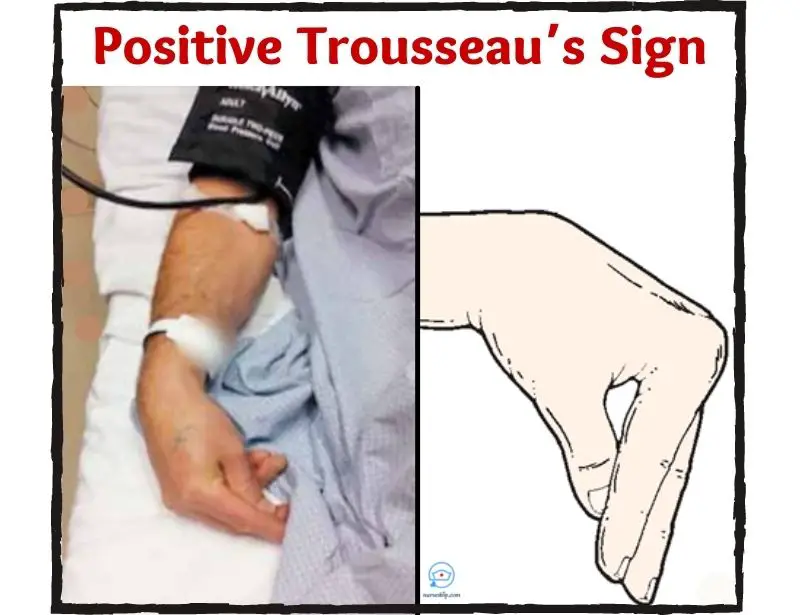
Trousseau's Sign Causes Assessment Treatment
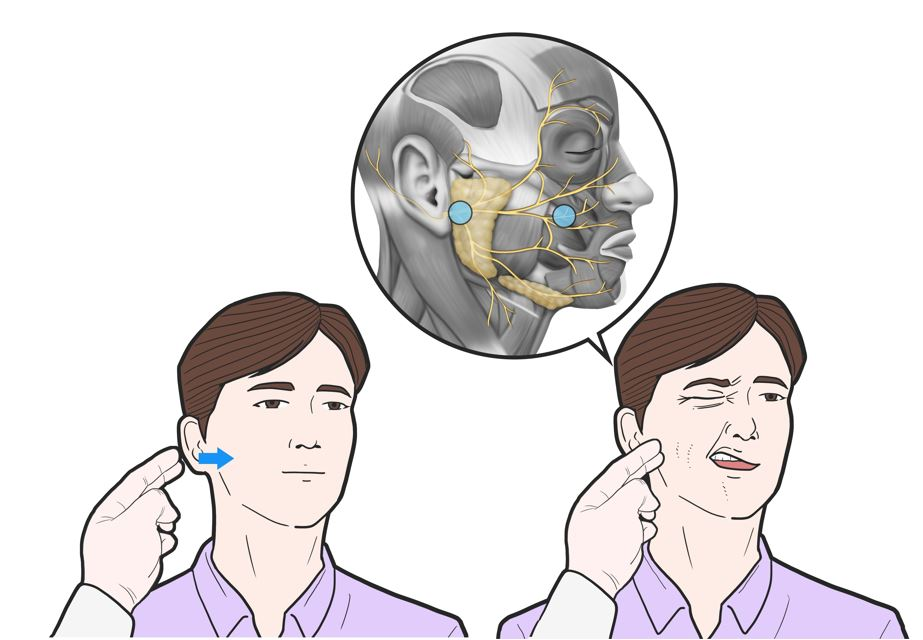
The Chvostek sign is the abnormal twitching of muscles that are activated (innervated) by the facial nerve (also known as Cranial Nerve Seven, or CNVII). [1] When the facial nerve is tapped in front of the ear, the facial muscles on the same side of the face will contract sporadically (called ipsilateral facial spasm).
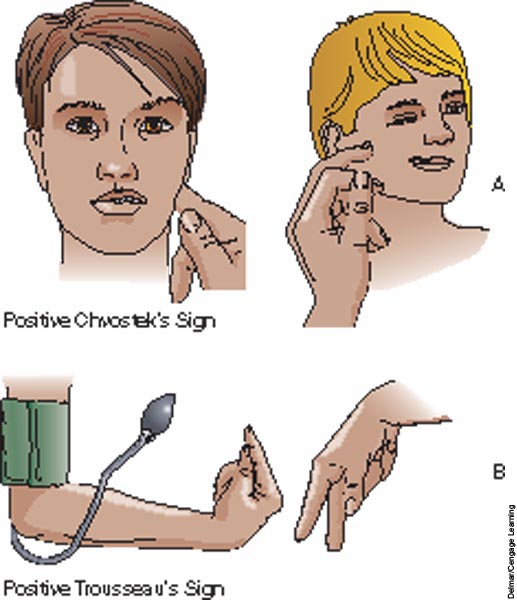
Chvostek and Trousseau sign (NBDE Part 1) 医療関係資格試験マニア
Trousseau sign is elicited in hypocalcemia when the ionized calcium level is 1.75-2.25 mmol/L. 1 The hand adopts a characteristic posture when the sphygmomanometer cuff is inflated above the systolic blood pressure within 3 minutes.

