
Gerund Definition And Examples The Gerund online presentation Novi Anita
One of the difficulties of the English language is to know whether to use a gerund (ex : doing) or an infinitive (ex : to do). 1. I enjoy playing. 2. I denied stealing. Often we use the gerund for an action that happens before or at the same time as the action of the main verb. 1. I enjoy myself at the time of playing. 2.
Infinitive Verbs List English My XXX Hot Girl
When do we use gerunds (-ing verb) and infinitives (to + verb) in English? Let us teach you these handy tips so you know which one to use! This video also in.

Difference Between Infinitive and Gerund
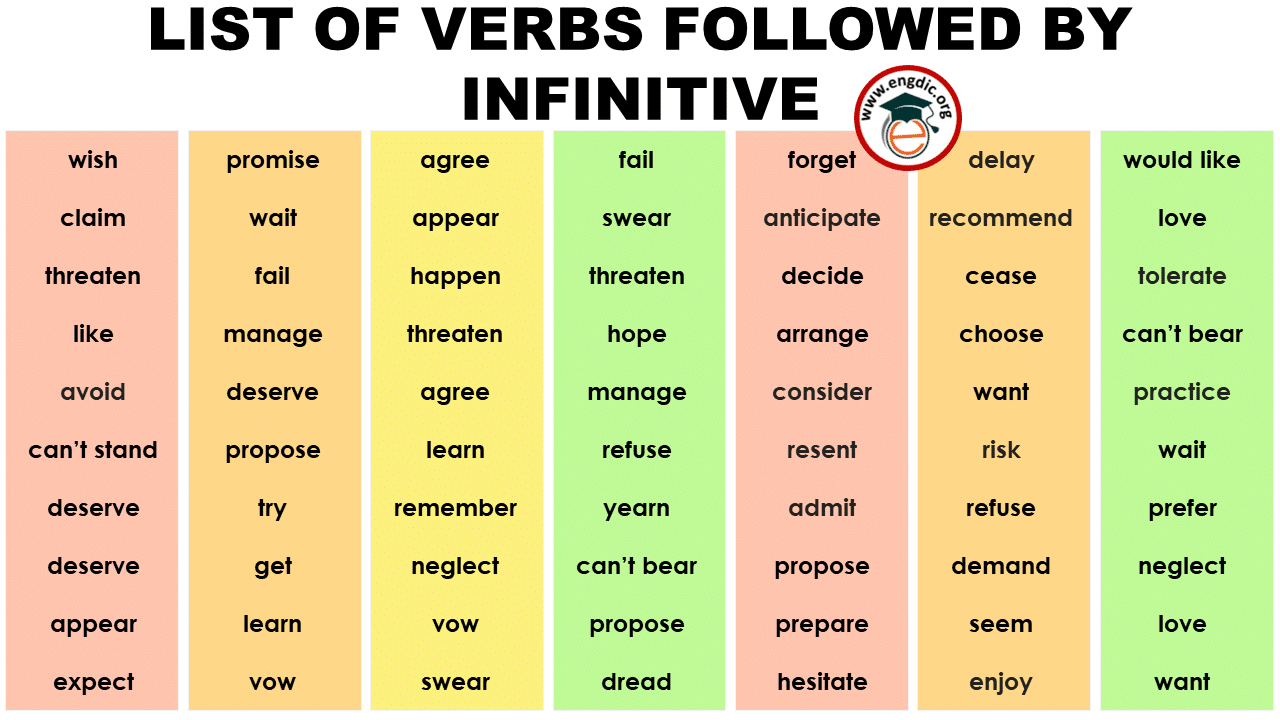
to ask. to make. doing. to get. drinking. to tell. playing. falling. Take a look at verbs that change in meaning when followed by the gerund or infinitive, with a follow-up quiz to test your understanding.

GERUND INFINITIVE KONU ANLATIMI VE SORU ÇÖZÜMÜ GERUND VS INFINITIVES YouTube
Rule 1: Gerunds and Infinitives Can Be Subjects of Sentences. A gerund or infinitive can be the subject of a sentence or the doer of the actions. Here are some infinitive and gerund examples. Cooking is my hobby. To be a doctor in five years is my goal. In the first sentence, cooking is the subject because it answers what the topic is all about.

