
laptop diagram Schematic Diagram Hplc Instrument Diagram
Rice University via OpenStax CNX. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate the components in a mixture, and to identify and quantify each component. It was initially discovered as an analytical technique in the early twentieth century and was first used to separate colored compounds.
Hplc Chromatogram Analysis
High-performance liquid chromatography or commonly known as HPLC, is an analytical technique used to separate, identify or quantify each component in a mixture. The mixture is separated using the basic principle of column chromatography and then identified and quantified by spectroscopy.

HP Liquid Chromatography (Laboratory Manual)
Figure 12.5.13 shows a block diagram of a typical HPLC-MS instrument. The effluent from the column enters the mass spectrometer's ion source using an interface the removes most of the mobile phase, an essential need because of the incompatibility between the liquid mobile phase and the mass spectrometer's high vacuum environment..
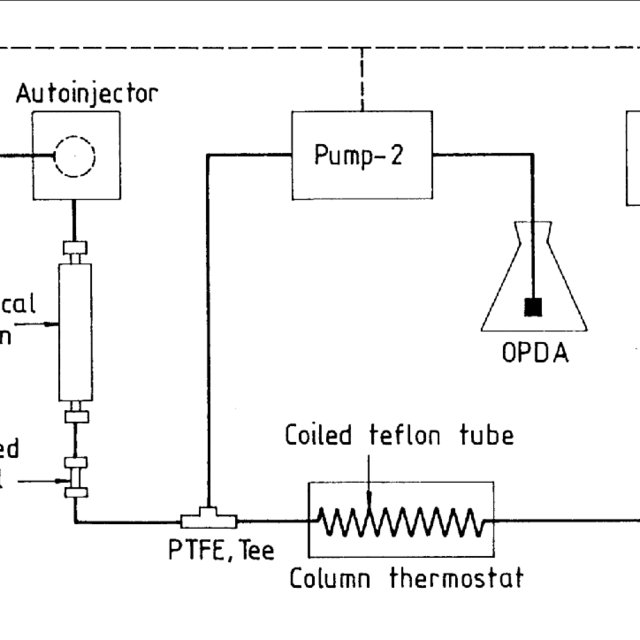
Block diagram of the HPLC system with inline postcolumn oxidation and
HPLC is a technique for disjointing, determinating, and quantifying each component in a mixture. Spectroscopy is used to identify and quantify the mixture, which is separated using the fundamental concept of column chromatography.
What are the Uses of HPLC? Imagination Waffle
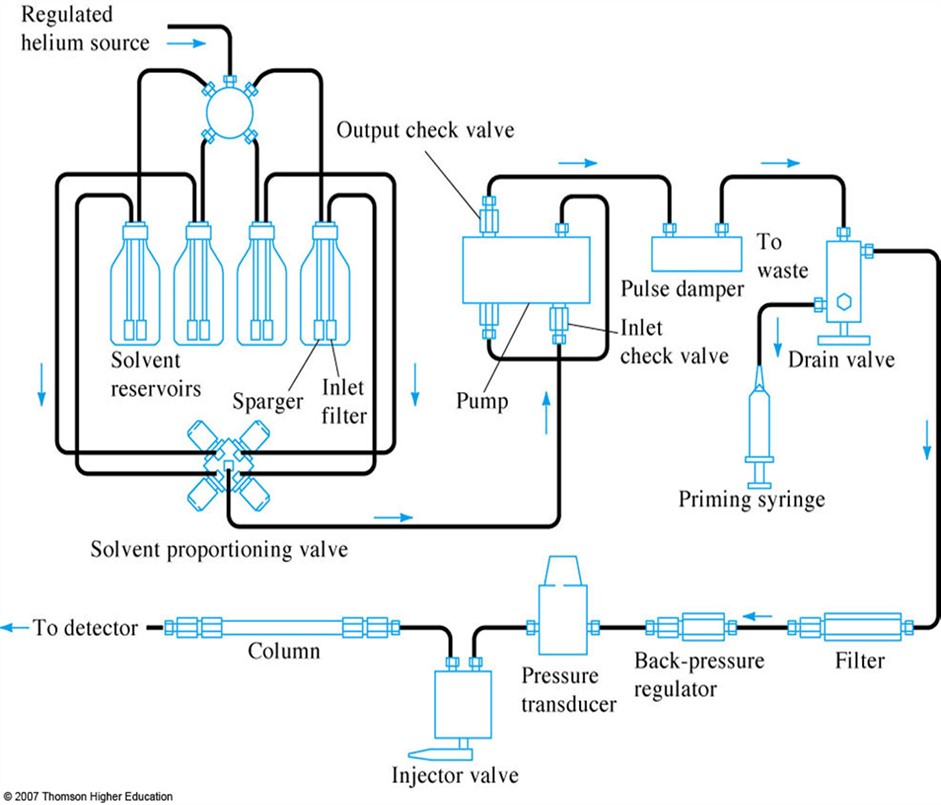
Most modern HPLC pumps have at least one pair of reciprocating pistons. One piston delivers the flow while the other aspirates the mobile phase at a programmed flow rate. Piston switching in pumps uses either one motor with a cam drive or multiple linear drive motors - one for each piston. The pistons are either series or parallel, with the.
HPLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT A REVIEW research journal
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) involves the injection of a small volume of liquid sample into a tube packed with tiny particles (3 to 5 microns (µm) in diameter called the stationary phase) where individual components of the sample are moved down the packed tube with a liquid (mobile phase) forced through the column by high pressu.
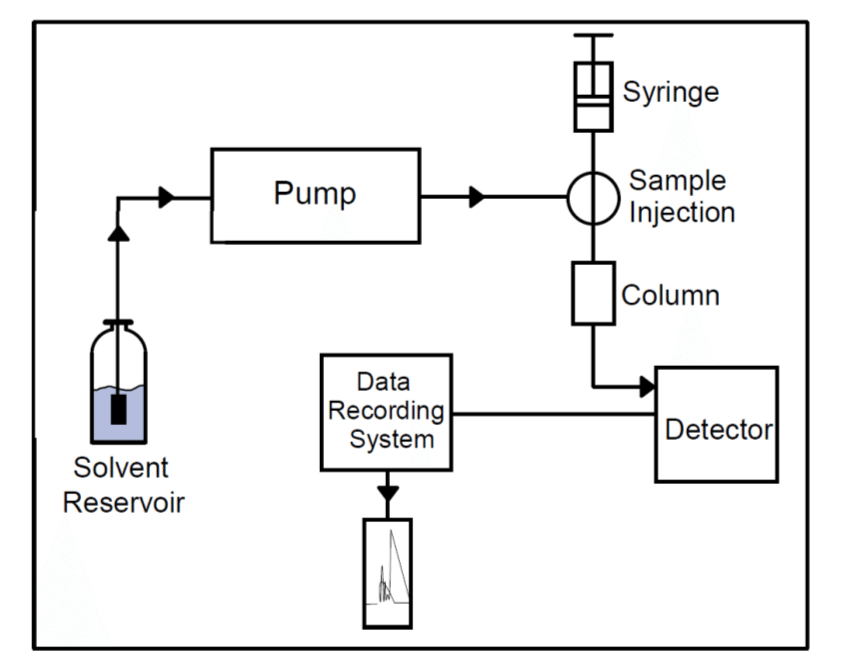
A Basic HPLC System Configuration Download Scientific Diagram
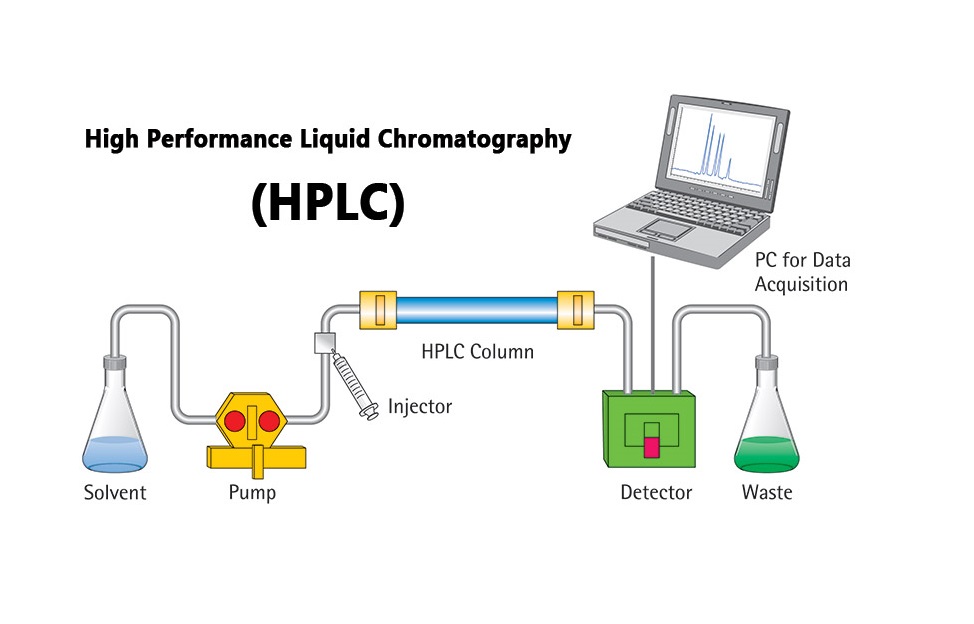
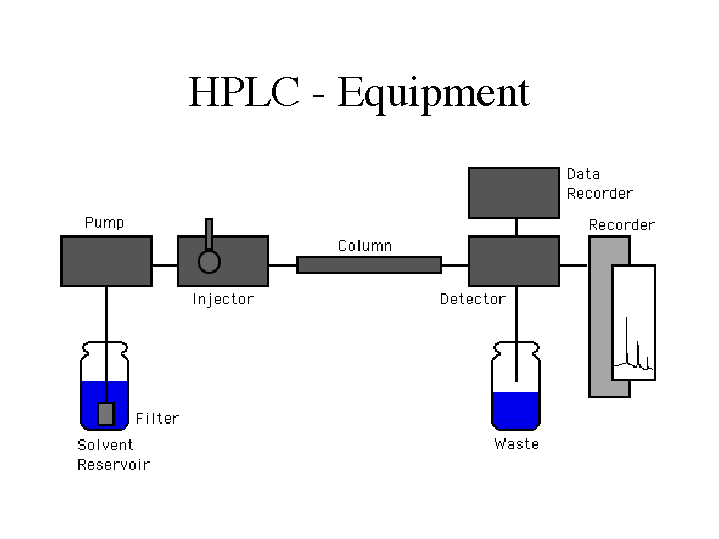
How Does High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Work? The components of a basic high-performance liquid chromatography [HPLC] system are shown in the simple diagram in Figure E. A reservoir holds the solvent [called the mobile phase, because it moves].
