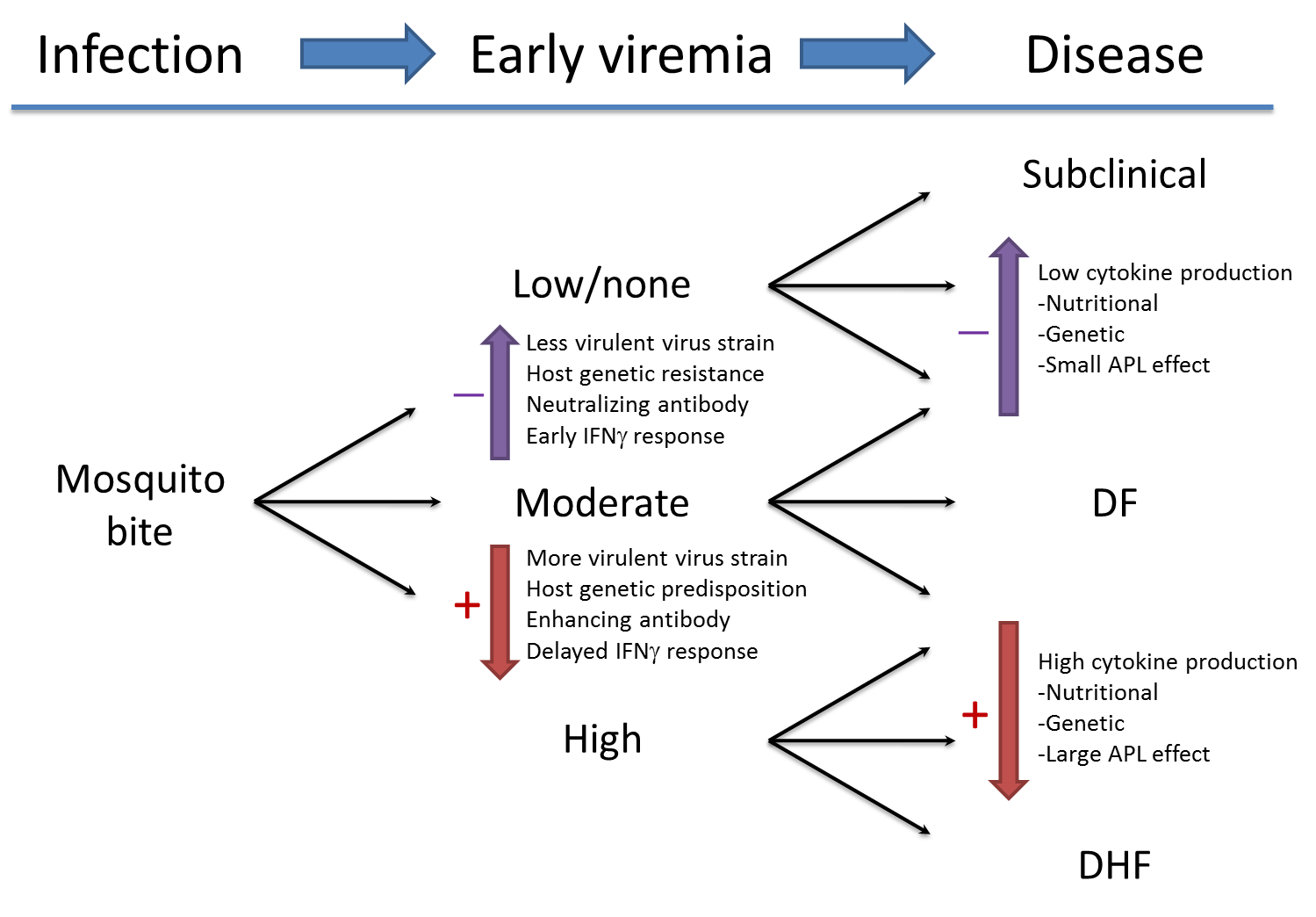
Research
Dengue is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a flavivirus. Dengue fever usually results in abrupt onset of high fever, headache, myalgias, arthralgias, and generalized lymphadenopathy, followed by a rash that appears with a recurrent fever after an afebrile period. Respiratory symptoms, such as cough, sore throat, and rhinorrhea, can occur.