
Stuff and Nonsense... Stepping up the Product Analysis using SOLO
Asking Questions I need help to ask a question Self and peer assessment rubrics coded against SOLO Taxonomy I can ask my family and close friends questions when seeking answers I can ask my family, friends, classmates and teachers questions when seeking answers I can ask my family, friends, teacher and people I don't know, like experts, relevant/

SOLO Taxonomy Question Chains Tom Barrett
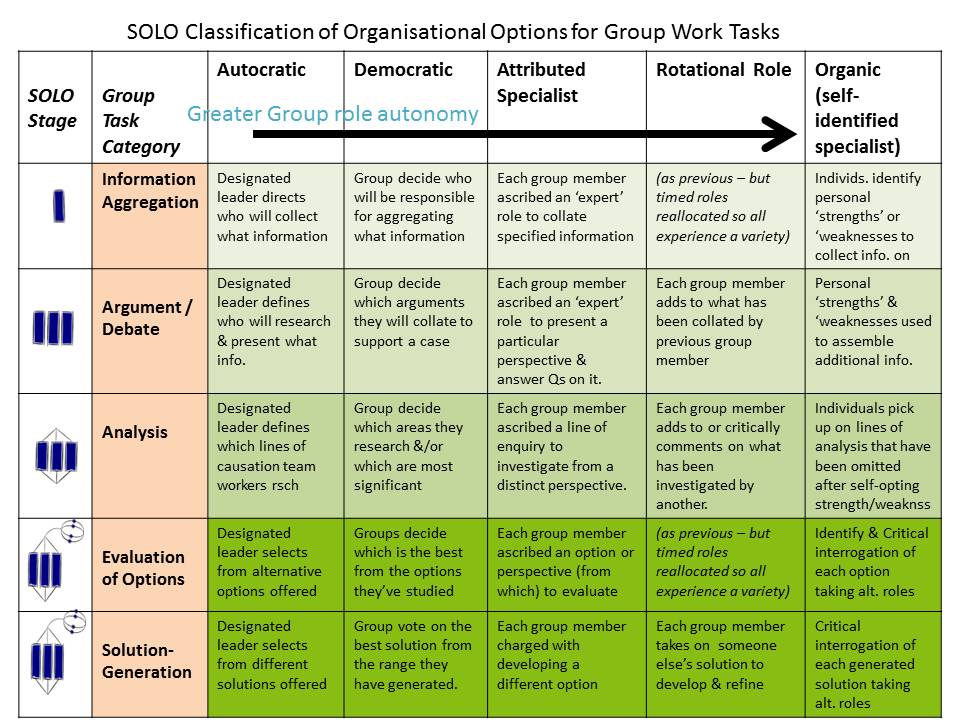
The interview questions were written using the SOLO taxonomy terms and therefore provided a building of complexity each time (see Table 2). They were therefore like those being used in the classroom by the teachers for the low-stakes tests and were based upon learning that was known to have taken place.

