
Hydrogen Bond Definition, Types, and Examples
Atomic Number: 1. Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table, meaning it has an atomic number of 1 or 1 proton in each hydrogen atom. The name of the element comes from the Greek words hydro for "water" and genes for "forming," since hydrogen bonds with oxygen to form water (H 2 O). Robert Boyle produced hydrogen gas in 1671 during an.
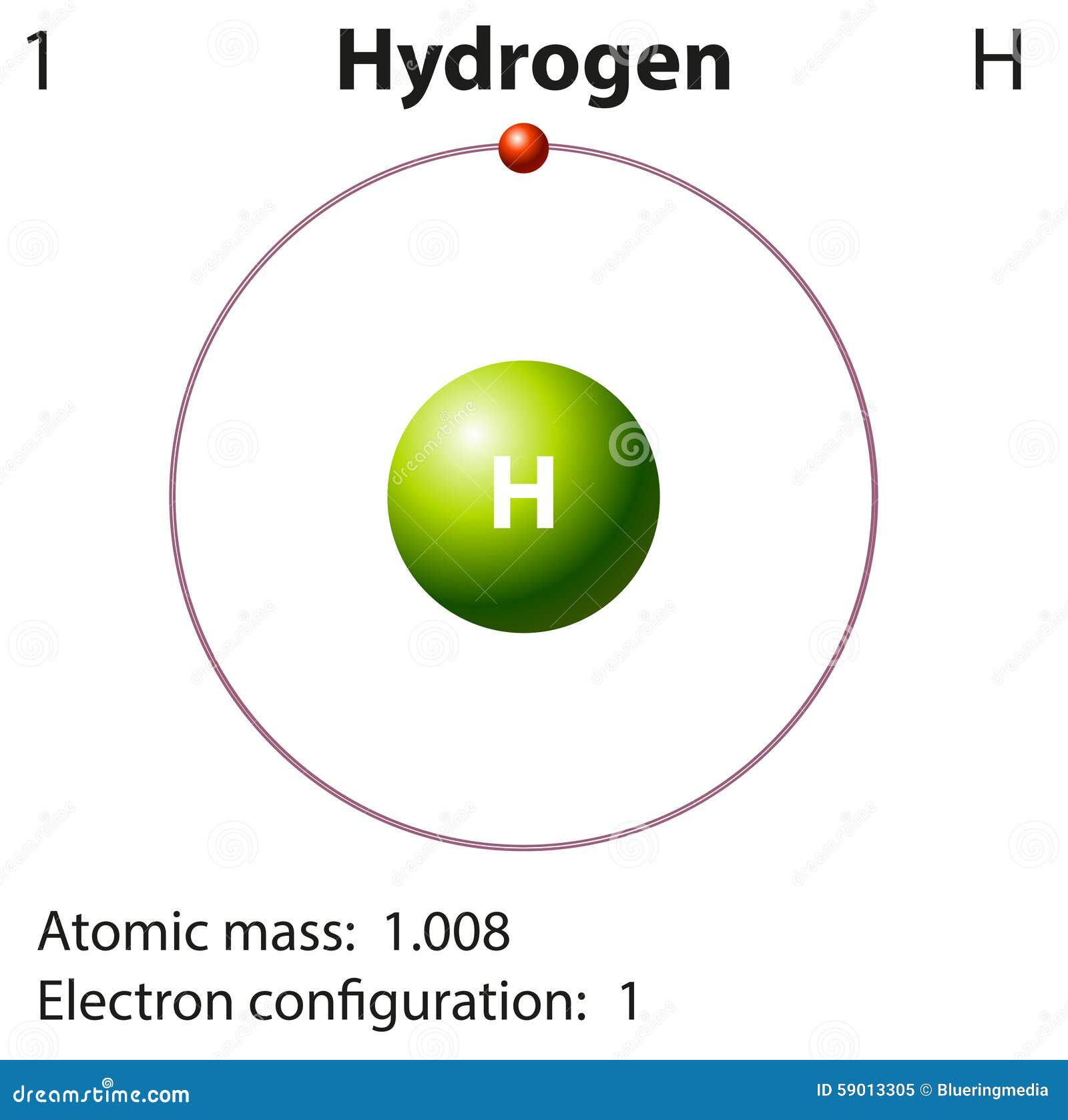
