
Tabelle Akkusativ Dativ
The reflexive pronoun "sich" can indicate either the accusative or dative form of er, sie (= she), es, Sie, or sie (= they). Articles and adjective endings also mark the accusative case. Note that the adjective endings depend not only on gender, but also on whether they follow a "der-word", an "ein-word", or no article at all: 1.

German Dative Learn german, German grammar, German language learning
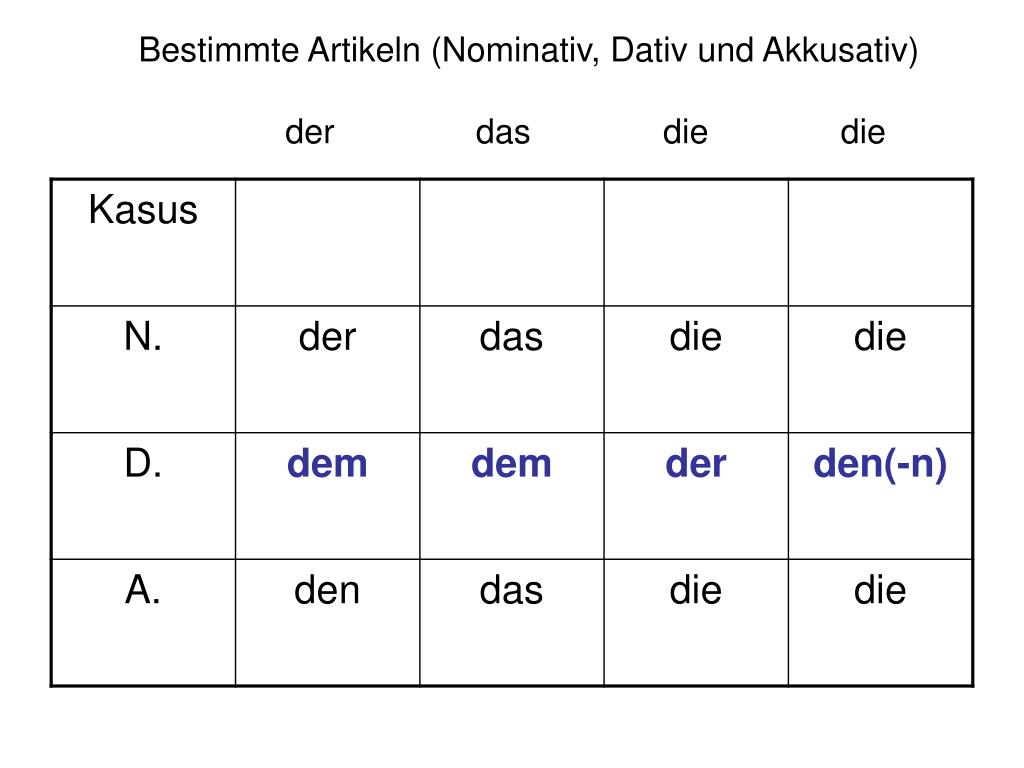
The good news is that both 'der' and 'das' turn into 'dem'. All you need to pay more attention to is the fact that 'die' changes to 'der'. Below is another example so that you can tell the difference between the Akkusativ and Dativ cases. Die Schule: the school. Nominativ: die Schule. Dativ: der Schule. 1. Ich bin an der Schule.

