
Flooring Flooring, Home construction, Floor framing
09 60 00 - Flooring ; 09 61 00 - Flooring Treatment ; 09 61 13 - Slip-Resistant Flooring Treatment ; 09 62 00 - Specialty Flooring ; 09 62 29 - Cork Flooring ; 09 62 48 - Acoustic Flooring ; 09 63 00 - Masonry Flooring ; 09 63 40 - Stone Flooring ; 09 65 00 - Resilient Flooring ; 09 65 13 - Resilient Base and Accessories ; 09 65 13.13.
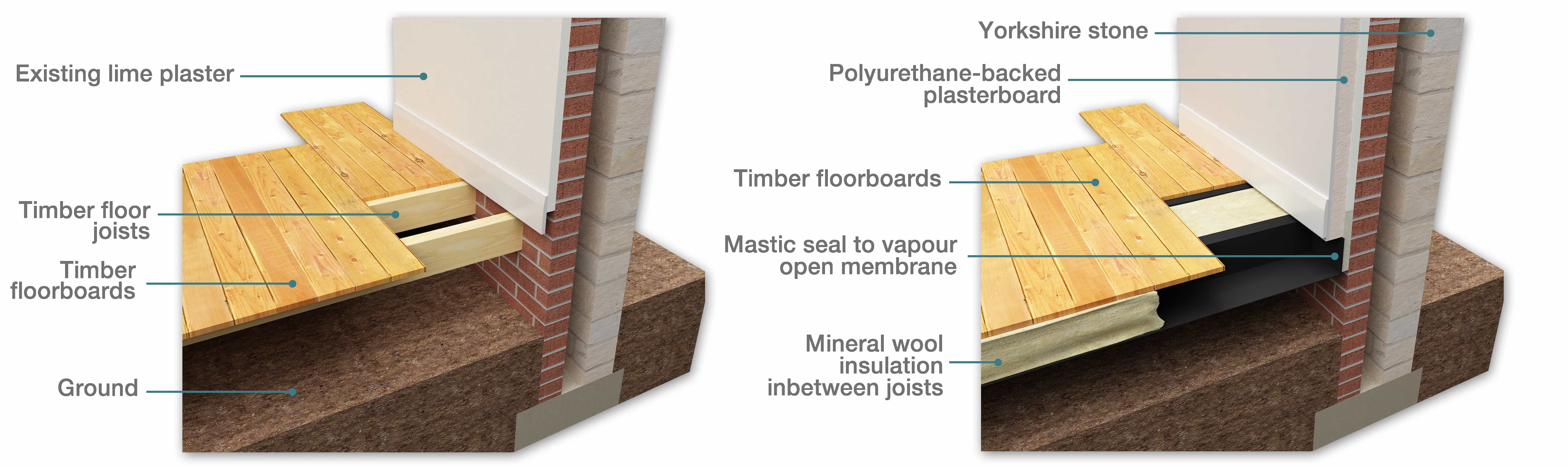
Insulating suspended timber floors
A floor's framework is made up mostly of wooden joists that run parallel to one another at regular intervals. Floor joists are typically 2 by 8s, 2 by 10s, or 2 by 12s; ceiling joists are usually 2 by 6s or sometimes 2 by 4s if it is an older home. Some newer homes have manufactured, I beam-shaped joists. Floor joists, spaced on regular.

Flooring Home construction, Floor framing, Building a house
Fig-3: Isometric View of Double Joist Timber Flooring Fig-4: Plan for Double Joist Timber Floor Fig-5: Section X-X Framed or Triple Joist Timber Floor. This type of timber flooring is suitable for spans between 5 to 7.50 m and the superimposed load is very heavy. The intermediate supports known as girders are provided for the binders.