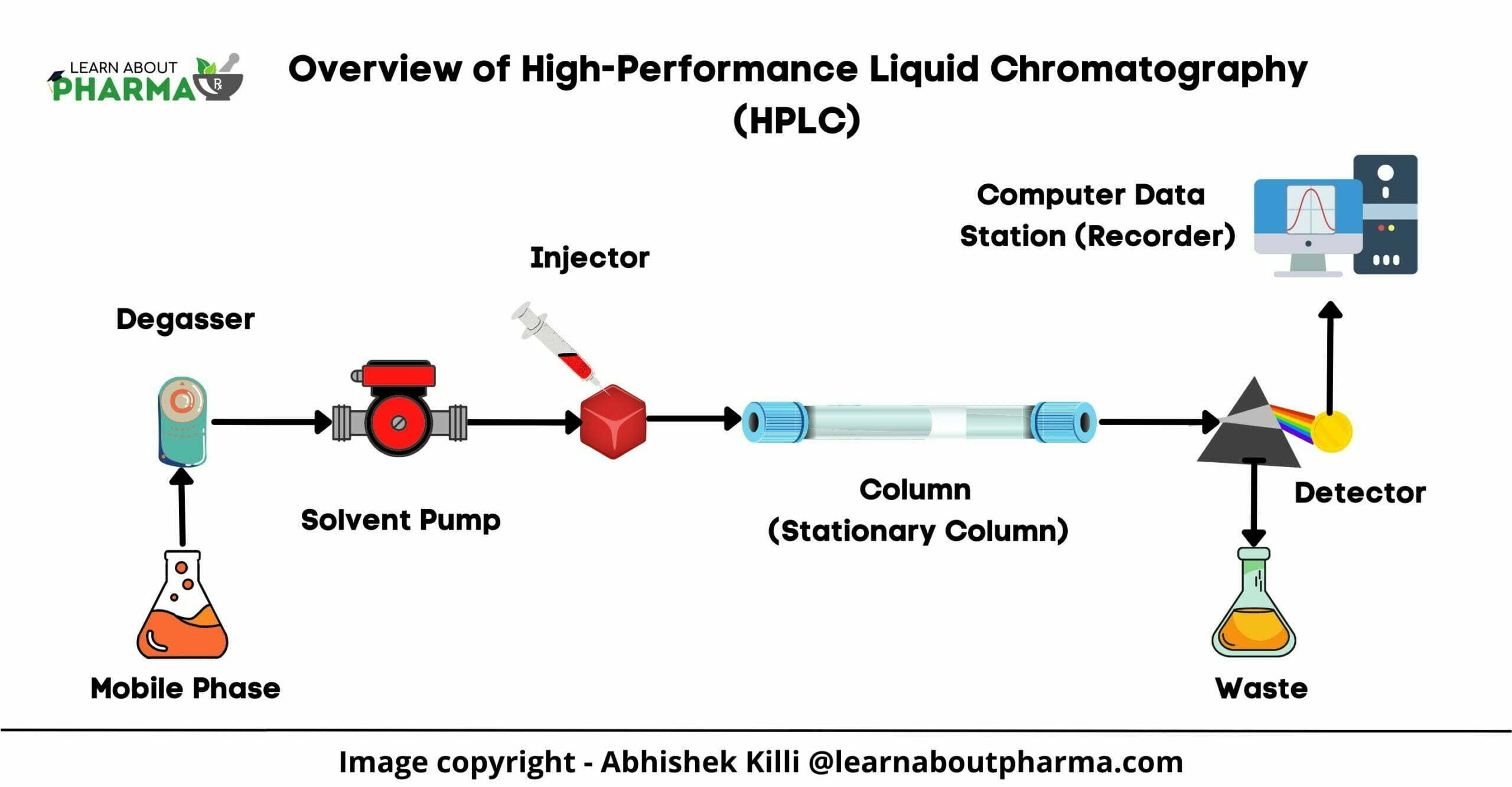
HPLC Definition, Principle, Diagram, Instrumentation, Types and
Note: It is important to read the introductory page about thin layer chromatography before you continue with this one - particularly the part about how thin layer chromatography works. High performance liquid chromatography works on the same basic principle. HPLC is essentially an adaptation of column chromatography - so it might be a good idea to have a (very quick) look at that as well.