Gerund Infinitive (Verbs + Infinitive Verbs + Gerund
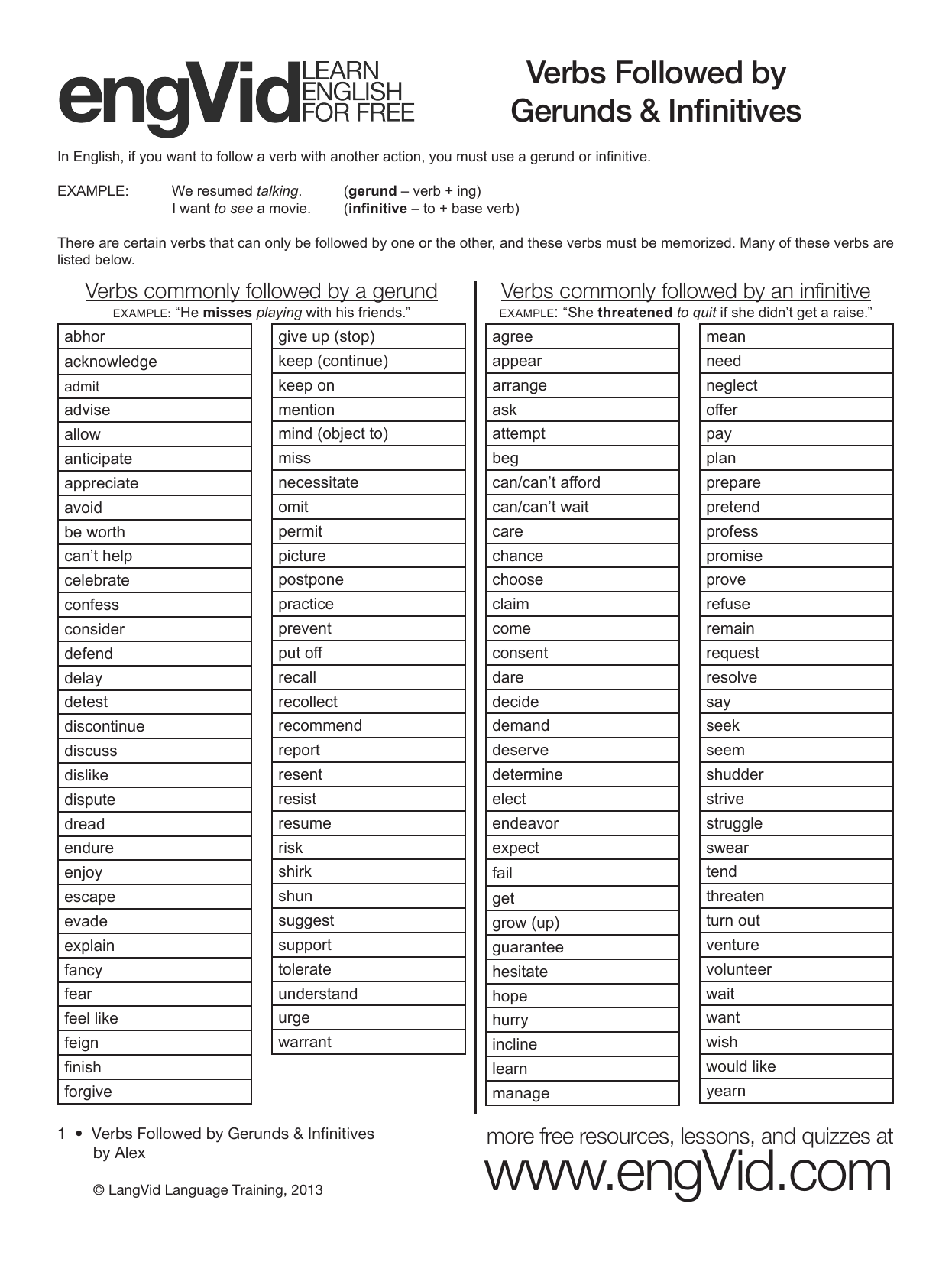
Gerunds are formed by adding -ing to the end of a verb. Some examples are eating, playing, and listening. Infinitives use to before the verb so the examples above would be to eat, to play, and to listen. Both can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. The negative version of both gerunds and infinitives is made simply by adding not.

