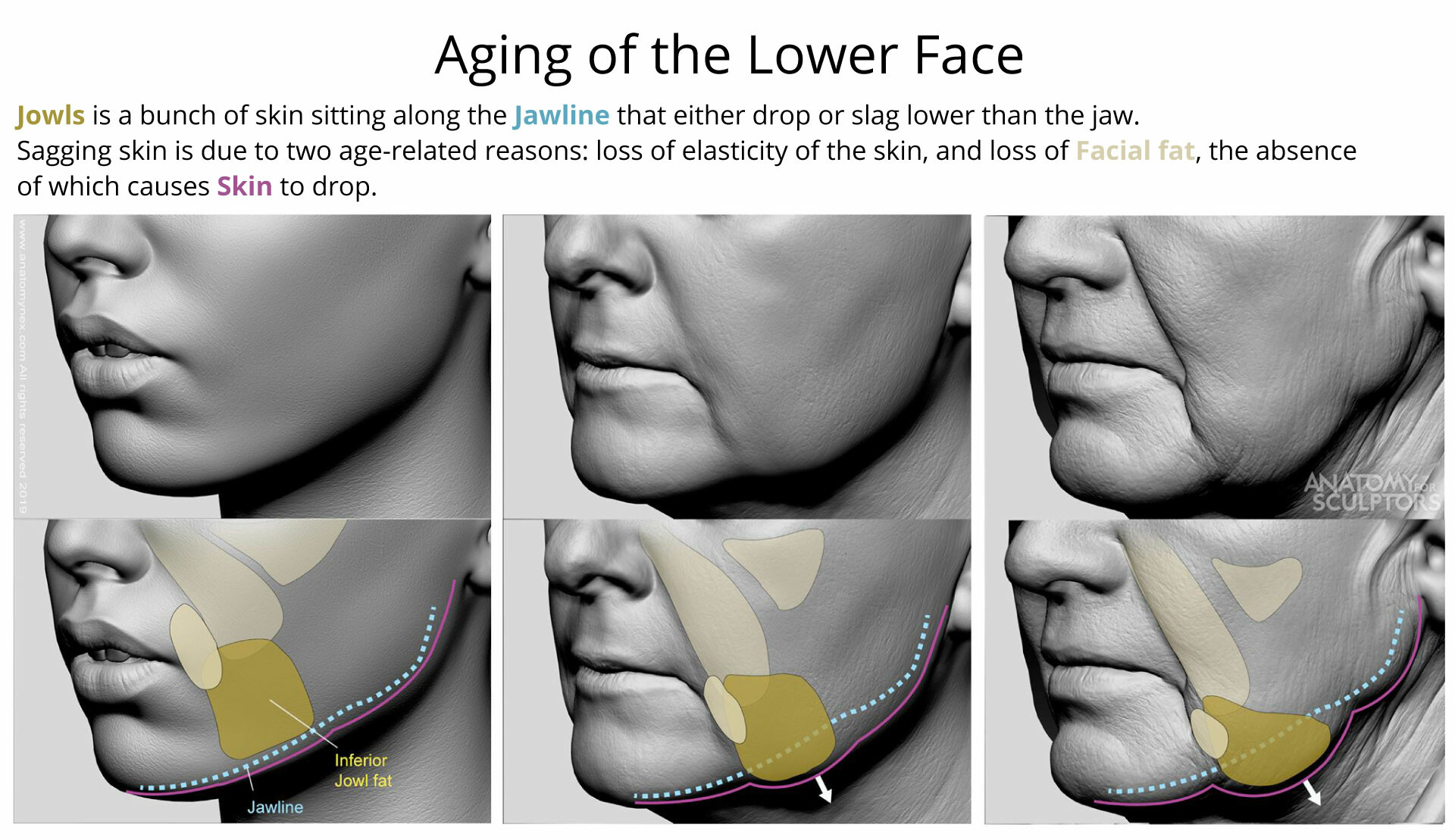
ArtStation Aging of the Lower Face
ISSN 2534-5079. We attempted to synthesize the anatomy of the face and neck in this anatomy module. We used MRI images T2-weighted with axial, sagittal and coronal planes. 512 anatomical structures were dynamically labeled, and some structures have been redesigned or enhanced with a graphic tablet for better readability.