Technical Details Book of Details Chapter 3 Timber frame construction, Timber architecture
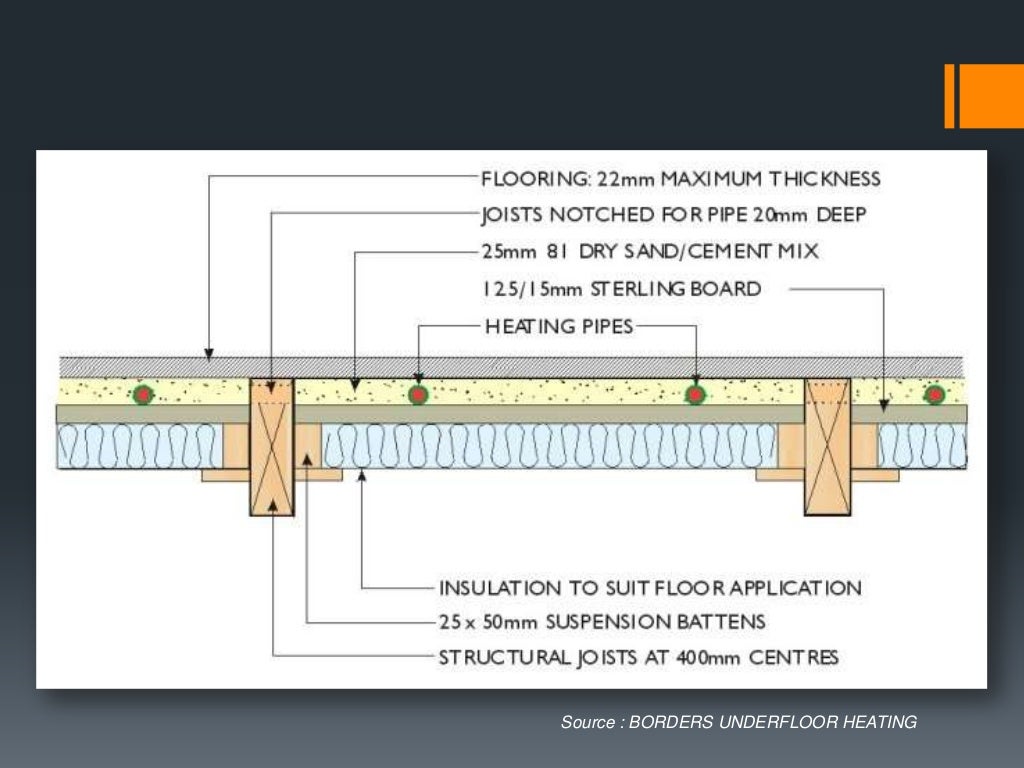
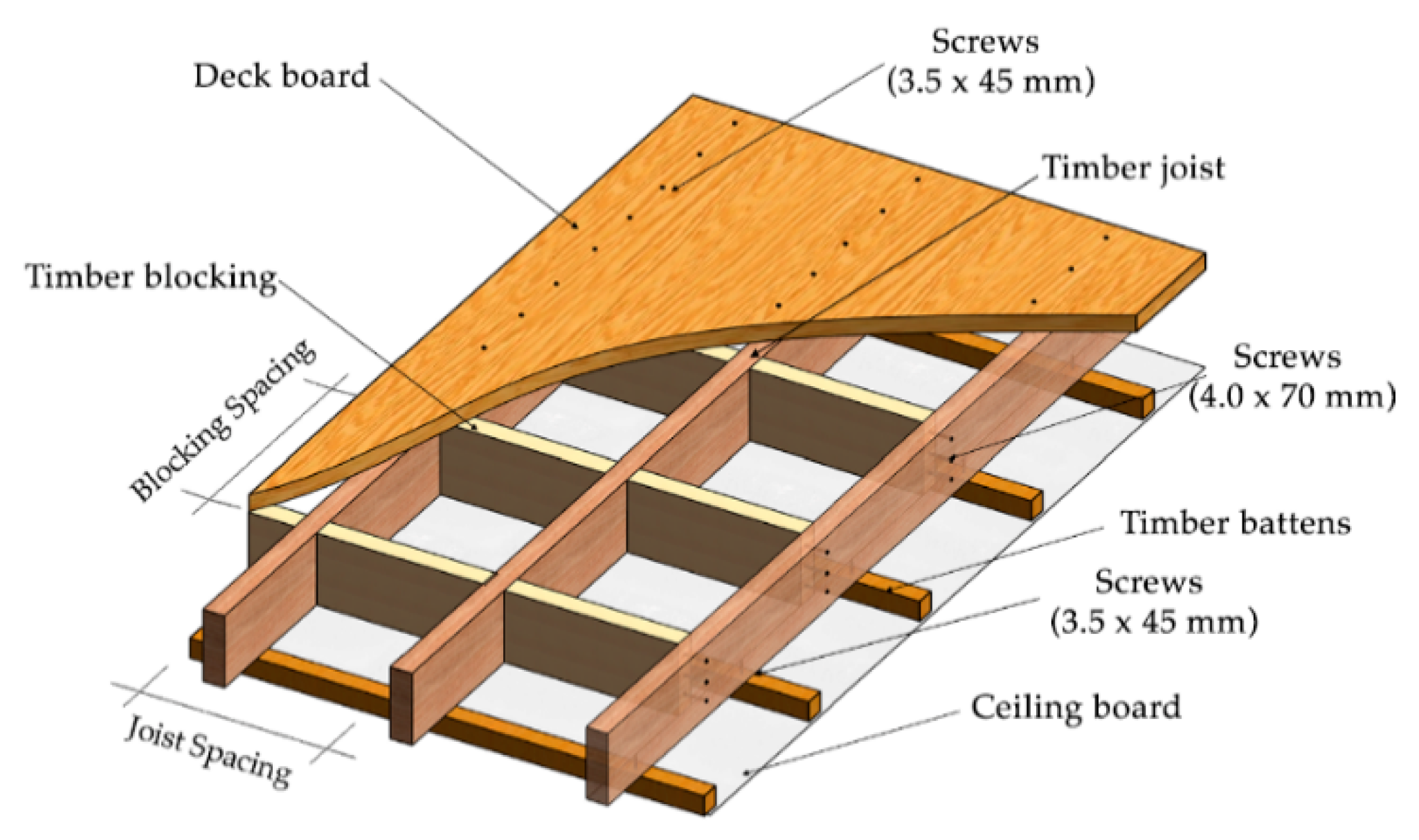
Floor Structure: Floating Floor type: Underfloor Heating Thickness Robust Detail Solid timber joist: Timber deck on resilient battens: No: 384mm E-FT-2: 423.5mm E-FT-8 Engineered I-joist: Timber deck on resilient battens: No: 403mm E-FT-1: 423.5mm E-FT-7: Wet screed: No: 451.6mm E-FT-4: Dry screed board: Yes: 346mm E-FT-5 Metal web joist.
Building Guidelines Suspended Timber Floors
Timber-Concrete Composite Floors. As part of its research work on wood buildings, FPInnovations has recently launched a Design Guide for Timber-Concrete Composite Floors in Canada. This technique, far from being new, could prove to be a cost-competitive solution for floors with longer-span since the mechanical properties of the two materials.
Timber floor
#09 • Timber Flooring Design Guide Page 4 Introduction Scope This publication provides a reference guide for the installation of solid timber strip flooring over bearers and joists, timber-based sheet flooring products and concrete slabs. Generally, floors of this type are of solid timber or a laminated product made from layers of timber,

Cross section of rigid core engineered hardwood showing the layers Engineered hardwood
Introduction to Floor Details. The most common materials used for the construction of ground and upper floors tend to be concrete or timber. Required span, resistance to passage of sound, and fire resistance will often be factors to consider when deciding which material to use in floor design. The Building Regulations in the UK provide guidance.