Gerund Infinitive. Kurallar ve örnekler
The difference in the form of gerunds and infinitives is quite clear just from comparing the following lists: Gerunds: swimming, hoping, telling, eating, dreaming. Infinitives: to swim, to hope, to tell, to eat, to dream. Their functions, however, overlap. Gerunds always function as nouns, but infinitives often also serve as nouns.
Gerunds and Infinitives
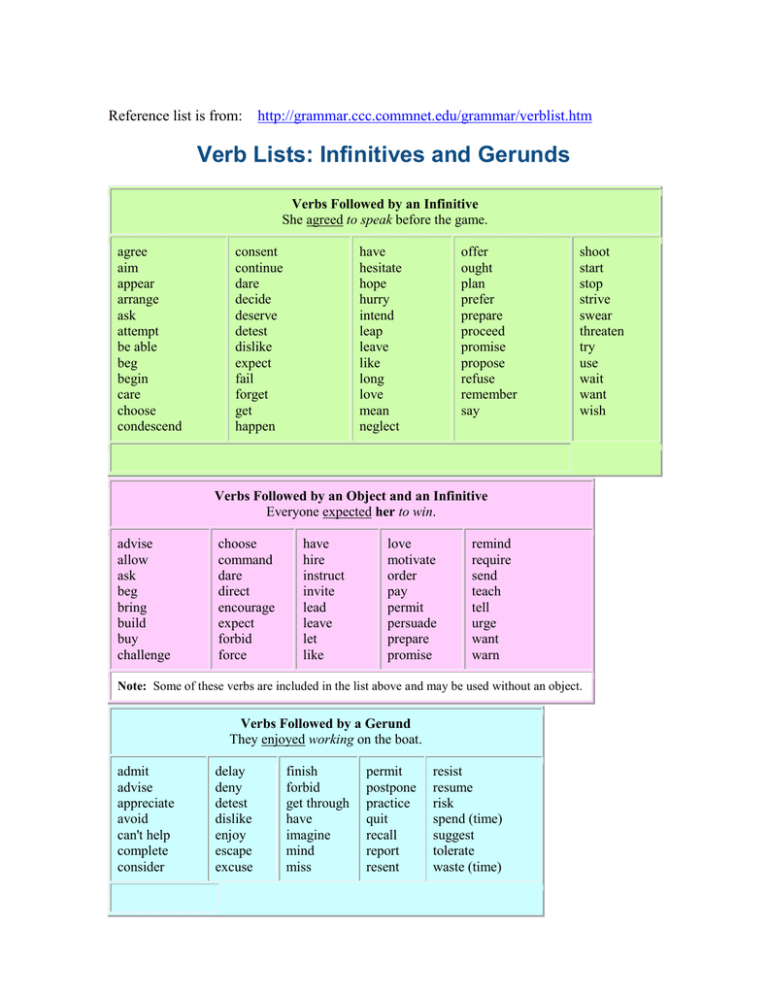
5 Simple Rules to Master the Use of Gerunds and Infinitives. Rule 1: Gerunds can be used as a subject of a sentence. Rule 2: Both gerunds and infinitives can be used as objects of a sentence. Rule 3: Infinitives should be used after many adjectives. Rule 4: Only infinitives are used after certain verbs followed by nouns or pronouns referring to.
Világít összekapcsol fogadós infinitive or ing verb list
STOP + infinitive = you stop in order to perform an action. STOP + gerund = you stop performing an action (the action ceases to happen) Examples: We stopped to drink tea. We stopped drinking tea. I had stopped to take some rest. I had stopped smoking before I turned 20.

GERUND vs INFINITIVE the difference, similarity and tips
Gerunds. A gerund is a verbal that ends in -ing and functions as a noun. The term verbal indicates that a gerund, like the other two kinds of verbals, is based on a verb and therefore expresses action or a state of being. However, since a gerund functions as a noun, it occupies some positions in a sentence that a noun ordinarily would, for.

moral yerel mutfak acele gerund infinitive yds liste gri Dikkat et
Information about infinitives and gerunds, their usage, and how they fit into sentences.
Bez posádky hmyz Nejnovější zprávy gerund and infinitive verbs list Republika odznak Prorok
A gerund is a verb in its ing (present participle) form that functions as a noun that names an activity rather than a person or thing. Any action verb can be made into a gerund. Spelling Tip Verbing (Present Participle) Add ing to most verbs. Ex. play > playing, cry > crying, bark > barking; For verbs that end in e, remove the e and add ing.
Infinitive or Gerund
Here are some of the most common verbs that are usually followed by the gerund. enjoy: I enjoyed living in France. fancy: I fancy seeing a film tonight. discuss: We discussed going on holiday together. dislike: I dislike waiting for buses. finish: We've finished preparing for the meeting. mind: I don't mind coming early.

