
View Image
Meckel's cave is a dural recess in the posteromedial portion of the middle cranial fossa that acts as a conduit for the trigeminal nerve between the prepontine cistern and the cavernous sinus, and houses the Gasserian ganglion and proximal rootlets of the trigeminal nerve.

A) CT scan (axial section) showing a calcific, punctate lesion... Download Scientific Diagram
The anatomy of the trigeminal cavum also known as Meckel's cave is still poorly understood despite the number of various descriptions available in the literature. The new concept of parasellar compartment means that Meckel's cave and the cavernous sinus constitute a unique entity. We sought to understand anatomic organization of the trigeminal cavum through dissection of 5 previously frozen.

Meckel's Diverticulum — With Report of a Case of Intussusception Due to Its Invagination NEJM
Meckel cave tumors account for only 0.5% of all intracranial tumors. The most common histologies are: trigeminal schwannoma : most common, ~33% of cases meningioma pituitary macroadenoma base of skull tumors metastases : including retrograde spread of head and neck tumors neurolymphomatosis epidermoid cyst lipoma Non-neoplastic

Cavum Meckeli Ars Neurochirurgica
Accessing Meckel's cave (MC) is surgically challenging. Open approaches are complex and often correlated with high morbidity. Endoscopic approaches emerged in the last decade as feasible alternatives to open approaches, especially for sampling indeterminate lesions.

ESPE 202 2014
Material and methods: We report a retrospective series of 5 patients with CTCs and the associated imaging features including the absence of diffusion restriction and solid contrast enhancement as well as their size, anatomical location with regard to adjacent structures and the remodeling or erosion of surrounding bony structures.

Meckels Cave
The trigeminal cavum arachnoid had a total width of 20.0 [17.5-25.0] mm and length of 24.5 [22.5-29.0] mm.Conclusion Our anatomical study revealed variable arachnoid extension, which may.

Meckel's cave, also known as trigeminal cave or Meckel's cavity, is a cerebrospinal fluid
Meckel's cave, also known as trigeminal cave, trigeminal cavity, or Meckel cavity, is a cerebrospinal fluid -containing dural pouch in the middle cranial fossa and opening from the posterior cranial fossa that houses the trigeminal ganglion . Gross anatomy Relations

Image
Meckel's cave is a natural mouth-shaped aperture in the medial portion of the middle cranial fossa that acts as a key conduit for the largest cranial nerve, the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It connects the cavernous sinus to the prepontine cistern of the posterior fossa.
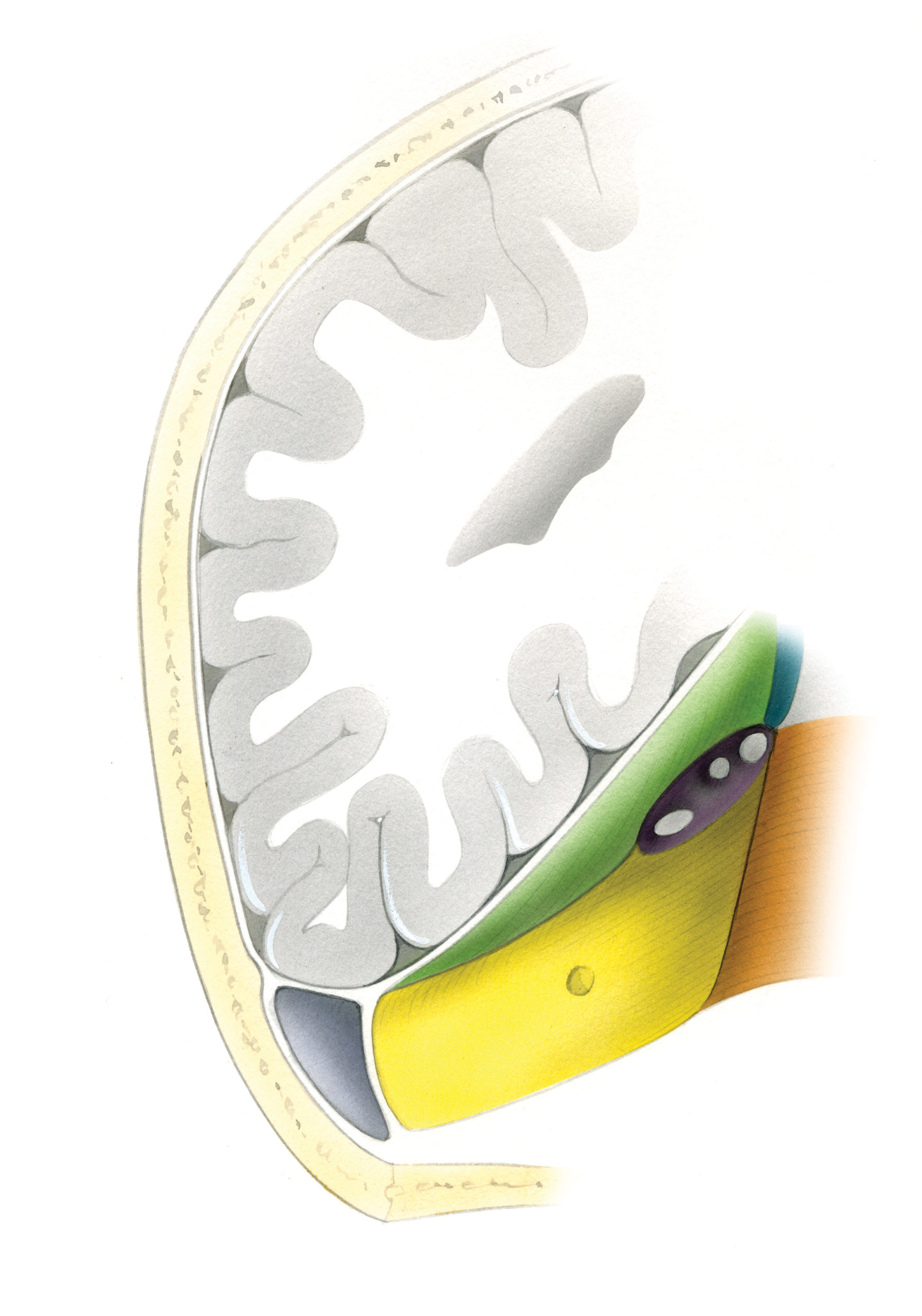
Posterior Fossa Approach Skull Base Surgery Atlas
Introduction. Cavum-trigeminale-cephaloceles (CTCs) are rare lesions of Meckel's cave and the petrous apex with few reports on their typical neuroradiological features [1], [2], [3].. Despite their distinctive imaging findings, CTCs are frequently mistaken for other petrous apex lesions such as cholesterol granulomas, mucoceles, cholesteatomas and effusion or inflammation of the petrosus apex.