Resultado de imagen para face anatomy Facial Anatomy, Head Anatomy
Structure and Function The anatomy of the face can divide into three main regions: upper face, middle face, and lower face. The entire face is covered by skin superficially, while the deep anatomy contains muscles, fat pads, nerves, vessels, and bones. Upper Face
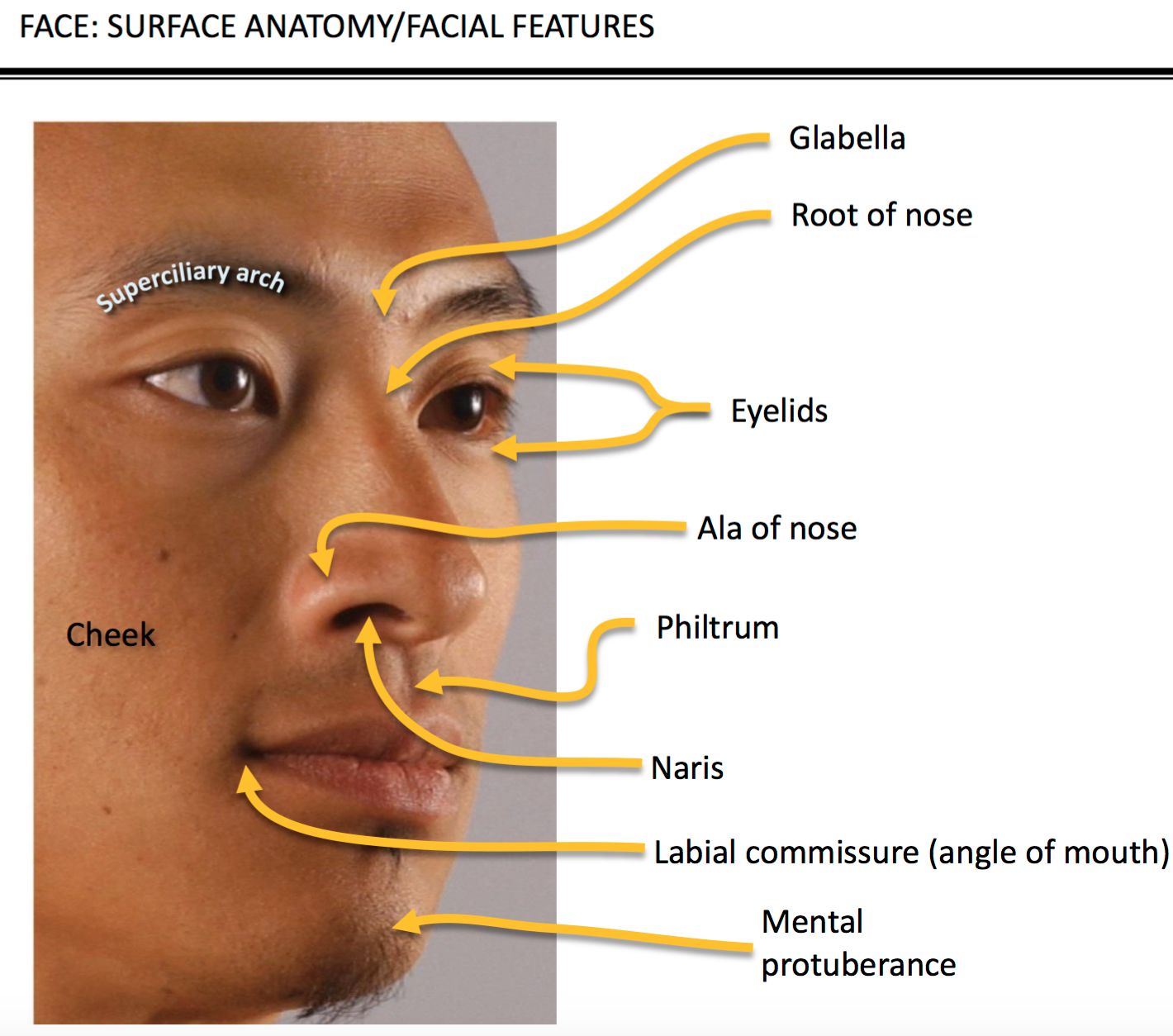
Surface Anatomy Of Face
Face Anatomy Anatomy Head and Neck Areas Face Anatomy Contents Skin of the Face Clinical Significance of the Skin of the Face Cleavage Lines of Skin in the Face Superficial Fascia of the Face Deep Fascia of the Face "Face Characteristic Features of the Muscles of Facial Expression Location and Function Muscles Around the Orifice of the Eye
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/2965/nzKZY8tzxy0re6hx184XA_regions-of-head-face_english.jpg)
Discover the Hidden Secrets of Your Face Muscle Anatomy Drawing to Amp
