The Superficial Muscles of a Cow ClipArt ETC
A baby cow is called a calf. A female calf is sometimes called a heifer calf and a male a bull calf. A heifer is a female that has not had any offspring. The term usually refers to immature females; after giving birth to her first calf, however, a heifer becomes a cow. An adult male is known as a bull.

Bovine Cow Muscle Anatomy Poster in 2021 Muscle anatomy
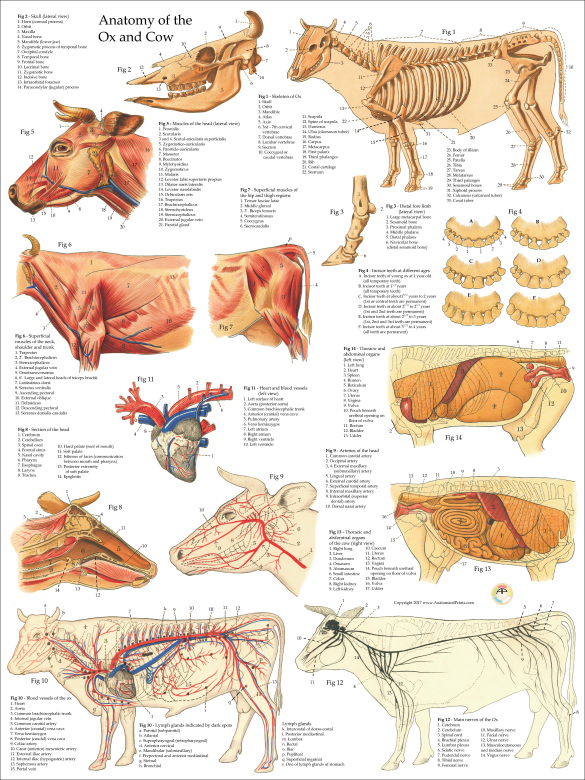
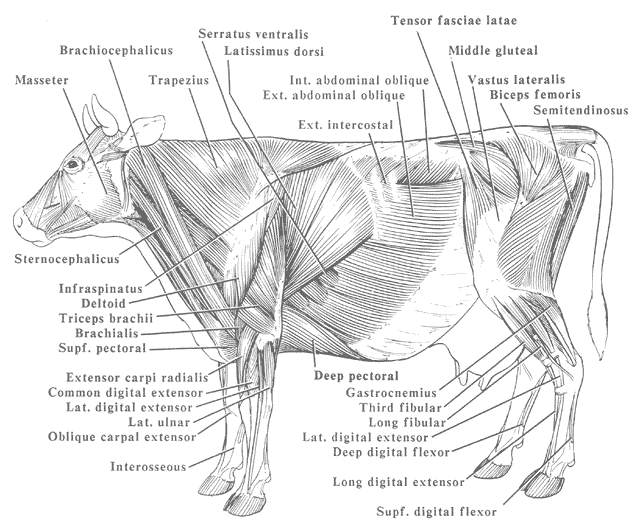
The superficial muscles of a cow are diagramed. Labels: 1, Occipito-Frontalis. 2, Orbicularis Palpaebrarum. 3, Masseter. 5, Sterno-cleido-Mastoid. 6, Trapezius. 7, Latissimus Dorsi. 8, Pectoralis. 9, 10, External and Internal oblique muscles. 11, Opening of the mammary artery and vein (milk vein). 12, Gluteii. 13, Rectus Femoris muscle.

Cow Bovine Veterinary Muscles Anatomy Chart Poster Zazzle
Muscles of thoracic limb of a cow Muscles of the hindlimb of a cow Cow anatomy organs Digestive organs of a cow Cow anatomy stomach Compartments of cow stomach Liver and pancreas of cow anatomy Organs of the respiratory system from a cow Lung anatomy of a cow Heart of a cow Cow hoof anatomy Cow anatomy labeled diagram

Cow muscles Mammals, Anatomy for artists
Reflect the scapular and acromial parts of the deltoideus muscle to uncover the distal part of the infraspinatus muscle on a cow forelimb. Transect the infraspinatus belly midway between its proximal and distal ends. Reflect the distal half from the infraspinous fossa to its insertion on the humerus. Verify the presence of the subtendinous bursa.

cow anatomy study, Robin de Jong Anatomy study, Creature design
Key Points For More Information Bovine secondary recumbency is defined as the inability of cattle to rise and stand for a period of at least 12-24 hours, resulting from the delayed or unsuccessful treatment of a different primary cause of recumbency.