Signs of Hypocalcemia Chvostek's and Trousseau's Signs Semantic Scholar
Chvostek's and Trousseau's Signs Metrics Chvostek's and Trousseau's Signs ( Images in Clinical Medicine, N Engl J Med 2012;367:e15-e15 ). In the fifth sentence (page e15), beginning, "His total.
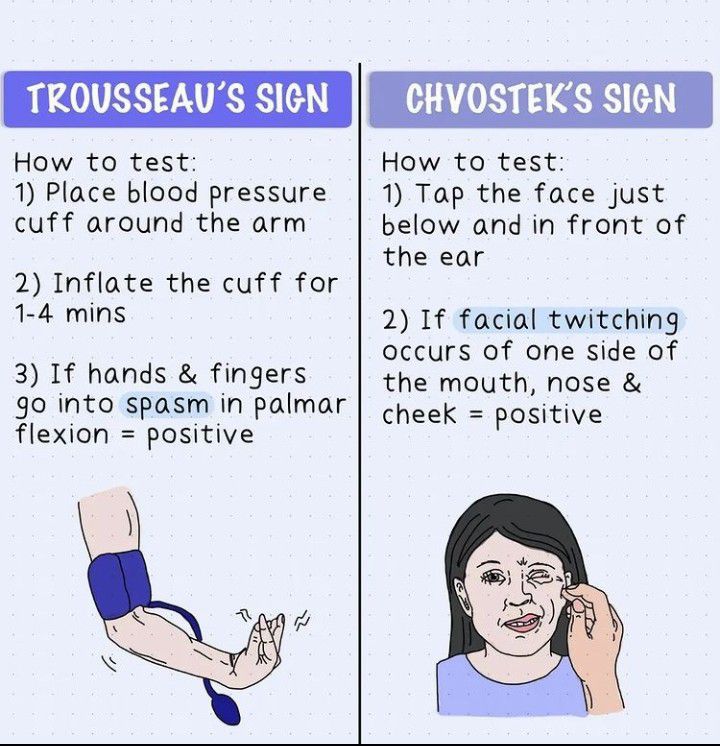
Trousseau's sign and chvostek sign MEDizzy
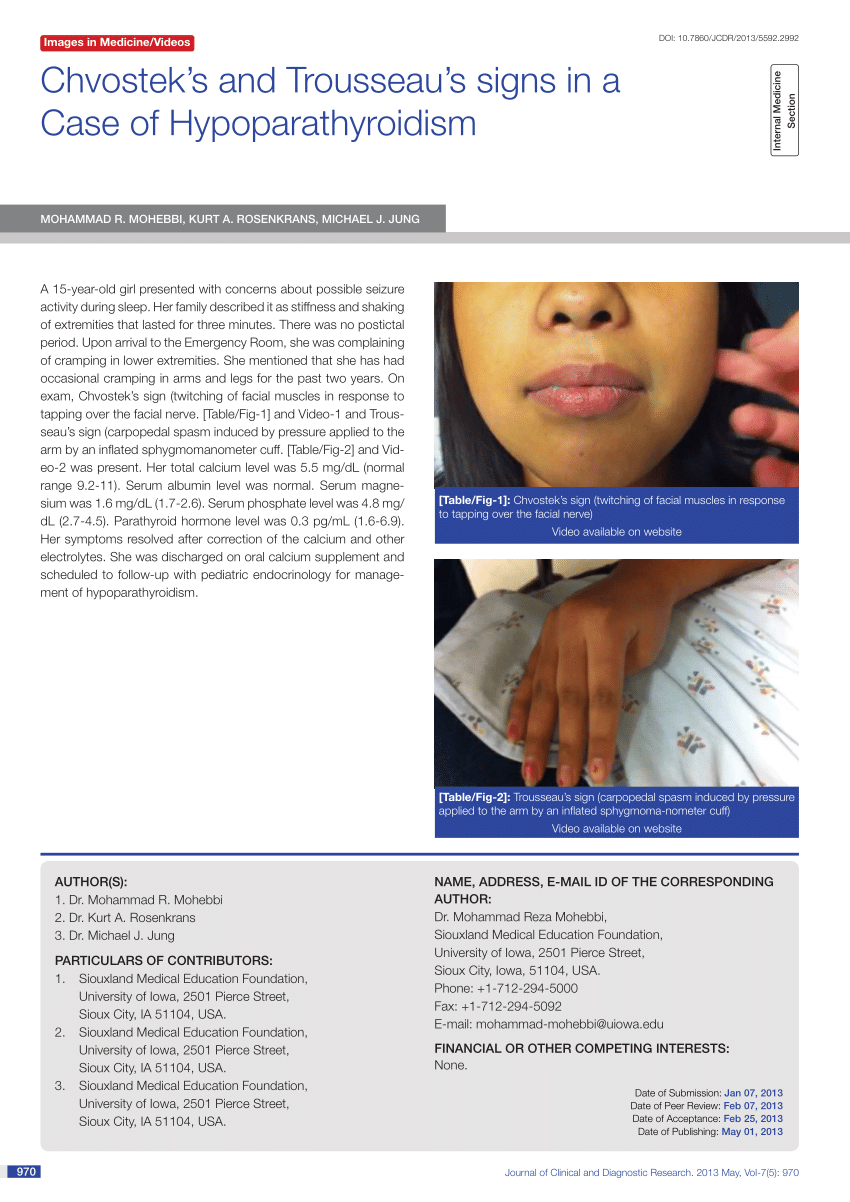
On exam, Chvostek's sign (twitching of facial muscles in response to tapping over the facial nerve. [ Table/Fig-1] and Video-1 and Trousseau's sign (carpopedal spasm induced by pressure applied to the arm by an inflated sphygmomanometer cuff. [ Table/Fig-2] and Video-2 was present. Her total calcium level was 5.5 mg/dL (normal range 9.2-11).