face, front part of the head that, in vertebrates, houses the sense organs of vision and smell as well as the mouth and jaws. In humans it extends from the forehead to the chin. During the course of evolution from the prehuman Australopithecus to modern humans ( Homo sapiens ), the face became smaller in relation to the overall size of the head.

Illustration Of The Anatomy Of A Female Human Face stock photo
The curved part of a bone that gives structural support to the rest of the bone. Above: Markings of the facial bones with the following views: (A) anterior view, (B) lateral view of the left side of the skull, (C) inferior view with the mandible removed, and (D) lateral view of the right side of the skull. Marking.

Anatomy The Face Study Hmong
Muscles of facial expression Musculi faciales Synonyms: Facial muscles, Craniofacial muscles , show more. The human face is the most anterior portion of the human head. It refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another.

Face anatomy by JosueVilela Medical Visualization Sculpture CGSociety
Fast and Free Shipping On Many Items You Love On eBay. Looking For Models Anatomical? We Have Almost Everything On eBay.
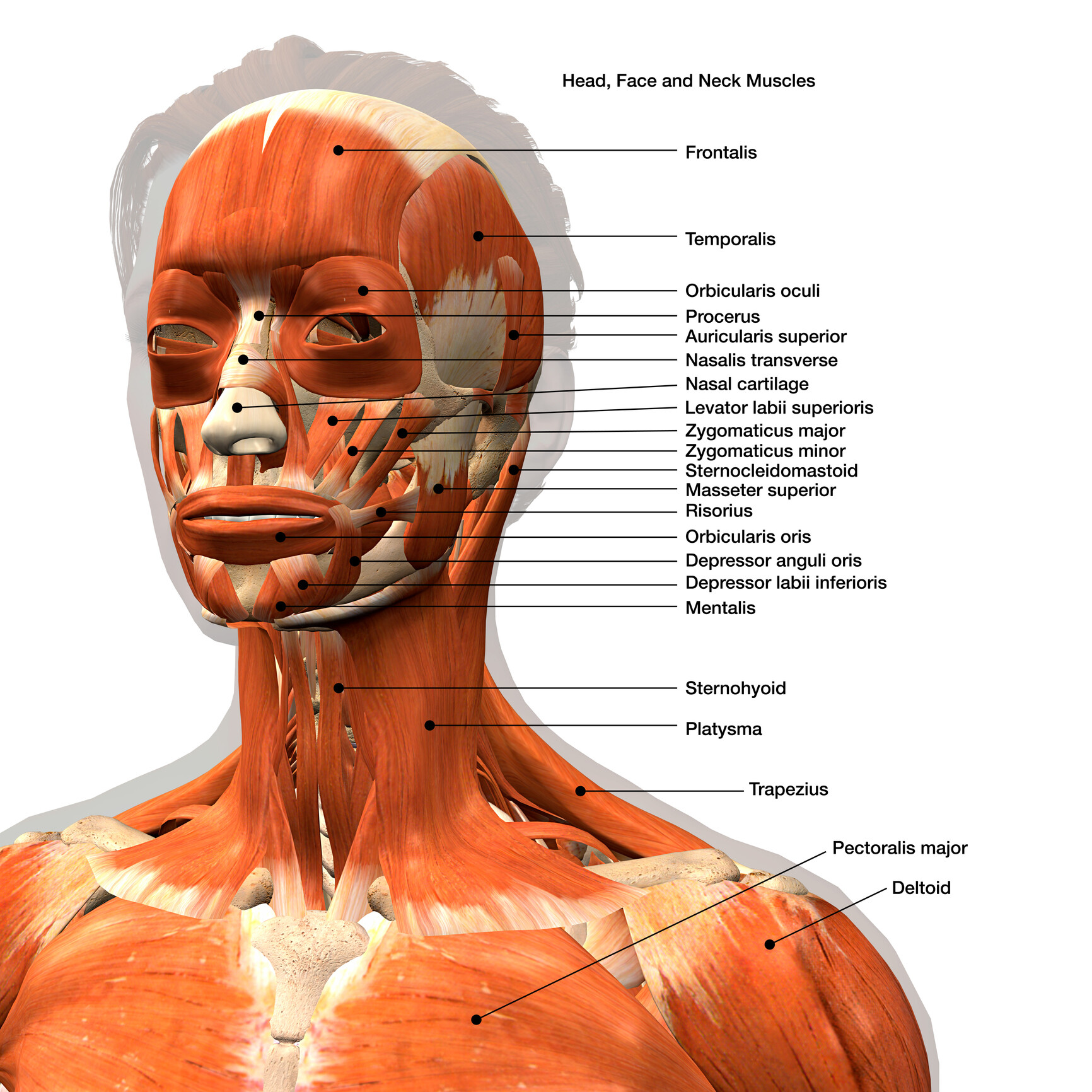
Muscles Of Face Diagram
Skeletal anatomy of the face The face is the feature which best distinguishes a person. Specialized regions of the human brain, such as the fusiform face area (FFA), enable facial recognition; when these are damaged, it may be impossible to recognize faces even of intimate family members.

Pin em Pilates
ISSN 2534-5079. This head and neck anatomy atlas is an educational tool for studying the normal anatomy of the face based on a contrast enhanced multidetector computed tomography imaging (axial and coronal planes). Interactive labeled images allow a comprehensive study of the anatomical structures.

Medical Science on Instagram “Wow! 😱Look at the amazing detail of the
Development of the Face and Palate. The external human face develops between the 4 th and 6 th week of embryonic development. The development of the face is completed by the 6 th week. Between the 6 th and 8 th week, the palate begins to develop. Consequently, this causes a distinction between the nasal and oral cavities.