Radiografia digital (topograma) mostrando a punção percutânea do cavum... Download Scientific
Introduction. Named after Johann Friedrich Meckel, a German anatomist, the cavum meckeli, also known as Meckel's cave, trigeminal cave or cisterna trigeminalis, is a region with a complex neurovascular array and, therefore, anatomically speaking, presenting a surgical challenge.. Meckel's cave is located at the petrous apex between two dural layers originating from the floor of the middle.
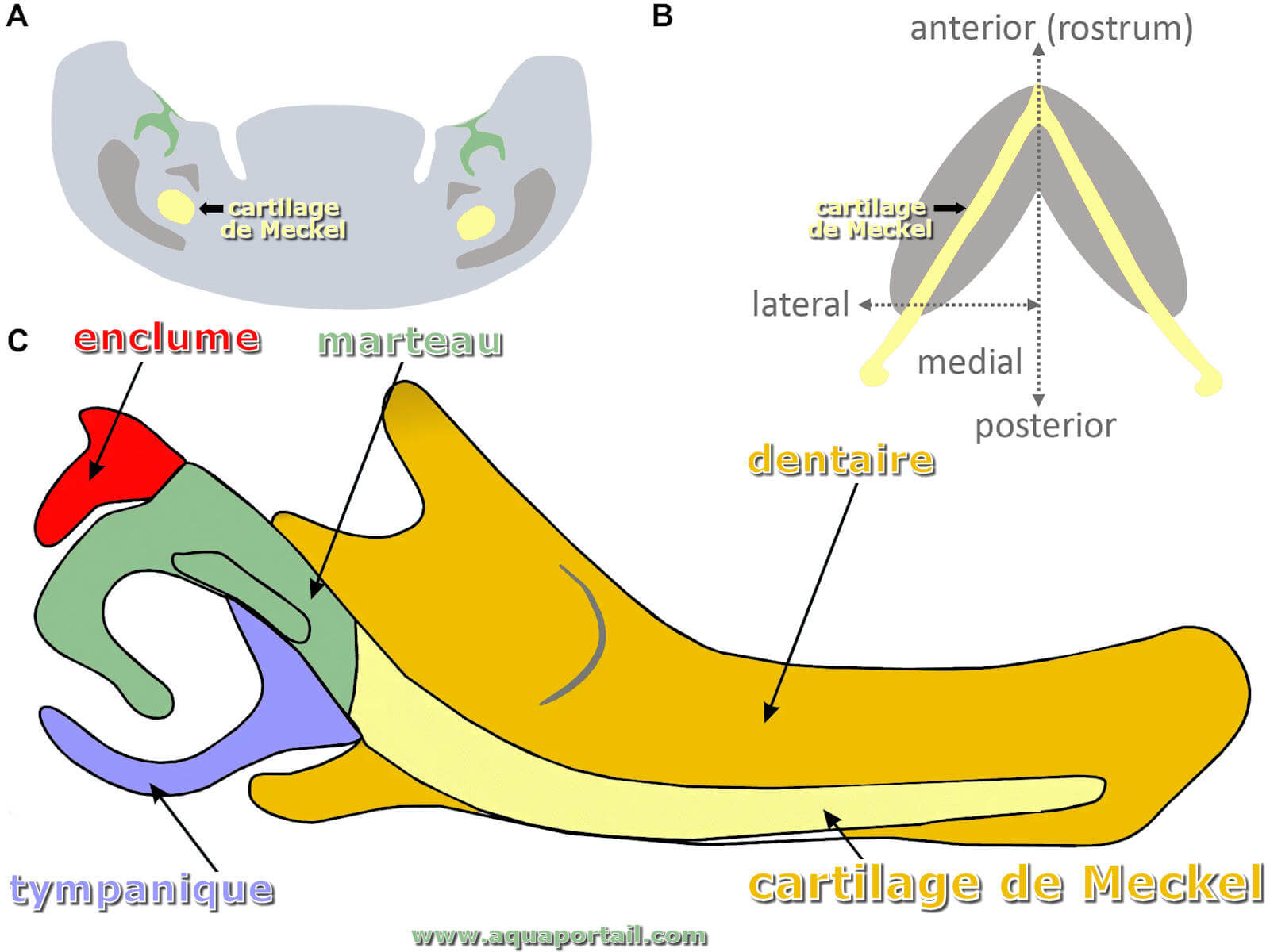
Cartilage de Meckel définition et explications
Trochlear Nerve. The Cavernous Sinus and Meckel's Cave. A, The outer layer of the dura of the right cavernous sinus has been peeled away from the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus and Meckel's cave. This exposes the oculomotor and trochlear nerves entering the roof of the cavernous sinus and passing forward through the superior orbital.