Video Hypocalcemia Signs & Symptoms (Trousseau's & Chvostek's Signs)
Trousseau's sign is a sign of tetany. (1,2) It is most often due to hypocalcemia but can occur with a normal calcium level and in other conditions. (3-7) Ischemia of the peripheral nerve trunks increases nerve excitability and causes spontaneous discharges that produce carpopedal spasm.

Pin on Nursing
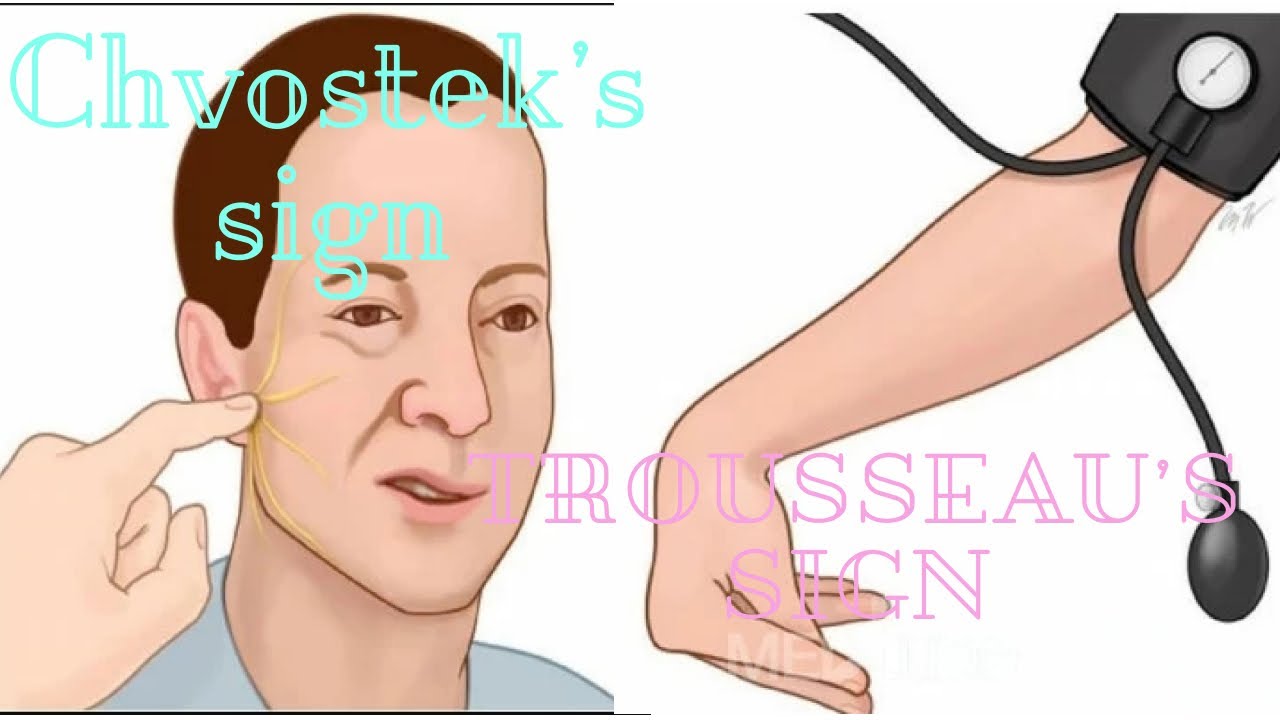
Chvostek's sign is the twitching of facial muscles in response to tapping over the area of the facial nerve, while Trousseau's sign is a carpopedal spasm (frequent and involuntary muscle contractions in the hands and feet) that results from ischemia (inadequate blood supply to the heart muscles), which is induced by pressure applied to the upper.