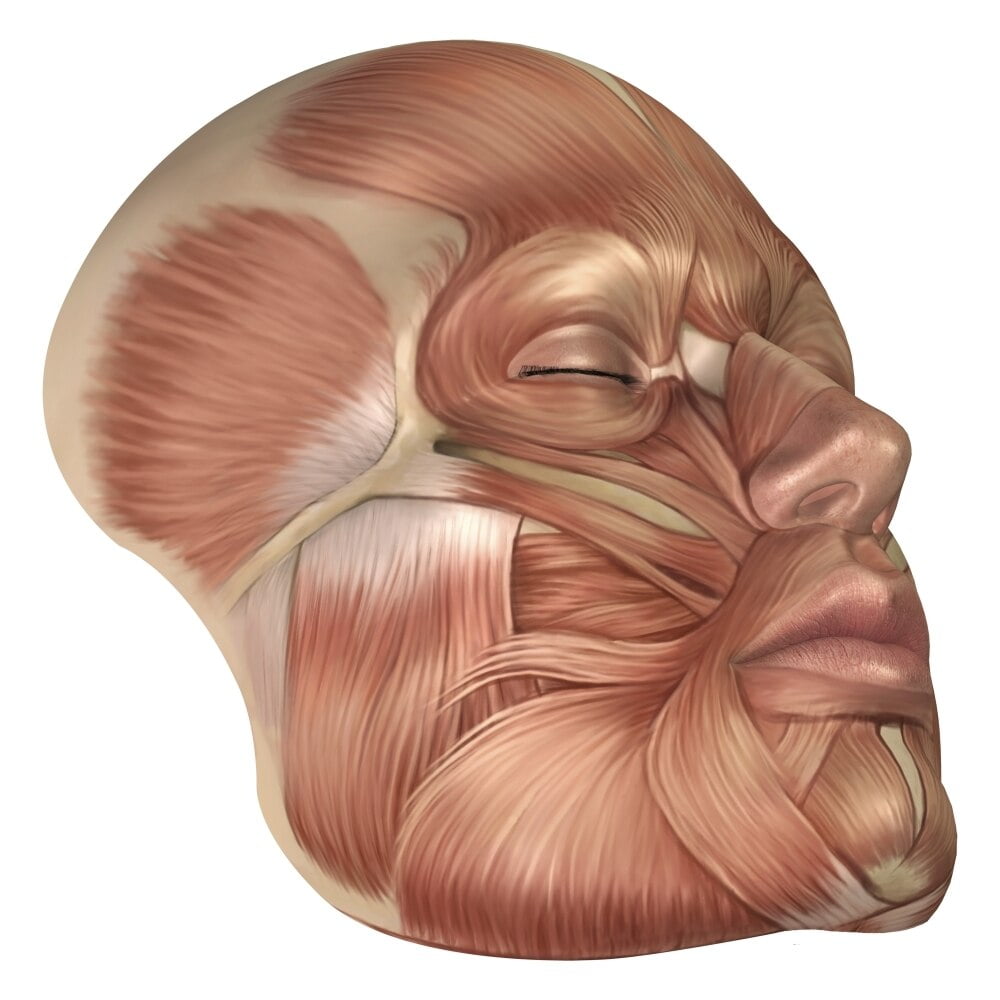
Anatomy of human face muscles Poster Print
F a c i a l B o n e s Functions Provide a structural framework for the face. So, the look or form of our face is due to our facial skeleton. Support the soft tissues of the face, head, and neck. Protect a part of the brain. Encase and protect the sensory organs — nose, eye, and tongue.

Surface Anatomy of the Face and Skin Medical Stock Images Company
In human face anatomy, all the features curve up and the ear moves up. Because the nose juts out, it oversteps its line (see figure) and the tip looks much closer to the mouth—if the face turns down enough, the nose will squarely overlap the mouth. Seen from this angle, the nose displays no details at all, just the wedge with a hint of wings.