Meckel’s Cave (cavum trigeminale), also known as the trigeminal cave, is a cavity between two
Gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI image showing a dumbbell-shaped mass originating from the left side of Meckel's Meckel's cave, medial to the temporal lobe, and extending caudally through Meckel's Meckel's cave to compress the brain stem (right). Download : Download high-res image (383KB) Download : Download full-size image; Fig. 2.
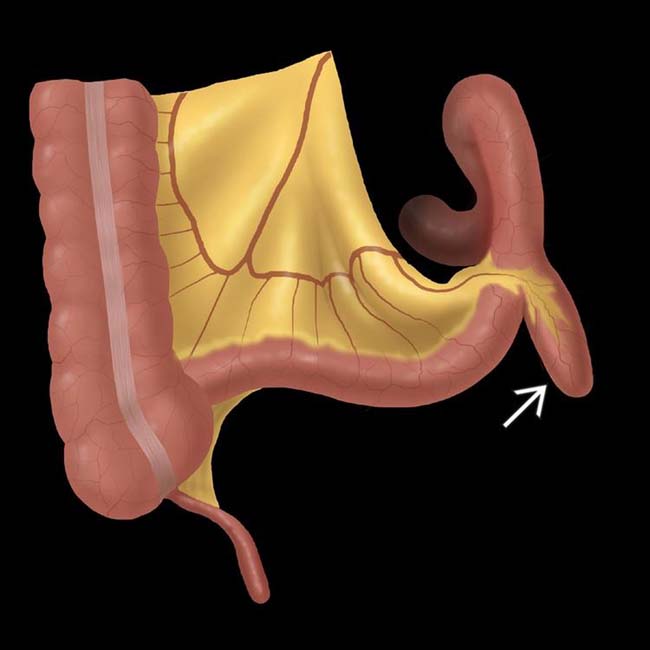
Meckel Diverticulum Radiology Key
Dilatation of the trigeminal cavum, or Meckel's cave (MC), is usually considered a radiological sign of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. However, the normal size of the trigeminal cavum is poorly characterized. In this study, we describe the anatomy of this meningeal structure. Methods

Neuroimaging of Meckel’s cave in normal and disease conditions Insights into Imaging Facial
Stanford Medicine Otolaryngology — Head & Neck Surgery Search for: Home About this Atlas Search for: Meckel's Cave ApproachesScott Stocker2020-09-23T15:25:00-07:00 Approaches to Meckel's Cave (Cavum Trigeminale) Posterior Fossa Approach Middle Fossa Approach Combined Middle and Posterior Fossa Approach

Image result for meckel's cave Medical, Anatomy, Image
The trigeminal cave (also known as Meckel's cave or cavum trigeminale) is a pouch of dura mater containing cerebrospinal fluid . Structure The trigeminal cave is formed by the two layers of dura mater (endosteal and meningeal) which are part of an evagination of the cerebellar tentorium near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone.

Cavum Meckeli Ars Neurochirurgica
Dilatation of the trigeminal cavum, or Meckel's cave (MC), is usually considered a radiological sign of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. However, the normal size of the trigeminal cavum is poorly characterized. In this study, we describe the anatomy of this meningeal structure.