Diagram Representation of the Element Hydrogen Stock Vector Illustration of
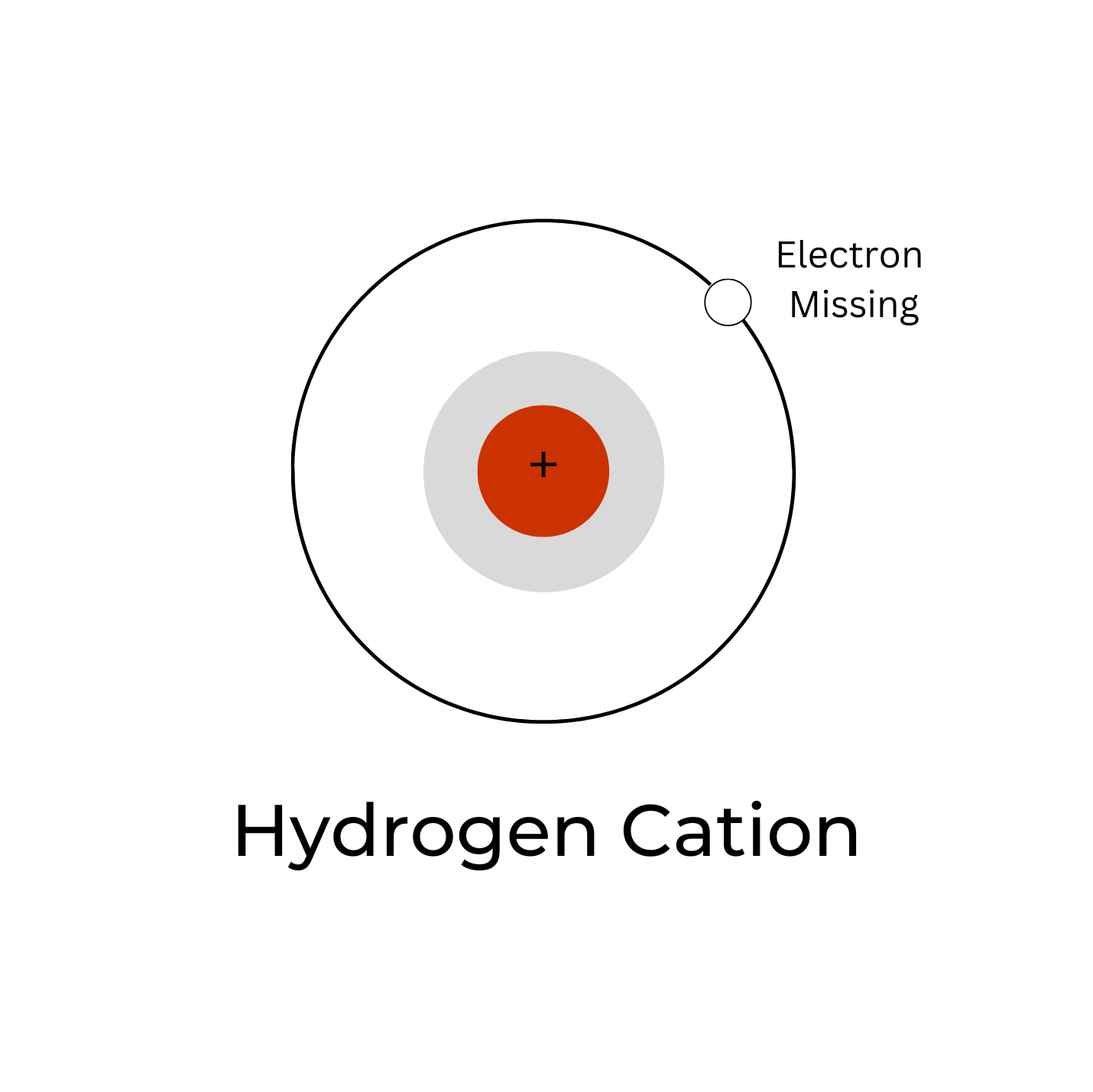
5.2: Hydronium Ions. A hydrogen ion, H +, is a hydrogen atom which has lost its single electron; that is, a hydrogen ion is just a proton. It does not, however, readily exist in an aqueous solution. Because a proton is only about one ten-thousandth as big as an average atom or ion, water dipoles can approach very close to a hydrogen ion in.

