
The spinal cord Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab (BSB 141)
Anatomy Cross-section of the spinal cord Functions Possible injuries Summary The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves and cells that extends from the lower portion of the brain to the.

March 2016
Next, the user will find anatomical sections of the spinal cord at different levels: cervical spinal cord (C2, C5), thoracic spinal cord (T10), lumbar spinal cord (L3) and sacral spinal cord (S3). Anatomy : Spinal cord, Funiculi of spinal cord, Tectospinal tract, Anterior funiculus; Ventral funiculus, Cuneate fasciculus, Gracile fasciculus.
PPT Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Nerves and Reflexes PowerPoint
Last update: Oct 24th, 2022 Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn Start Now The spinal cordis made up of 31 segments. Each segment gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves. 1 2 In cross-section (c.s.), the segments appear to be divided into two zones. The outer zone contains many myelinated axonsthat run up and down the spinal cord.

Cross section of 4 of the spinal cord's 31 segments. Source Pearson
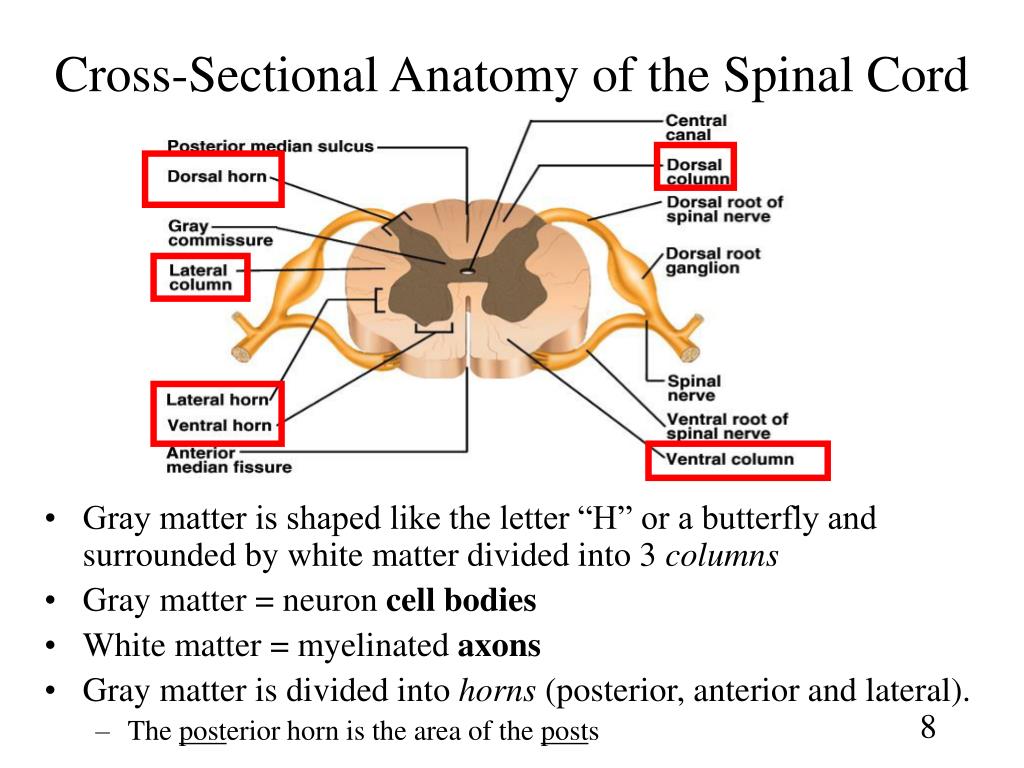
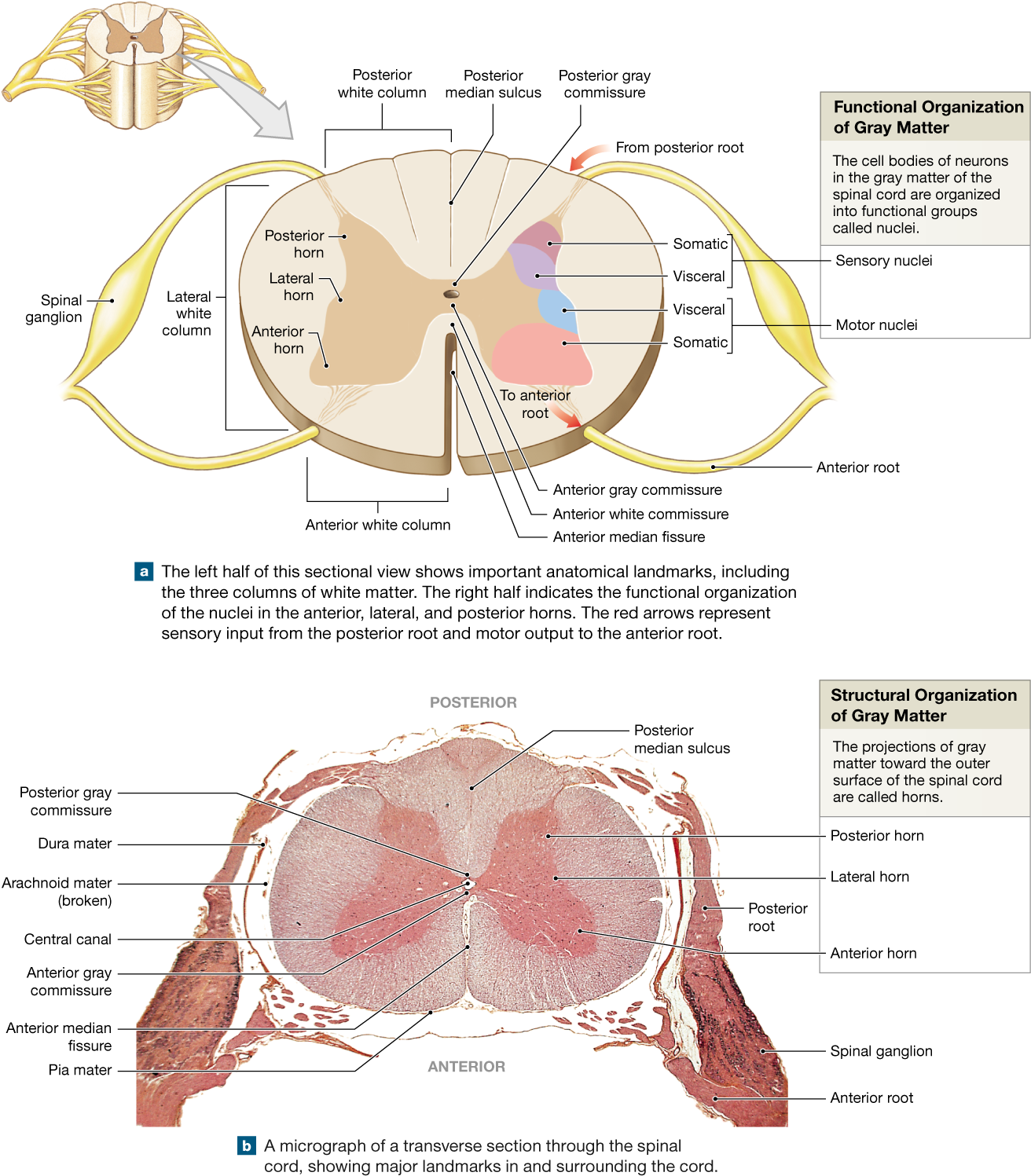
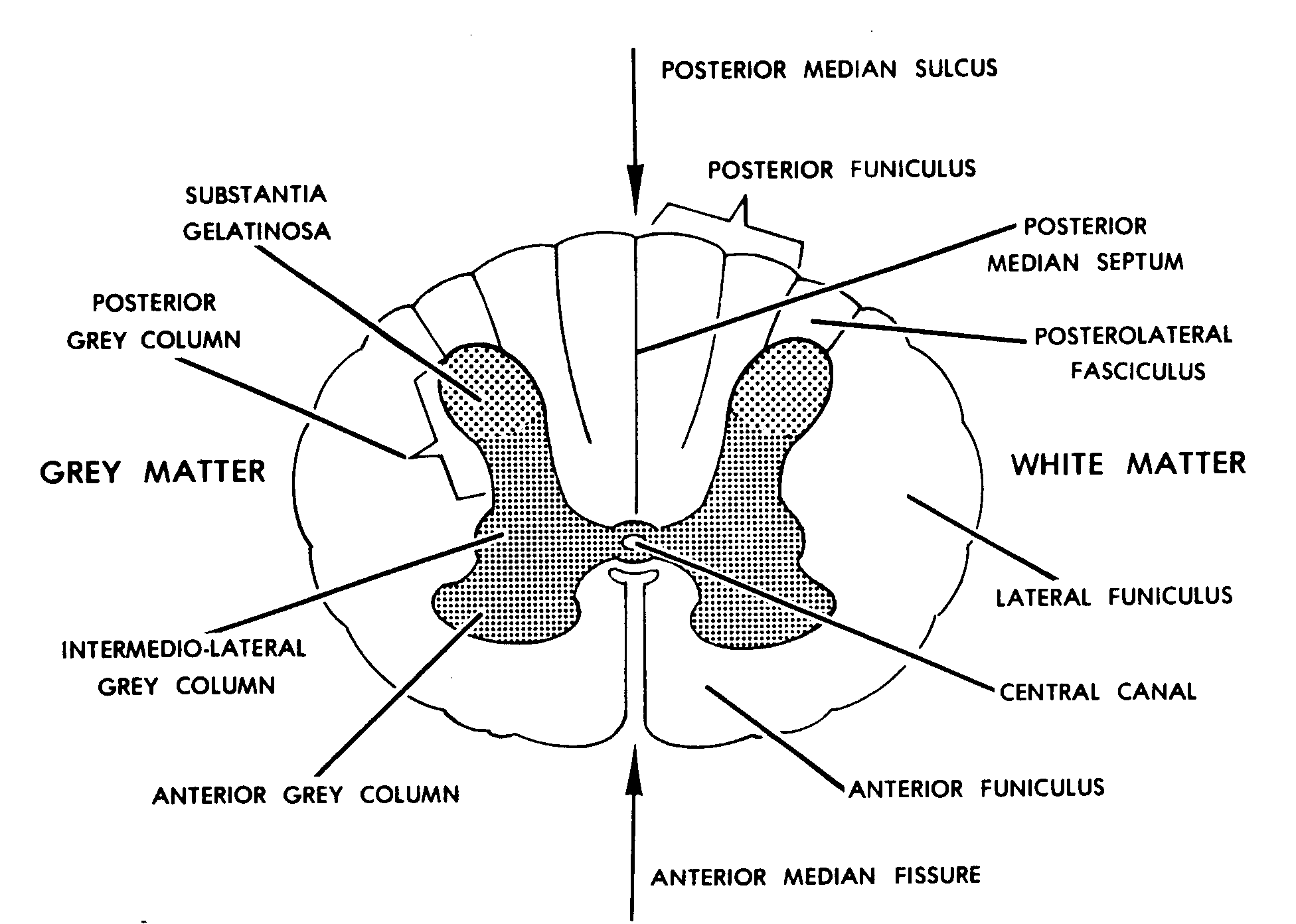
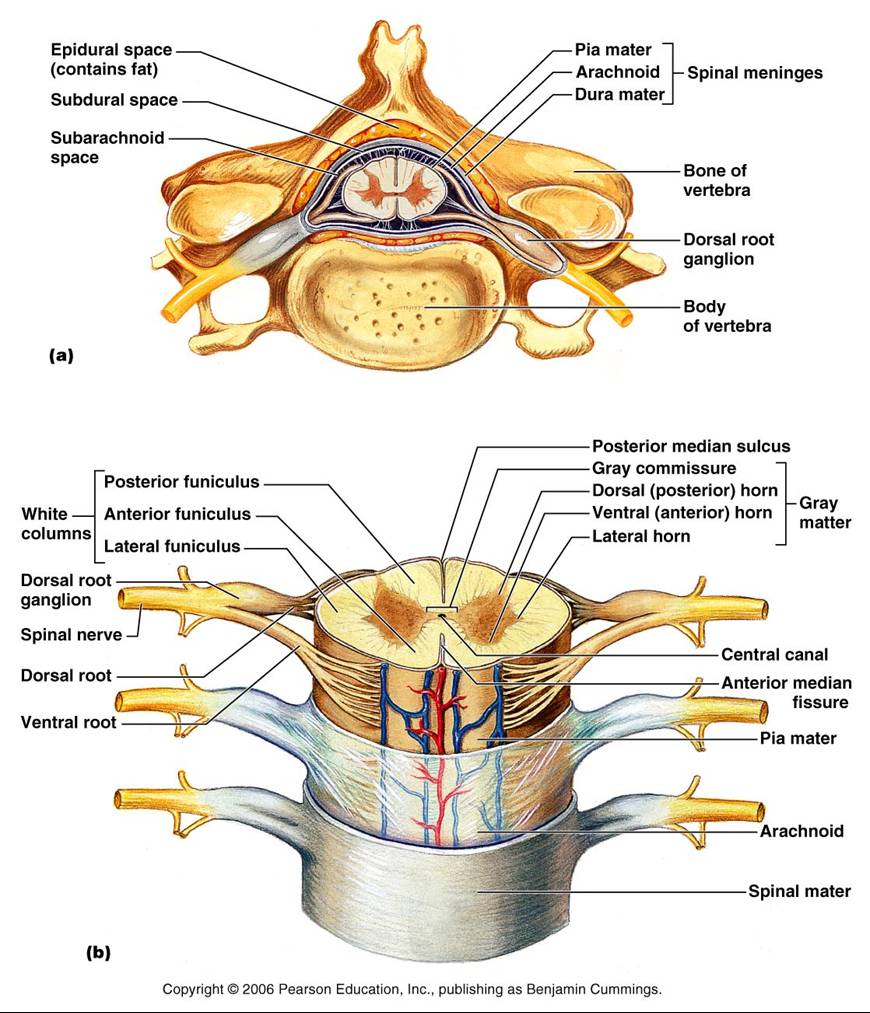
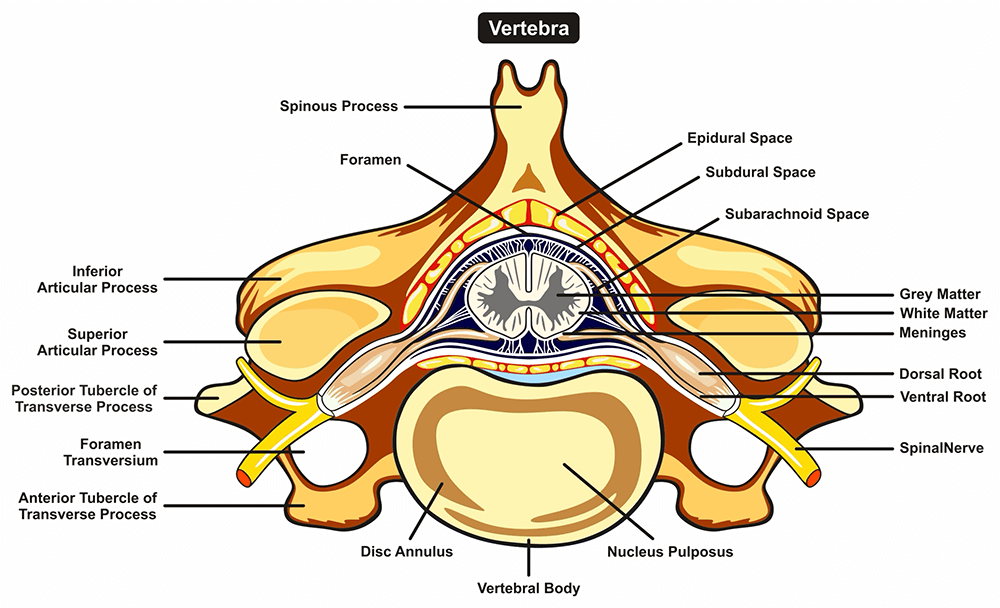
A cross-section through the spinal cord is illustrated schematically in Figure 2.6 and 3.4. The gray matter forms the interior of the spinal cord; it is surrounded on all sides by the white matter. The white matter is subdivided into dorsal (or posterior), lateral, and ventral (or anterior) columns.