PPT הגישה להיפוקלצמיה PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5182378
Watch on What is Chvostek's Sign? Chvostek's sign is the name given to a clinical finding associated with hypocalcemia (low levels of calcium in the blood). It appears as a twitch of the facial muscles following gentle tapping over the facial nerve in front of the ear.
Signs of Hypocalcemia Chvostek's and Trousseau's
Acute hypocalcemia can lead to paresthesia, tetany, and seizures (characteristic physical signs may be observed, including Chvostek sign, which is poorly sensitive and specific of hypocalcemia, and Trousseau sign).

Mechanism of Chvostek's sign explained, associated conditions, sign value, how accurate is it
The Chvostek sign is a clinical finding associated with hypocalcemia, or low levels of calcium in the blood. This clinical sign refers to a twitch of the facial muscles that occurs when gently tapping an individual's cheek, in front of the ear.

Pin on Other stuff
Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs are classic manifestations of hypoparathyroidism, a condition characterized by low levels of parathyroid hormone and calcium. This article reports a case of a 35-year-old woman with these signs and discusses the diagnosis and management of hypoparathyroidism.

低血钙导致的Chvostek sign和Trousseau sign 哔哩哔哩
Chvostek's sign is a specific type of facial muscle twitching that occurs when cranial nerve VII (the facial nerve) is manually stimulated by tapping the finger over the masseter muscle of the jaw. A positive sign demonstrates hyper-excitability of the facial nerve. This is not to be confused with Trousseau's sign of latent tetany, which is.
Positive Chvostek Sign My Endo Consult
Physical examination revealed apparent Chvostek's sign (Figure 1A and Video 1) and Trousseau's sign (Figure 1B and Video 2), a result of postsurgical acquired hypoparathyroidism. His total.
(PDF) Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs in a Case of Hypoparathyroidism
Chvostek's sign was attributed initially to increased sensitivity of the facial nerve to mechanical stimuli in idiopathic epidemic tetany. 1 2 Traditionally, it is elicited by tapping on the face at a point just anterior to the ear and just below the zygomatic bone. 3 A positive response is represented by twitching of the ipsilateral facial muscles, suggesting neuromuscular excitability caused.

Two neurological test to evaluate the presence of hypocalcemia (Chvostek and Trousseau signs
Chvostek Sign - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf HHS Vulnerability Disclosure In the late 1800s, Dr. Chvostek noticed that mechanical stimulation of the facial nerve (as with the examiner's fingertip, for example) could lead to twitching of the ipsilateral facial muscles. [1]
Chvostek's sign and Trousseau's sign YouTube
NIH HHS USA.gov Trousseau's sign for latent tetany is most commonly positive in the setting of hypocalcemia. [1] The sign is observable as a carpopedal spasm induced by ischemia secondary to the inflation of a sphygmomanometer cuff, commonly on an individual's arm, to 20 mmHg over their systolic blood pressure for 3 minutes. [1]

Figure 031_4_4998. Chvostek sign. Illustration courtesy of Dr Shannon Zhang. McMaster Textbook
Symptoms and Signs Diagnosis Treatment Key Points Hypocalcemia is a total serum calcium concentration < 8.8 mg/dL ( < 2.20 mmol/L) in the presence of normal plasma protein concentrations or a serum ionized calcium concentration < 4.7 mg/dL ( < 1.17 mmol/L). Causes include hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, and renal disease.