Using SOLO Taxonomy to Think Like a Scientist Essential Resources
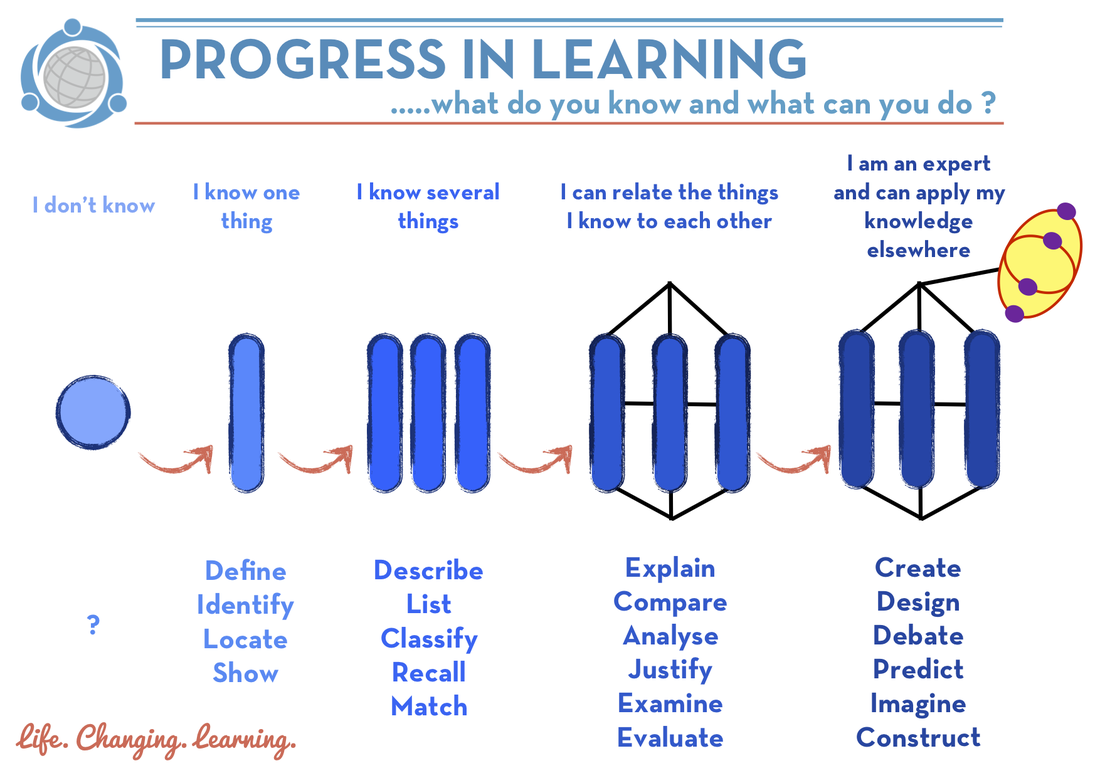
SOLO (structure of observed learning outcomes) taxonomy is an illustrated model of learning that classifies depth of understanding into categories.

The SOLO Taxonomy with sample verbs indicating levels of understanding
2.1. The SOLO Taxonomy. The SOLO Taxonomy is a taxonomy that classifies how students' thinking levels fall into five categories: pre-structural, uni structural, multi structural, relational, and extended abstract levels [10] [11]. Criteria for each level based on SOLO taxonomy can be seen in Table 1 [17] [18]. Tabel 1.

solo taxonomy Google Search Solo taxonomy, Taxonomy, Special
SOLO was developed as a taxonomy in 1982 by John Biggs and Kevin Collis as an alternative to Bloom's cognitive domain. Looking at the range of responses and outcomes that learners produce, they determined that the following structure is common to all subject areas. SOLO isn't a hierarchy, but a series of stages.

Rates of reaction SOLO Resources TES Solo taxonomy, Visible
SOLO Taxonomy Question Chains This is an example of a SOLO Taxonomy Question Chain. A series of connected question that explores a subconcept. Written by Tom Updated on August 25, 2022 Discussion 2 Comments If you're keen to learn more about AI, you may enjoy my newsletter: Promptcraft. Thanks for exploring!
SOLO Taxonomy
The Structure of the Observed Learning Outcome (SOLO) Model (also referred to as the SOLO Taxonomy), developed by Biggs and Collis ( 1982 ), is a general model of intellectual development concerned with assessing a particular learning episode based on the quality of the learners response.
Knowledge seeker's blog SOLO, Bloom's Taxonomy and five different ways
the SOLO Taxonomy What is a Learning Outcome? Learning outcomes are statements that indicate what students will know, value or be able to do by the end of the course. They are the assessable ends of education, written from the students' perspective, focused on what

Maths questioning prompts using SOLO taxonomy Teaching Resources
How to Classify Learning Outcomes Using SOLO Taxonomy. 1. Identify the Learning Outcomes. Start by clearly defining the specific learning outcomes you want students to achieve. These outcomes should reflect what students should know, understand, or be able to do by the end of the learning experience.

SOLO Taxonomy Lesson Plan Coaches
The SOLO Taxonomy (Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes) was devised by Biggs and Collis in 1982 as an alternative to Bloom's ( cognitive Domain) Taxonomy. Bloom's Taxonomy has been used for several decades to develop learning and teaching strategies. Bloom's categorizes learning from simply remembering to more complex cognitive structures.