Download Spinal Cord Gray Matter Integrates Information And Label
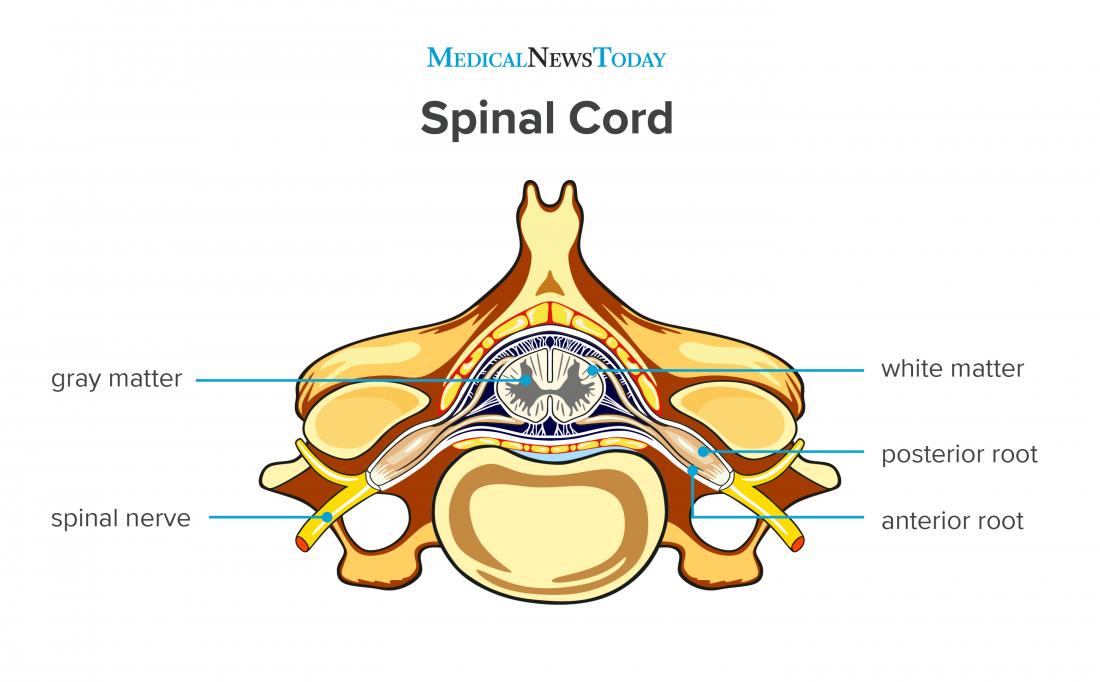
The spinal cord is a thick cable of nervous tissue extending from the medulla oblongata of the brain stem to the neck and torso. Viewed in a cross-section, it has a roughly oblong shape with white matter on its exterior and a butterfly-shaped region of gray matter on its interior. A small, circular tube-like cavity known as the central canal.

Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system found within the vertebral column's spinal canal. The cord extends from the corticomedullary junction at the foramen magnum of the skull down to the tip of the conus medullaris within the lumbar cistern .

Spinal Cord Neurology Medbullets Step 1
Start Now An interactive quiz covering Spinal Cord Cross-Sectional Anatomy through multiple-choice questions and featuring the iconic GBS illustrations.
Spinal Cord Cross sectional Anatomy rdiOlogY dE aruN
Cross Section of Spinal Cord. 18 terms. Larry_Moore4. Preview. Cross Section of spinal cord. 21 terms. ninna_rivera. Preview. spinal cord labeling- cross section. 14 terms. Jane_Schoenbaechler. Preview. ANATOMY EXAM 3. 51 terms. KAYVAS9. Preview. Cross-section of Spinal Cord. 16 terms. Kendra_Wiley7. Preview. A&P 1 Final Exam . 109 terms.
Spinal cord Anatomy, functions, and injuries
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities.. The spinal cord carries nerve signals from the brain to other.

Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
The vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs.It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx.The spinal cord runs through its center. The vertebral column is divided into five regions and consists of 33 vertebrae interlaced by strong joints.

Spinal Cord
In the spinal cord cross-section labeled diagram, we have shown Dorsal horn, Visceral sensory nuclei, Somatic sensory nuclei, afferent sensory information, efferent signals to muscles and glands via the ventral root, somatic motor nuclei, autonomic efferent nuclei, ventral horn, ventral root, lateral horn, and dorsal root ganglion. Tag biology
BY 411 Advanced Human Anatomy Blog Neuroanatomy Post 3 Development
Start studying Label the cross section of the spinal cord. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.. Figure 26.3 Spinal Cord Cross Section Microscope Slide. Teacher 8 terms. THagge. Preview. CSIT 100 Midterm. 94 terms. faythb6202. Preview. 4.2 Subnets. 16 terms. Lilian_Miller85.

14.4 The Spinal Cord Anatomy & Physiology
Reading time: 5 minutes So you've started the business of learning about the central nervous system and next up on the list is the spinal cord. Simply looking at the diagrams in your textbook has sent alarm bells ringing in your head: "Danger! Danger! This looks complicated!". Don't worry. In the article to follow, we've got you covered.

Ch. 12 Spinal Cord Objectives at Mount Royal University StudyBlue
The spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem. It extends from the foramen magnum at the base of the skull to the L1/L2 vertebra where it terminates as the conus medullaris (medullary cone).
Sectional Anatomy Of Spinal Cord Anatomy Book
Figure 12.6. 6: Spinal Nerve. The ventral and dorsal nerve roots exiting a cross section of spinal cord fuse together to form a spinal nerve, which then splits into the dorsal and ventral rami. The white and gray ramus form the rami communicantes that connect spinal nerves to autonomic ganglia.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1900/4wg7EtKVwtWY7wcLa4OtAA_anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_english.jpg)
Ascending tracts of the spinal cord Anatomy Kenhub
The spinal cord, when viewed in cross section, is composed of central gray matter and peripheral white matter. The gray matter resembles a butterfly in shape and may be subdivided into three pairs of horns: dorsal, lateral (found only between the first thoracic and second lumbar spinal levels), and ventral. Sensory neurons enter the spinal cord.