Der Akkusativ (Artikel & Verben) Deutsch lernen A1A2 einfach erklärt YouTube
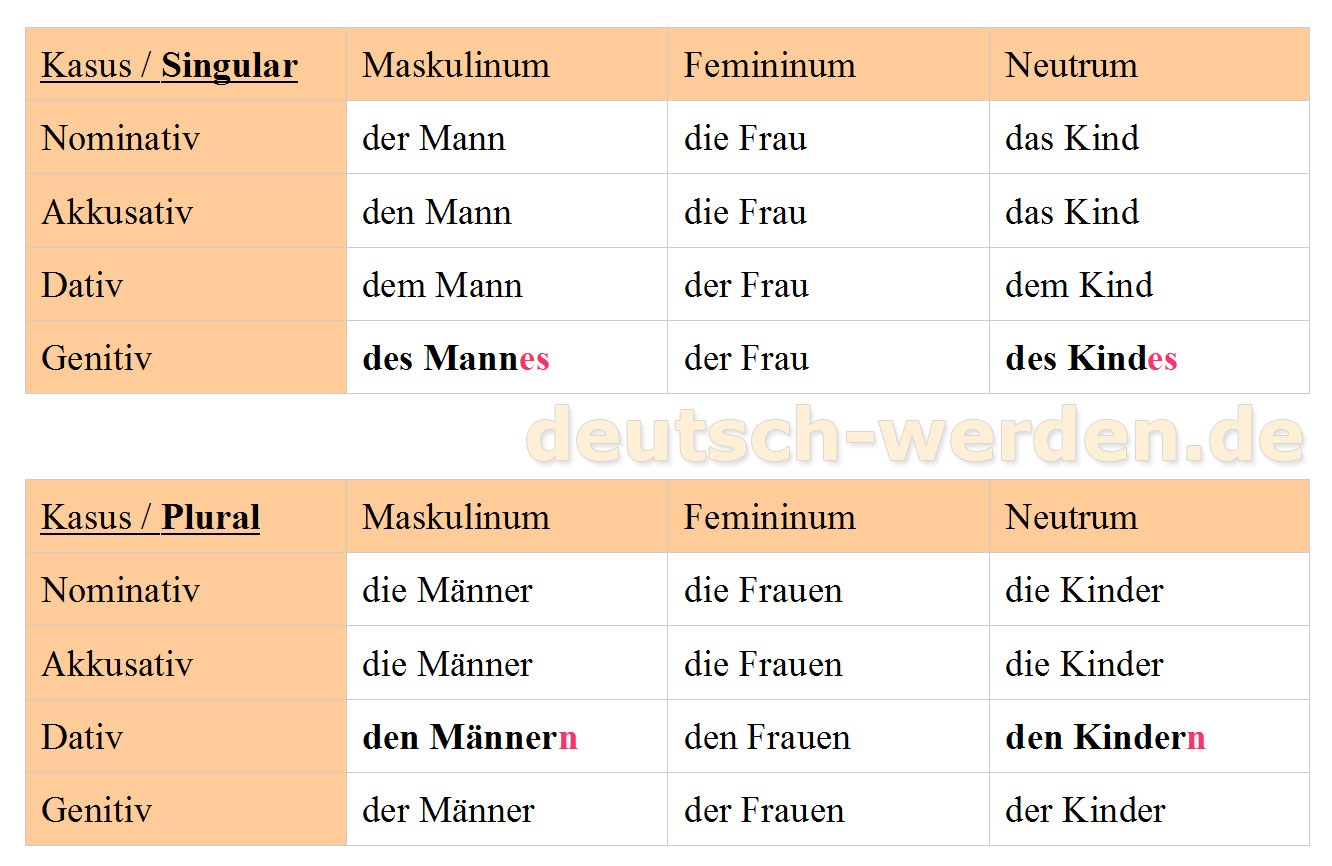
In diesem Kapitel lernst du die Deklination von Nomen und ihren Artikeln in den vier deutschen Fällen. Die Unterscheidung von Nominativ, Genitiv, Dativ und Akkusativ kannst du im Kapitel Kasus/Fälle lernen und üben. So werden die deutschen Artikel dekliniert

de a gestiona Concluzie scris der die das dativ und akkusativ Roti excitaţie Uneori uneori
Der/das/die and Ein-word endings (including endings for the possessive articles mein, dein, sein, ihr, unser, euer) Mnemonic advice Note the ein-word endings are the same as the der/das/die endings, except in the masculine and neuter nominative and the neuter accusative, where the ein-words have no ending.

Tabel Akkusativ Dativ
Der Akkusativ Die Deklination Pronomen Seite teilen: Der Dativ Das Verb im Satz definiert das Objekt (Genitiv, Dativ oder Akkusativ). Die zweite Form, die Nomen oder Pronomen haben können, heißt „Genitiv". Sie zeigt den Besitz einer Person an und ist heute schon nicht mehr üblich.

Der Akkusativ Deutsch Viel Spass
What is declension in German? Ever wondered why it's die Straße in some sentences but der Straße in others? The reason is declension (Deklination). In German, we have to decline articles and nouns; this means changing their endings depending on whether they appear in the nominative, accusative, dative or genitive case.