Solo Taxonomy for Self/Peer Assessment Solo Taxonomy with levels (for
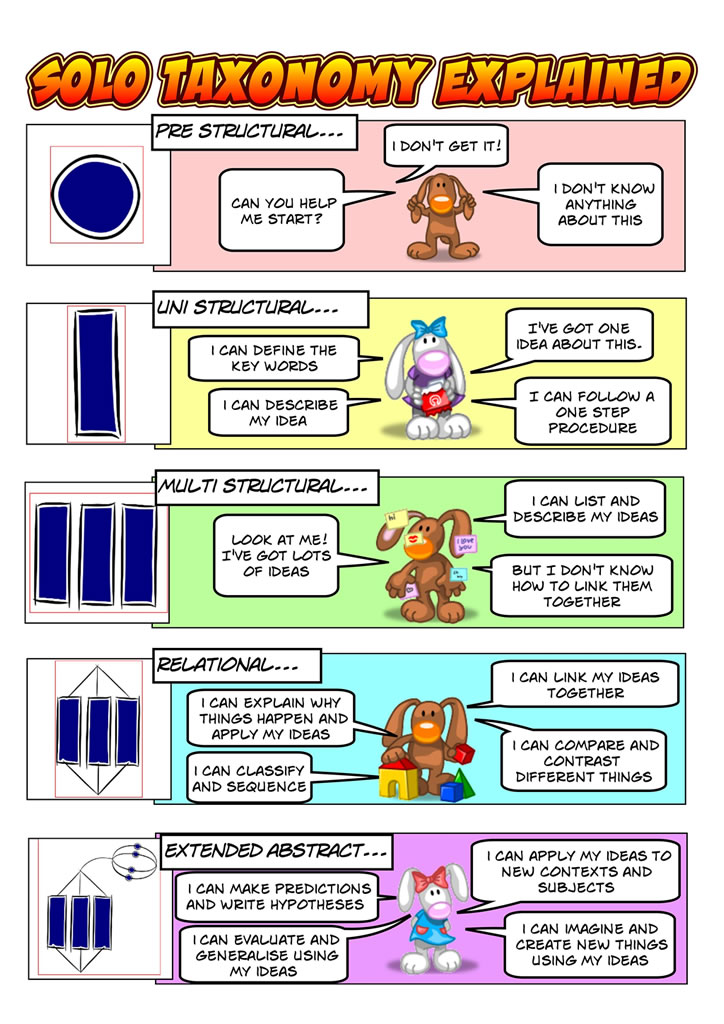
"The SOLO taxonomy is a model that describes levels of increasing complexity in students' thinking and understanding. It was proposed by academics Biggs and Collis (1982) after classifying student's thinking across a range of ages and a range of subjects.
My Learning Journey Teaching SOLO taxonomy through SOLO taxonomy
The structure of observed learning outcomes ( SOLO) taxonomy is a model that describes levels of increasing complexity in students' understanding of subjects. It was proposed by John B. Biggs and Kevin F. Collis. [1] The model consists of five levels of understanding: [2]

SOLO Taxonomy Questioning by HookED Educational Consultancy issuu
This paper examines how the Structure of the Observed Learning Outcomes (SOLO) taxonomy can influence assessment and instructional approaches in fostering students' mathematical problem-solving.