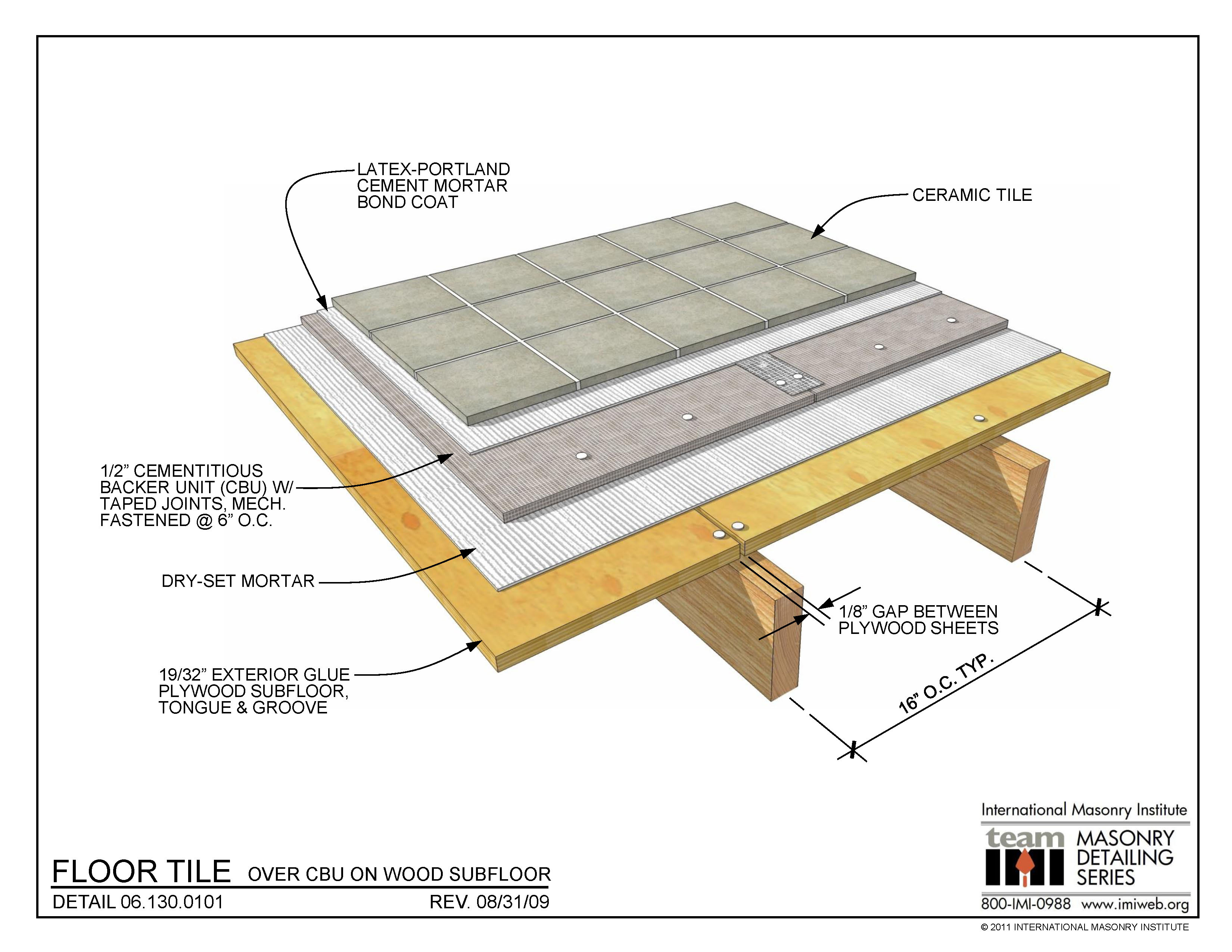
06.130.0101 Floor Tile Over CBU on Wood Subfloor International Masonry Institute
Strip: Often considered a "traditional" wood floor. Strips range in thickness from 5/16 inches to 3/4 inches and are available in widths that range from 1 inch to 3 inches. Plank: Wider than strip wood, planks are available in 1/2-inch and 3/4-inch thicknesses and multiple widths ranging from 3 inches to 12 inches, in 1-inch increments.