Hydrogen Electron Configuration And Full Orbital Diagram
The dihydrogen cation or hydrogen molecular ion is a cation (positive ion) with formula H+. 2. It consists of two hydrogen nuclei ( protons) sharing a single electron. It is the simplest molecular ion . The ion can be formed from the ionization of a neutral hydrogen molecule ( H. 2) by electron impact. It is commonly formed in molecular clouds.
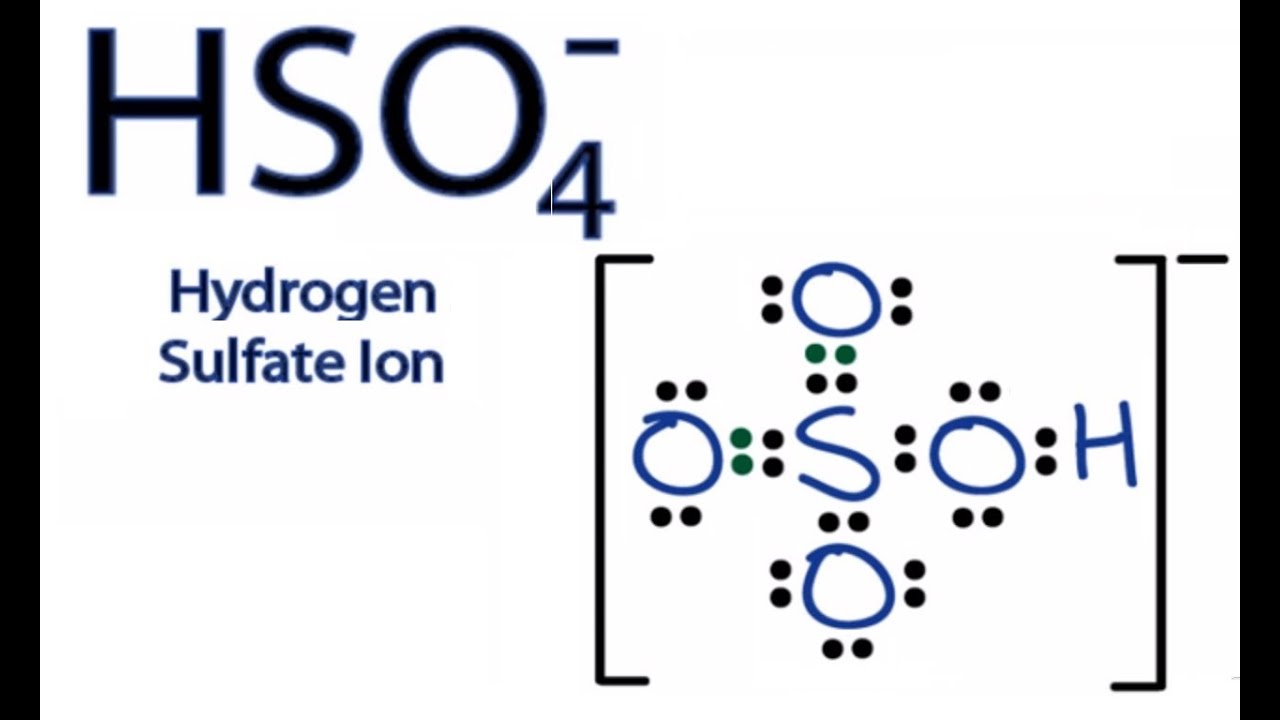
Hydrogen Hydrogen Ion Formula
A hydrogen ion is the nucleus of a hydrogen atom that has been isolated from its electron. A proton is a molecule with a unit of positive electric energy that makes the hydrogen nucleus. Therefore, the disconnected hydrogen ion, signified by the image H +, is usually used to depict a proton.So the above-given definition assists with getting what is H + ion and hydrogen ion Formula.