A teacher's guide to SOLO Taxonomy
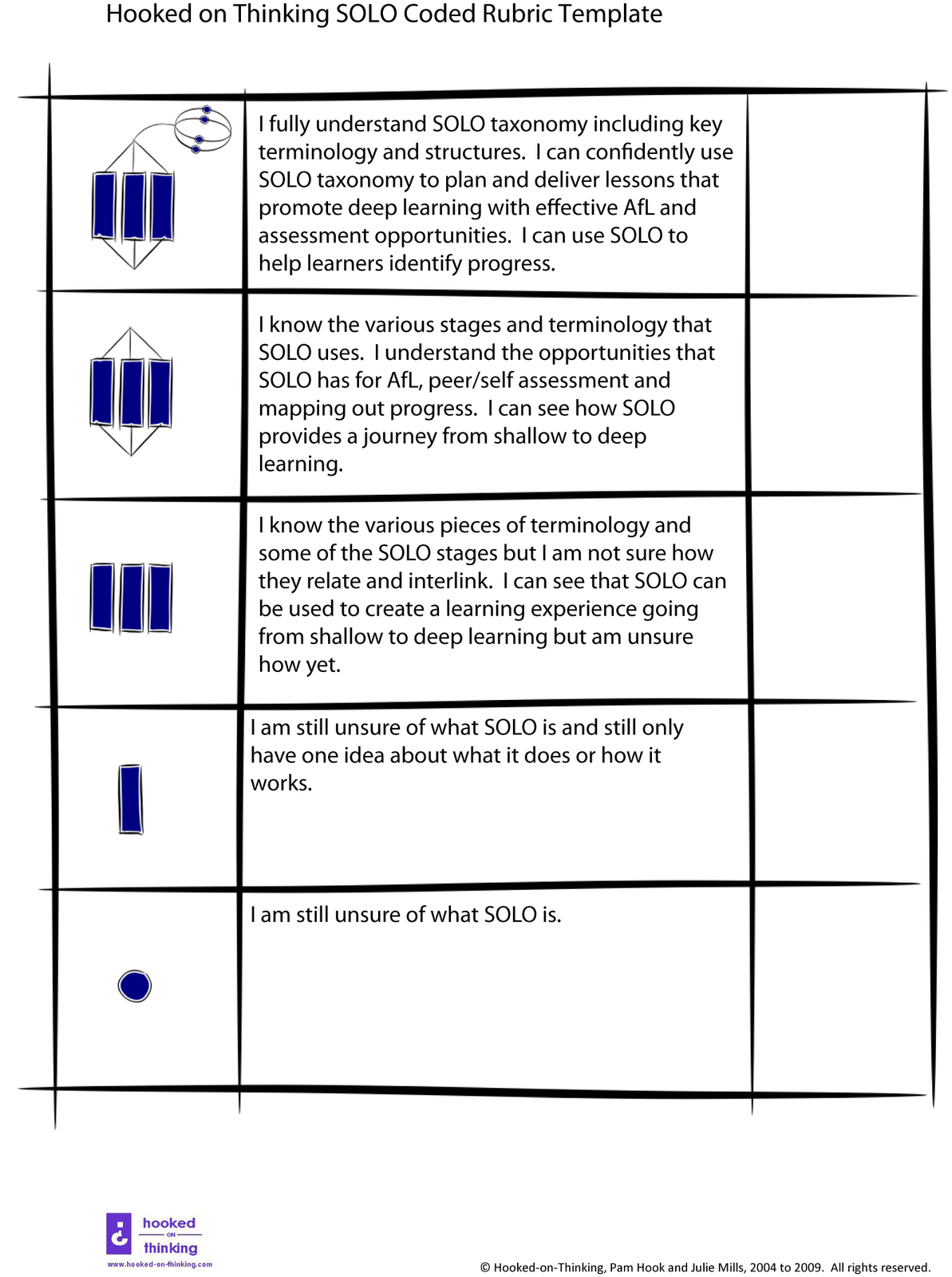
The SOLO taxonomy contains 5 levels of knowledge, from simple to complex: Prestructural Unstructural Multistructural Relational Extended Abstract At the lower levels, students demonstrate lower-order cognitive skills, while at higher levels students demonstrate the ability to use complex inductive reasoning strategies. Contents show

What is SOLO Taxonomy? Lesson Plan Coaches
Essentially, SOLO taxonomy is a model that represents the complexity of an observed learning outcome. In categorising learning outcomes SOLO also outlines the learning process.
MBMS Science Solo Taxonomy
SOLO Taxonomy is a valuable tool for assessing the depth of knowledge that students have achieved in a particular subject or task. It allows teachers to identify where students are in their learning journey and determine what steps need to be taken to move them to a deeper level of understanding.