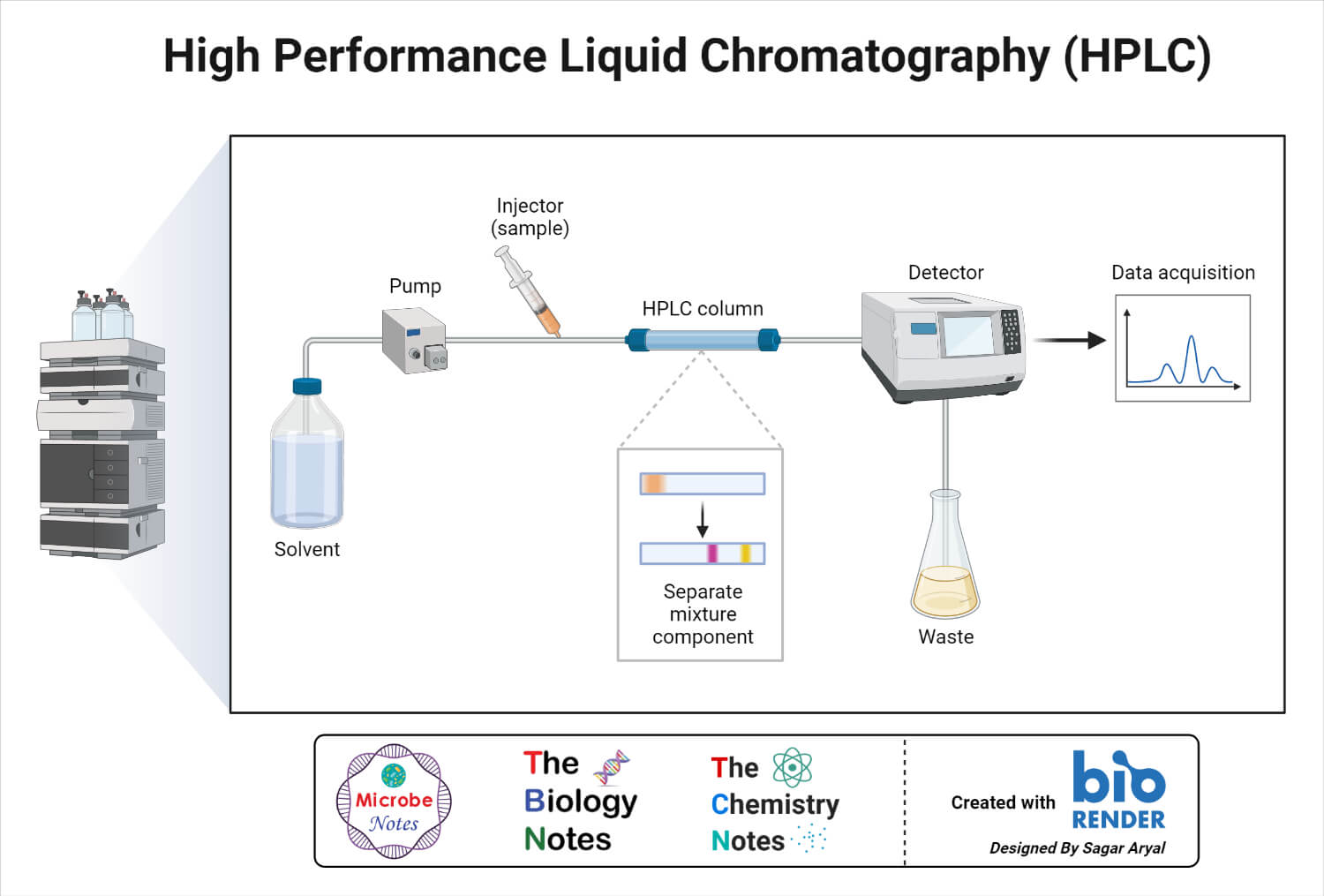
HPLC Definition, Principle, Parts, Types, Uses, Diagram
In this study, we developed a novel offline high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method based on 2,2′-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) radicals for antioxidant screening.