Hydrogen ion YouTube
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest element and, at standard conditions, is a gas of diatomic molecules with the formula H2, sometimes called dihydrogen, [10] but more commonly called hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen or simply hydrogen. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, [11] non-toxic, and.
Diagram representation element hydrogen Royalty Free Vector
The glass electrode for H + is an ion-selective electrode (ISE) widely used in clinical medicine. The potential that develops in this electrode is proportional to the log of the hydrogen ion activity in the test solution. The term used is pH which is now defined as: Definition: pH. pH = −log10 aH+ (1.3.2) (1.3.2) p H = − log 10 a H +.

Hydrogen ion Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
Figure 11.5.1 11.5. 1 Hydrogen and hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. (a) Hydronium ion, H 3 O +; (b) hydroxide ion, OH -; Like other ions in aqueous solution, both hydronium and hydroxide ions are hydrated. Moreover, hydrogen bonds are involved in attracting water molecules to hydronium and hydroxide ions. In both cases three water.

FileElectron shell 001 hydrogen.png
Depiction of a hydrogen atom showing the diameter as about twice the Bohr model radius. (Image not to scale) A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen.The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the baryonic mass of the.
Dummies Guide To Hydrogen MHI
Hydrogen. Formula: H 2. Molecular weight: 2.01588. IUPAC Standard InChI: InChI=1S/H2/h1H. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. IUPAC Standard InChIKey: UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. CAS Registry Number: 1333-74-. Chemical structure:

How to Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for H+ (Hydrogen ion) YouTube
A hydrogen atom that has gained or lost an electron, and thus has an electric charge. The positive hydrogen ion, H +, has lost its only electron and therefore consists of a single proton. A nebula containing H + ions is known as an H II region. The negative hydrogen ion, H −, has gained a second electron. H − ions are found in the outer.

Hydrogen Definition, Structure, Properties & Uses Embibe
It has the lowest density of all gases. Uses. Some see hydrogen gas as the clean fuel of the future - generated from water and returning to water when it is oxidised. Hydrogen-powered fuel cells are increasingly being seen as 'pollution-free' sources of energy and are now being used in some buses and cars.
Hydrogen atom orbital structure hires stock photography and images Alamy
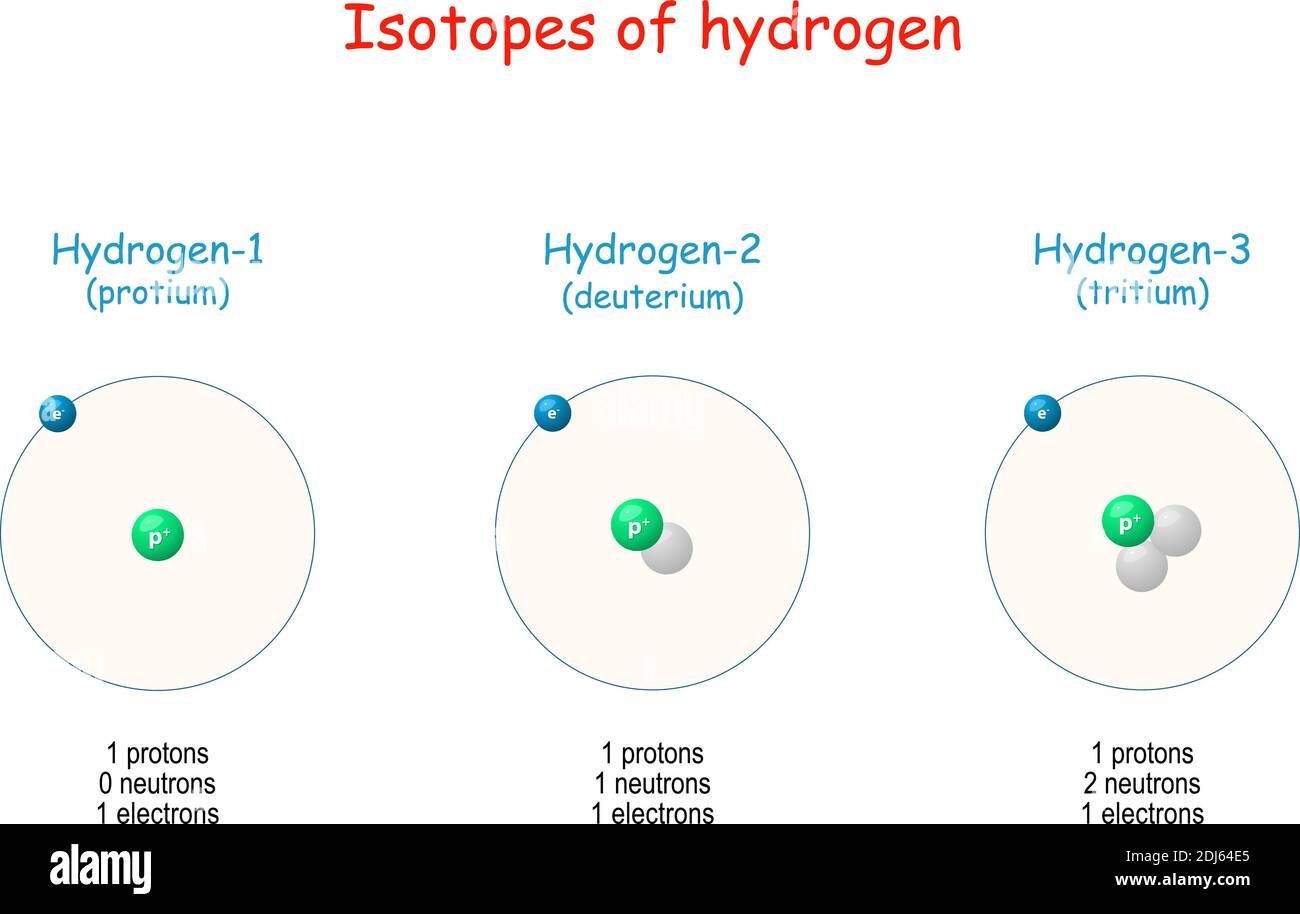
When hydrogen loses its electron, the cations can be formed: Hydron: general name referring to the positive ion of any hydrogen isotope (H +) Proton: 1 H + (i.e. the cation of protium) Deuteron: 2 H +, D +. Triton: 3 H +, T +. The ions produced by the reaction of these cations with water, as well as their hydrates, are also called 'hydrogen ions'.