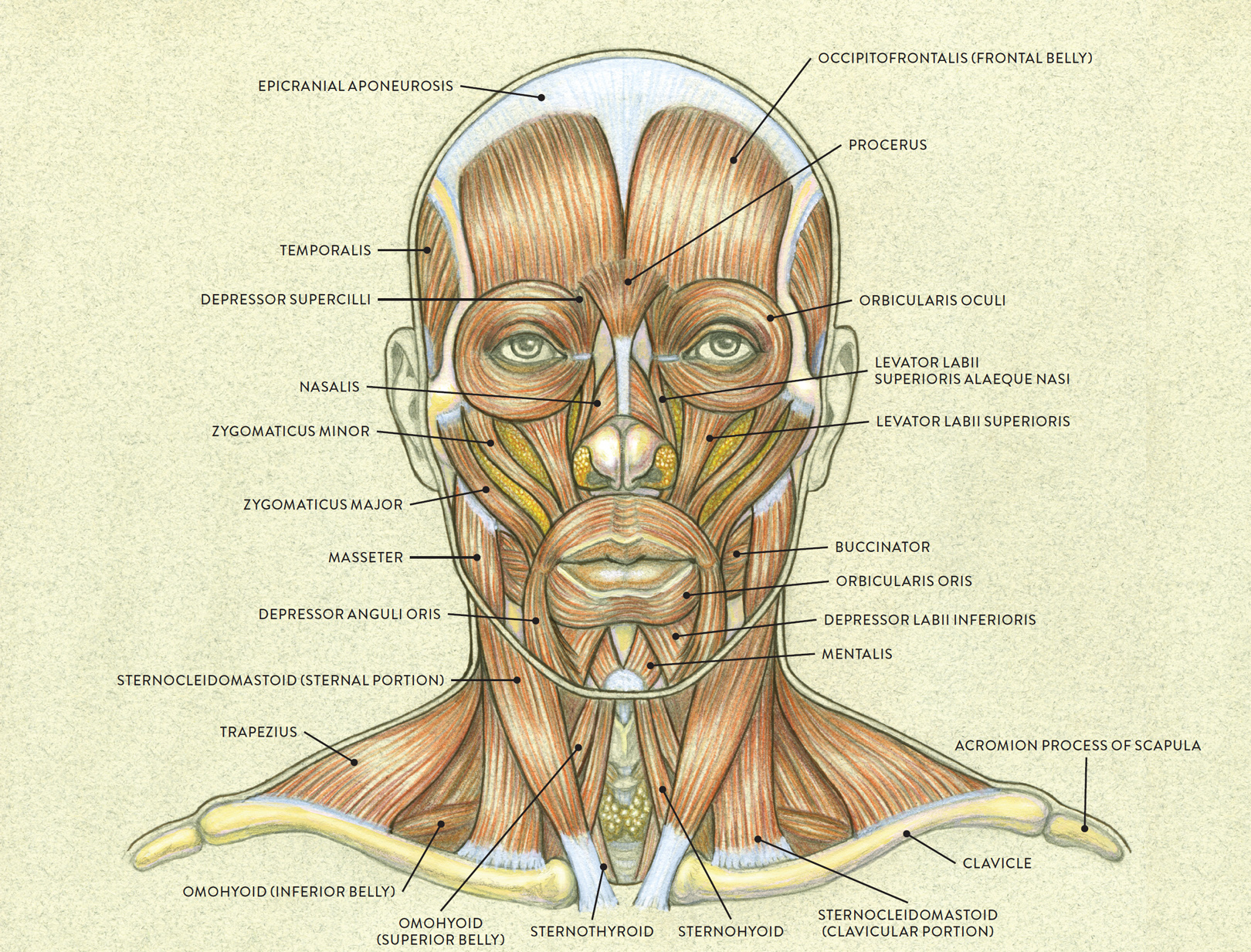
MUSCLES OF THE FACE—LATERAL VIEW
The facial vein is a large vessel of the face and is much less tortuous than the artery of the same name. It lies posterior to the facial artery and begins from the lateral side of the nose. It drains the external palatine vein and will go on to join the retromandibular vein. This then forms the common facial vein.

External Face Anatomy (Good Galleries)
The facial muscles, also called craniofacial muscles, are a group of about 20 flat skeletal muscles lying underneath the skin of the face and scalp. Most of them originate from the bones or fibrous structures of the skull and radiate to insert on the skin.