PPT “DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SIMPLE ANALYTICAL METHODS FOR THE
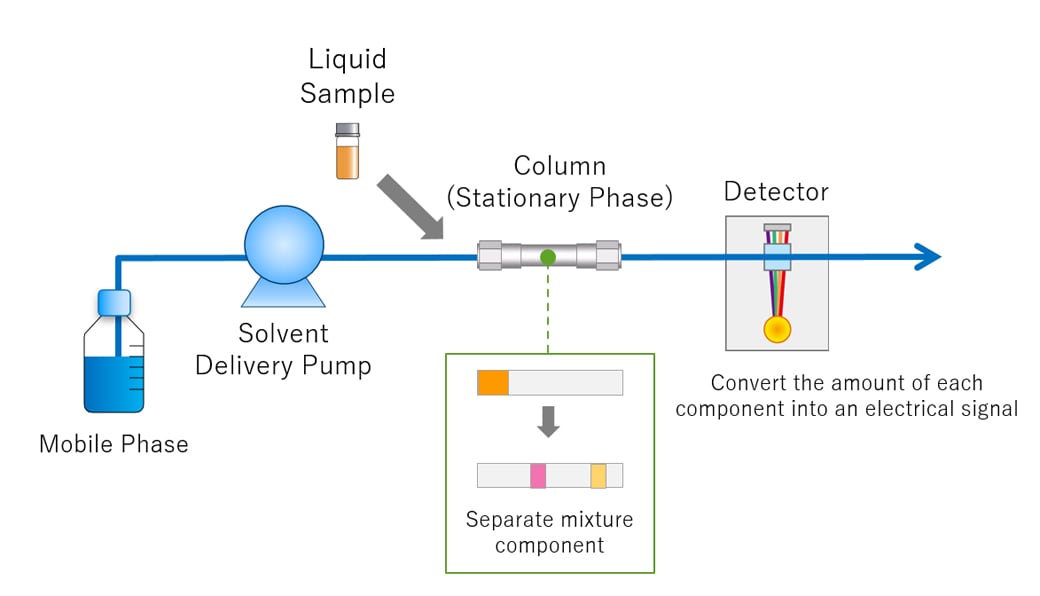
Fig.2 shows the HPLC flow diagram and the role of each component. Fig.2 HPLC Flow Diagram As for HPLC, the pump delivers the mobile phase at a controlled flow rate (a). Air can easily dissolve in the mobile phase under the standard atmospheric pressure in which we live in.
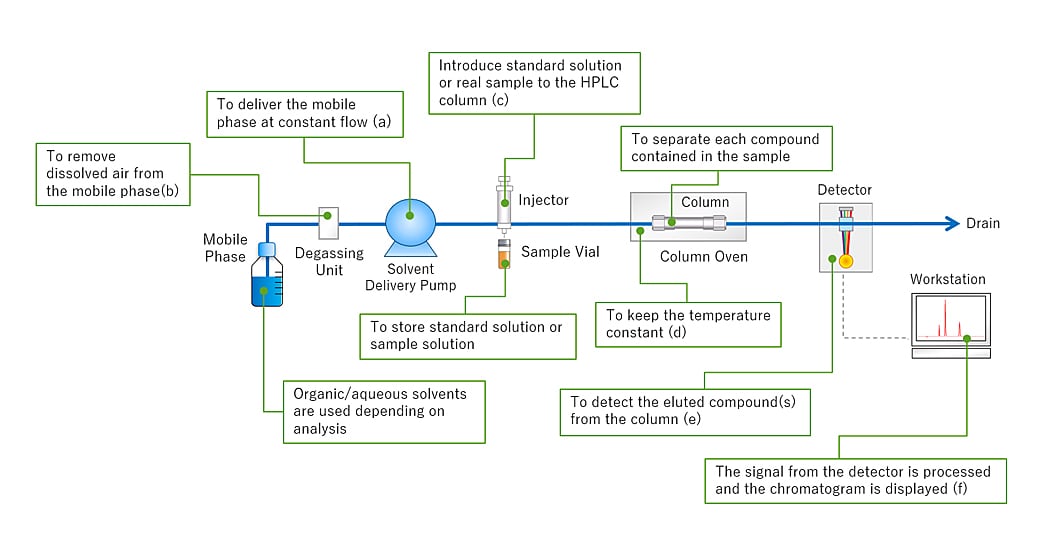
What is HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) ? SHIMADZU
Block diagram of an HPLC-MS. A three component mixture enters the HPLC. When component A elutes from the column, it enters the MS ion source and ionizes to form the parent ion and several fragment ions. The ions enter the mass analyzer, which separates them by their mass-to-charge ratio, providing the mass spectrum shown at the detector..