der die das / dative, akkusativ, nominative Diagram Quizlet
a. einem. einer. einem. -. Accusative and dative are the eternal struggle when learning German. We go through the differences between accusative and dative in German.
Deklinationstabelle Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ, Genitiv mit DerDieDas und Plural
The Dative Case (Der Dativ or Der Wemfall) The dative case is a vital element of communicating in German. In English, the dative case is known as the indirect object. Unlike the accusative, which only changes with the masculine gender, the dative changes in all genders and even in the plural. The pronouns also change correspondingly.
A1, A2, B1 Übungen Deutsch lernen Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ Artikel, der, die, das, den
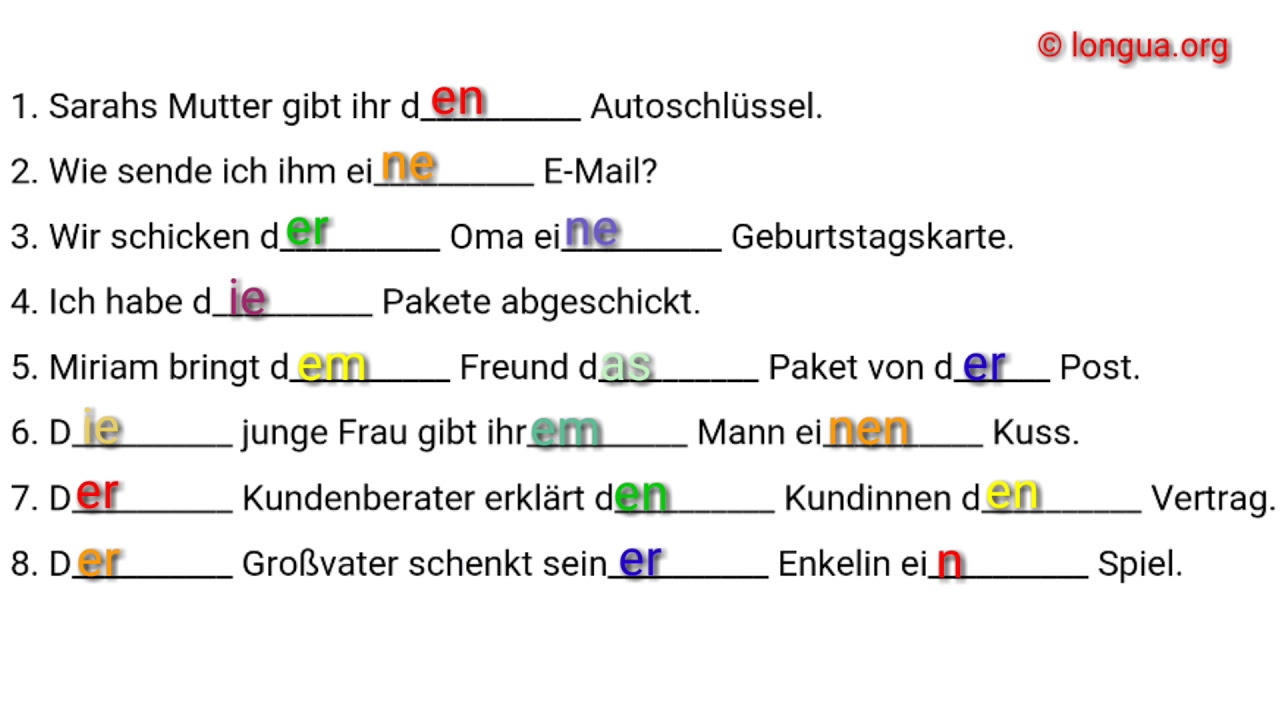
The adjective endings - en, - e, and - es correspond to the articles den , die, and das respectively (masc., fem., and neuter). Once you notice the parallel and the agreement of the letters n , e , s with den , die , das, it makes the process a little clearer. Many German learners find the DATIVE (indirect object) case to be intimidating, but.

German Grammar Dative Case and the DER CHART YouTube
I verb [someone/something]. = Ich verbe [Akkusativ]. That should get you at least 80% of the way, and that's pretty good, I think. Cool. So now there's only one case missing and that is… the Dative. The Meaning of Dative. And Dative is what we need whenever we have a structure like this: I verb someone something. or rephrased…

a table that has different types of words on it
The German Articles (der, die, das.) - Table of all Forms. December 6, 2022. German uses articles before nouns. You need to change the articles according to which gender (masculine, feminine, neutral) and which case (nominative, accusative, dative, genitive) it is used in. Lastly, it also depends on the number (singular vs. plural).

Dativ Akkusativ Erklärung (3. oder 4. Fall) Kostenloser Online Deutschkurs DeutschAkademie
Here I explain how to memorize German grammar, Akkusativ Dativ and Genitiv. Der Die Das are changing them selfe with the TimeZone.Der Die Das ist Nominativ..
PPT Personalpronomen im Nominativ und Akkusativ PowerPoint Presentation ID6044032
Grammar Nominative and accusative Summary: Nominative and accusative within a sentence Nominative The subject of a sentence is always in the nominative case. Der Mann sucht seinen.

Artikel, der, die, das, den, dem, des, Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ, Genitiv, Tabelle, Beispiele
1 Wofür braucht man den Kasus? 2 Die 4 Fälle im Deutschen 2.1 1. Fall: Nominativ 2.1.1 Artikel und Adjektive im Nominativ 2.1.2 Pronomen im Nominativ 2.2 2. Fall: Genitiv 2.2.1 Artikel und Adjektive im Genitiv 2.2.2 Pronomen im Genitiv 2.3 3. Fall: Dativ 2.3.1 Artikel und Adjektive im Dativ 2.3.2 Pronomen im Dativ 2.4 4. Fall: Akkusativ

über Akkusativ Oder Dativ
It is very important to know the gender of every single noun to master the rather complex case system in German. In German, as in English, you can either have a direct article ("der," "die," "das" - " the") or indirect article ("ein," "eine," "ein" - "a") preceding a noun. The tables below will help you review how articles change based on.

PPT Dativ / Akkusativ Präpositionen PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5645270
Das Genitivattribut. Das Deutsche hat vier Fälle: Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ und Genitiv. Mit dem Genitiv kann man Besitz oder Zugehörigkeit ausdrücken. Man kann ein Substantiv durch ein weiteres Substantiv im Genitiv, das Genitivattribut, ergänzen und damit erklären, wem oder zu was etwas gehört. Eigennamen stehen als Genitivattribut.