Posterior view of cow muscles anatomy Pet vet
It is a triangular depression bounded by lumbar transverse processes and the epaxial muscle dorsal to the processes, the last rib, and an oblique muscular thickening of the internal abdominal oblique m. extending from the tuber coxae to the costal arch. (see image below)

Muscles of Hindlimb of Equine and Bovine YouTube
Bull-Cow - Muscles Bull-muscles Bull-Cow - Digestive system Bull-digestive systeme Bull-Cow - Sagittal section-Manus Bull-sagittal section of manus Bull-Cow - Terms of position and direction Bull-terms of position and direction ANATOMICAL PARTS Abaxial tendon Abdomen Abomasum Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor pollicis muscle

Cow anatomy sceleton muscles ligaments, Igor Lapshin C. on
Cow's Eye Dissection - step 2. Without moving your head, look up. Look down. Look all around. Six muscles attached to your eyeball move your eye so you can look in different directions. Cows have only four muscles that control their eyes. They can look up, down, left, and right, but they can't roll their eyes like you can.

Very Muscled Cow In Green Field by Compuinfoto Green fields, Cow
Quick overview: there are several muscles in the body of a cow, but I will identify the most used and useful muscles from the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, and limbs. Muscles from the neck and limbs are most important for field practices.
Cow Ox Anatomy Poster
Despite its name, the is located laterally in meat animals. It covers the lateral face of the ilium and appears as the large muscle area in sirloin steaks and chops. The flank and belly of the animal are formed by sheets of muscle and connective tissue.

musclecows026 Built Report
25/04/2023 28/10/2022 by Sonnet Poddar The cow leg anatomy consists of bones, muscles, nerves, and vessels. Bones are the hardest and main component of the cow leg structure. Again, the muscles are also essential as most vessels and nerves pass along or within them.

183 best Anatomie Bovine images on Pinterest Animal anatomy, Cow and Cows
These are the gastrocnemius and soleus, (the 'calf muscles' in humans). Some of the more fragile edges of this calcaneus are missing, but you can still see the main features. This photo is pretty much a close-up of the photo above, from the bottom end. © Saffron Walden Museum.

The Reason This Cow Is So Insanely Muscular The Dodo
1 Pelvic Girdle and Hip 1.1 Bones 1.1.1 Bovine Bone Specifics 2 Joints and Synovial Structures 2.1 Sacroiliac Joint 2.2 Coxafemoral/Hip Joint 3 Musculature 4 Proximal Hindlimb including Stifle and Tarsus 4.1 Bones 4.1.1 Bovine Bone Specifics 4.2 Joints and Synovial Structures 4.3 Musculature 5 Vasculature of the Hindlimb 6 Webinars
Anatomy
5 Muscles of the Forelimb 5.1 Extrinsic Musculature 5.2 Intrinsic Musculature 6 Muscles of the Shoulder 6.1 1. Lateral 6.2 2. Medial 6.3 3. Caudal (Flexors) 7 Muscles of the Elbow 7.1 Extensors 7.2 Flexors 8 Muscles of the Carpal and Digital Joints 8.1 Extensors 8.2 Flexors 9 Vasculature of the Forelimb 10 Webinars

MODEL OF A COW'S ANATOMY, THE MUSCLES, FRAGONARD MUSEUM, NATIONAL
A3.2 Identify and describe the joints, joint angles, joint actions, and muscle groups of the pelvic limb. Joints of the pelvic (hind) limb. Clinical Notes: joint pouches are extensions of the synovial capsule and cavity past joint surface. In more mobile joints these pouches can be more expansive/extensive.

Muscle cow by Goutofang1 on DeviantArt
Category: Anatomy This chart shows views of the cow's left lateral view with the dorsal and vertebral regions indicated. In addition, superficial muscles and the cow's veins, deep cervical muscles, major joints, in situ viscera, and udder are also shown.