Hplc
The schematic block diagram of LC-MS detection is figure 1. The different parts of LC-MS instrument a. b. Liquid Spectrometry Chromatography separation of components is a Chroma performance ography (HPLC): of mixture liquid The Liquid Chromatography chromatography be carried in liquid mobile and solid stationary are different of

Block diagram of the HPLC system with inline postcolumn oxidation and
Where can blockages occur? Where are the consumable parts? Where can leaks occur ? What can I do to eliminate, reduce or anticipate potential problems with the LC ? Filters and Bottle necks for blockages Reduce Downtime by Understanding Common Problems Solvent inlet filters in solvent bottles glass: 20um - replace if needed!

Schematic diagram of a typical HPLC or HPIC setup with a simple
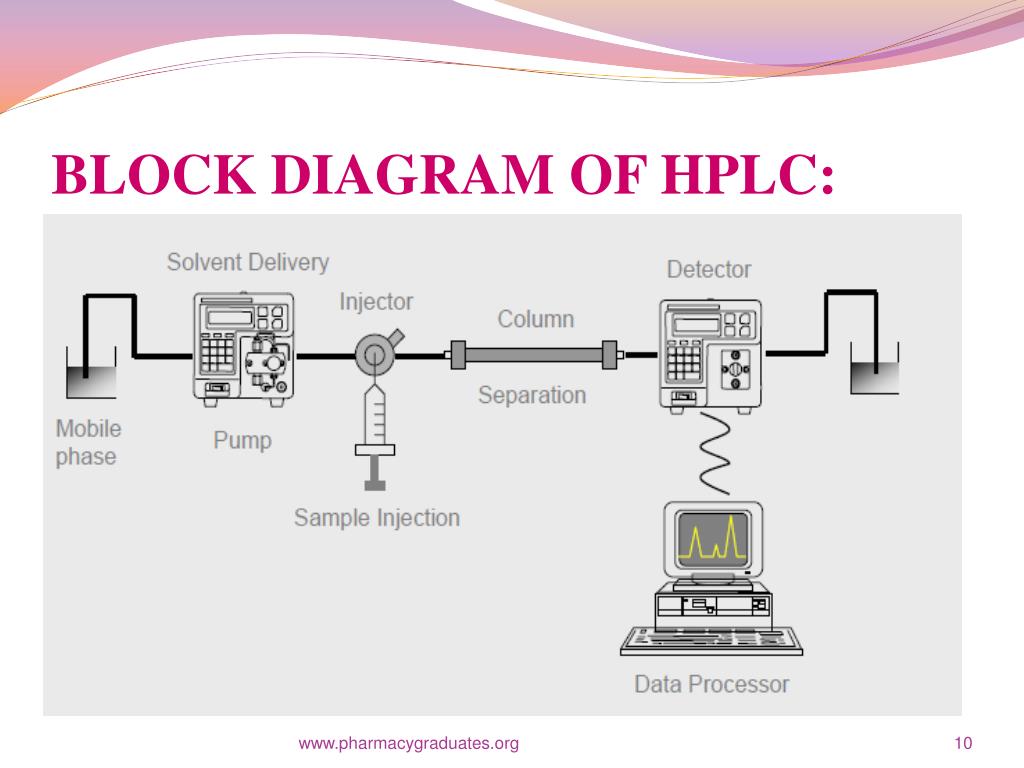
HPLC system diagram. Click to enlarge An HPLC instrument generally has four major hardware components: a pump, an autosampler, a column compartment, and a detector. Many factors, including mobile phase composition, stationary phase chemistry, and temperature, influence HPLC separations.

Simplified schematic representation of an HPLC system. Download
Block diagram of the HPLC system with in-line postcolumn oxidation and derivatization. Source publication Simple In-Line Postcolumn Oxidation and Derivatization for the Simultaneous Analysis of.
Exam 2 1992
Figure 12.50 shows a block diagram of a typical HPLC-MS instrument. The effluent from the column enters the mass spectrometer's ion source using an interface the removes most of the mobile phase, an essential need because of the incompatibility between the liquid mobile phase and the mass spectrometer's high vacuum environment. In the.