What’s So Great About Molecular Hydrogen? by KOR Water Medium
There is a direct relationship between hydrogen ions and pH. The pH of a solution depends on the hydrogen ion concentration in that solution. pH value is the logarithmic value of the inverse of the hydrogen ion activity. Since the concentration of the hydrogen ions is often very low, ion activity is considered as equal to the concentration of.

Hydrogen atom on white background Royalty Free Vector Image
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses an electron.A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particle-free space. Due to its extremely high charge density of approximately 2×10 10 times that of a sodium ion, the bare hydrogen ion cannot exist freely in.
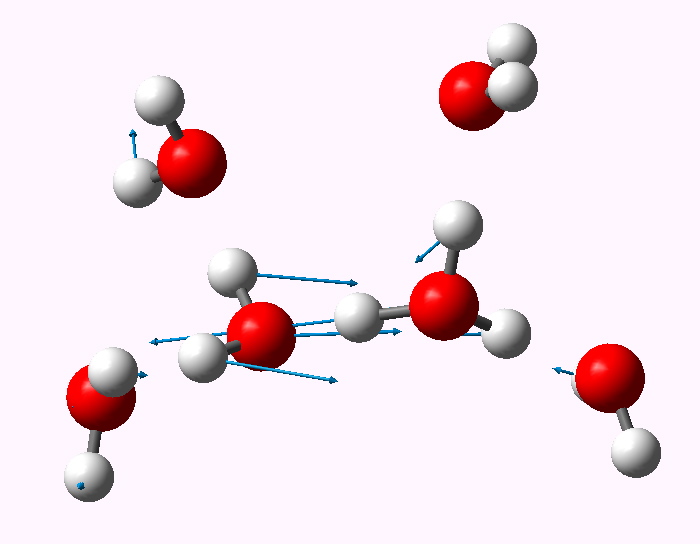
The structure of the hydrogen ion in water. Henry Rzepa's Blog Henry Rzepa's Blog
hydrogen ion, strictly, the nucleus of a hydrogen atom separated from its accompanying electron.The hydrogen nucleus is made up of a particle carrying a unit positive electric charge, called a proton.The isolated hydrogen ion, represented by the symbol H +, is therefore customarily used to represent a proton.Because the bare nucleus can readily combine with other particles (electrons, atoms.

Hydrogen Periodic Table and Atomic Properties
Hydrogen has three known isotopes. The mass numbers of hydrogen's isotopes are 1, 2, and 3, the most abundant being the mass 1 isotope generally called hydrogen (symbol H, or 1 H) but also known as protium.The mass 2 isotope, which has a nucleus of one proton and one neutron and has been named deuterium, or heavy hydrogen (symbol D, or 2 H), constitutes 0.0156 percent of the ordinary mixture.