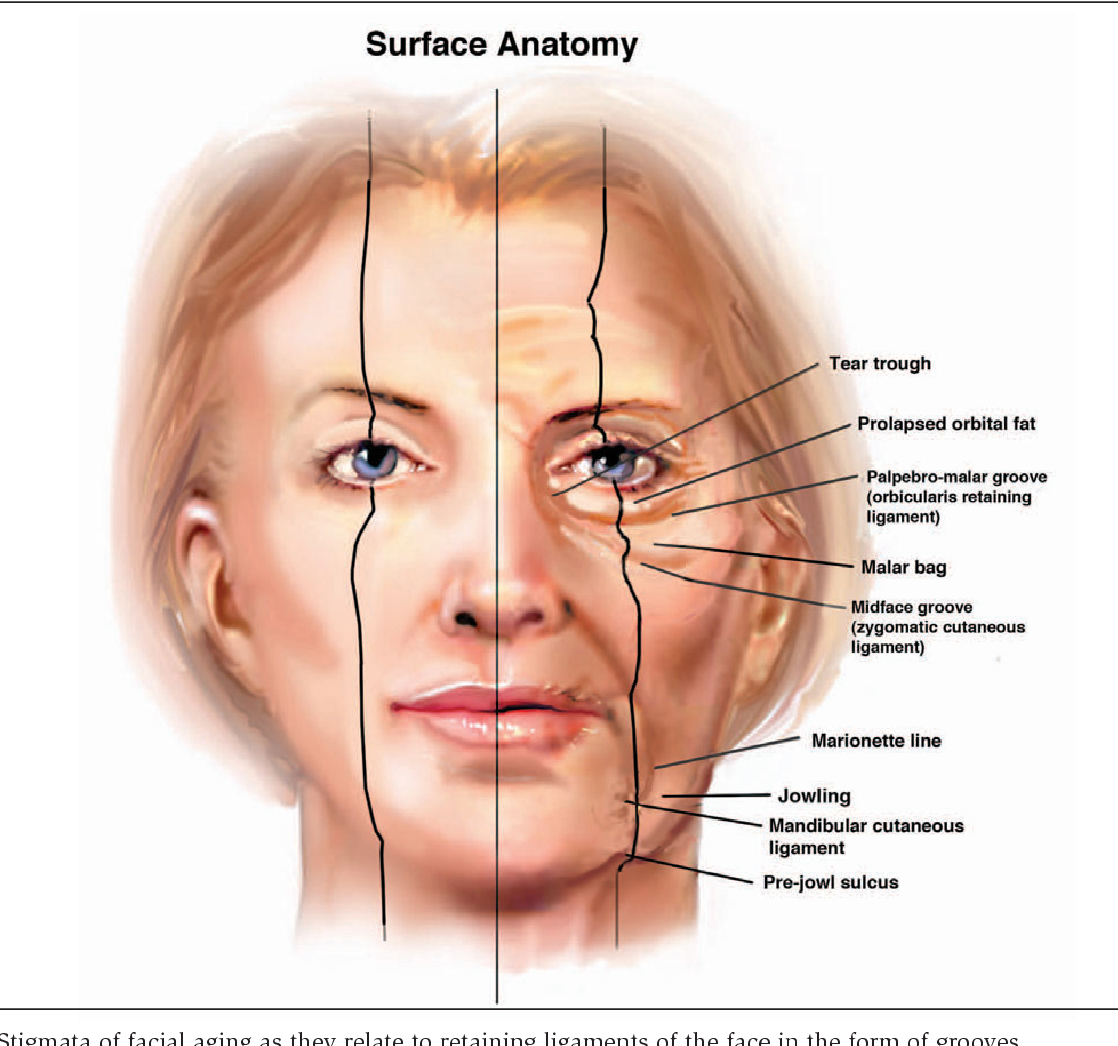
Anatomy Of Face Anatomical Charts & Posters
A, Facial esthetic subunits. Forehead subunits: 1A, Central; 1B, Lateral; 1C, Eyebrow. Nasal subunits: 2A, Tip; 2B, Columellar; 2C, Dorsal; 2D, Right and left dorsal side wall; 2E, Right and left alar base; 2F, Right and left alar side wall. Periorbital subunits: 3A, Lower eyelid; 3B, Upper eyelid; 3C, Lateral canthal; 3D, Medial canthal.

FileLateral head anatomy.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Anatomy of the viscerocranium. Viscerocranium Synonyms: none The skull (cranium) is a complex bony structure composed of two distinct regions: the neurocranium and viscerocranium. The viscerocranium is a collection of bones that make up the face skeleton.