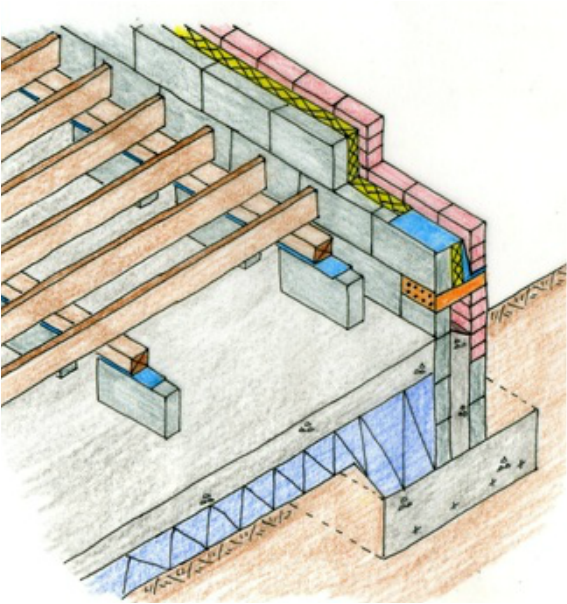
Suspended Timber Floor Construction Studies Q1
The timber cladding is also susceptible to water damage from splash zones - ie at the base of the building, so the cladding must be lifted by a minimum of 200 to 250mm. Battens are usually placed at 600mm centres, and sized no less than 38x38mm. For diagonal boards the battens are brought a little closer at 400mm centres.
Building Guidelines Suspended Timber Floors
The mass required for a timber floor is less than that of a concrete floor because the material is softer and radiates sound less efficiently. Diagram HE28 - Types of floors - Extract from TGD E. To ensure floor construction is fully effective, care should be taken to correctly detail the junctions between the separating floor and other.
Timber Timber Massivholzbett Bei Hoffner Mobel Hoffner Wood, especially when suitable for
Timber floor construction consists of boarding supported by timber joists (bridging joists or floor joists) which are nailed to wall plates on their ends and supported by a sleeper or dwarf wall lengthways. The different types of timber joists. Timber joists are essential components in many construction projects, providing a framework to.

timber floor detail floating Google Search Timber flooring, Acoustic insulation, Floating floor
Cite: Franco, José Tomás. "21 Detailed Construction Sections for Wood Structures" [En Detalle: Cortes Constructivos / Estructuras de Madera] 04 Mar 2018. ArchDaily. (Trans. Gosselin, Marina.

Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture
Timberlinx (877.900.3111) is a Canadian firm that offers a unique range of hidden timber fasteners that require nothing more than accurately drilled 1 1/8" holes. A special jig makes it easy to bore these holes square. The system works in traditional solid wood beams as well as modern glulam or microlam timbers.

Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture
Modified — timber physically modified in a process that changes its properties to enhance its durability to an appropriate level. Larch is a great example of a naturally durable commonly used softwood in cladding. It weathers to a lovely grey and can be purchased pressure treated, helping to further extend its lifespan to a minimum of 10 years.

FloorFraming Design Fine Homebuilding
Diagram B47 - Typical detail of timber floor suspended by tassel walls. If the fill depth is greater than 900mm, joists should span from perimeter to perimeter, if required an intermediate support can be provided (i.e. a steel beam). If steel is to be used to reduce the span, steel must be designed by an engineer.

Floating Wood Floor Install One in 8 Steps This Old House
This concept should be maintained when the ground level externally is level with the internal finish floor level. All the same considerations as above should be taken to account as well as the foundation or timber structure being raised 150 mm above the external ground level, usually 150 mm higher than the internal finished floor level.