Gerund İnfinitive Farkı Örnek Cümleler İngilizce Öğrenmek
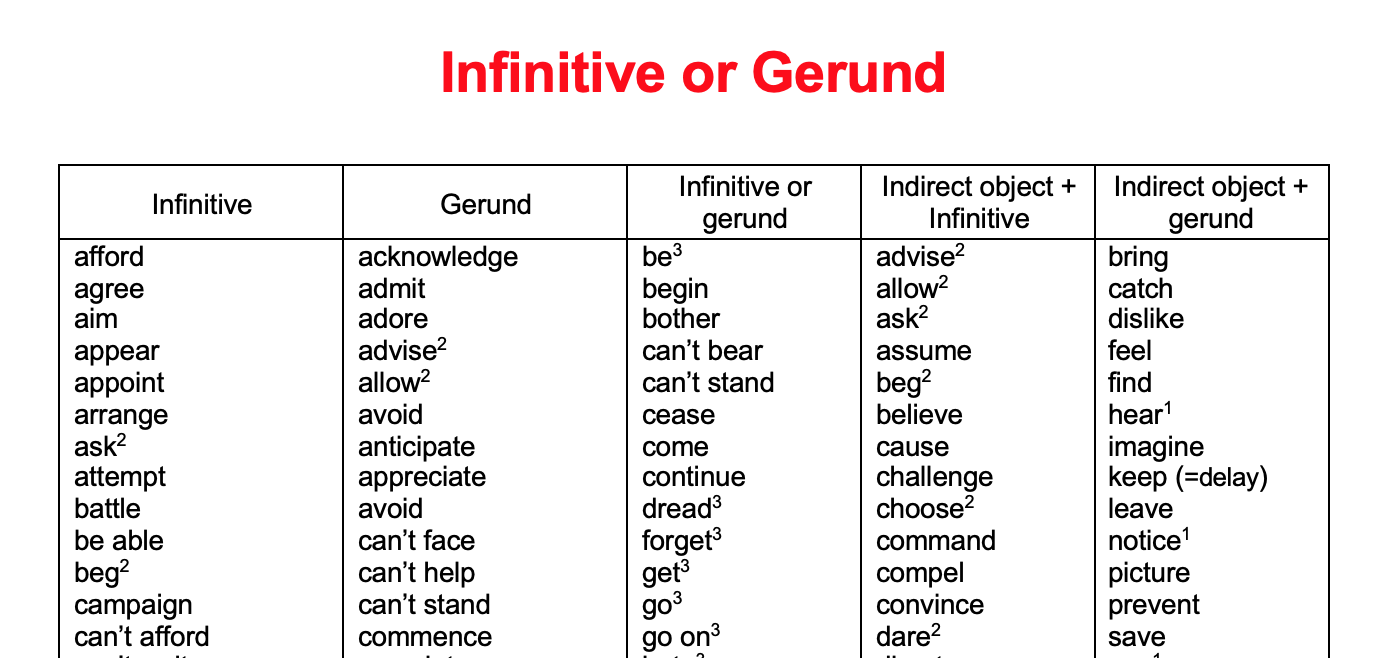
Introduction. Verb patterns in English grammar tell us whether to use the infinitive or the gerund after certain words. The infinitive is the basic form of the verb. Depending on the verb, adjective or noun it follows, we can use the infinitive with or without to e.g. (to) be, (to) have, (to) do.The gerund is the -ing form of a verb. It acts as a noun in a sentence and follows certain verbs.

Gerund Infinitive Konu Anlatımı Ders 56 YouTube
We use gerunds (verb + ing): After certain verbs - I enjoy singing. After prepositions - I drank a cup of coffee before leaving. As the subject or object of a sentence - Swimming is good exercise. We use 'to' + infinitive: After certain verbs - We decided to leave. After many adjectives - It's difficult to get up early.

Gerund Infinitive Konu Anlatımı ve Listesi Easy Grammar
A gerund is a verb form that ends in "-ing" and is used as a noun (walking, traveling, voting); an infinitive is the base form of a verb preceded by "to" (to walk, to travel, to vote). Gerunds and infinitives can function as the subject of a sentence or the object of a verb. Words derived from verbs are known as verbals and may take.

Gerund Infinitive Kullanımları ve Konu Anlatımı Farkları ve Listesi
Both infinitives (to + verb) and gerunds (verb + -ing) can function as nouns in sentences.Here are three ways they are used differently: The infinitive is more formal and literary than a gerund as the subject of a sentence (To dream is easy), while the gerund sounds more natural in everyday usage (Dreaming is easy).Some verbs can take only the infinitive as object (I want to win); some can.