
MBTI explained Personality types chart, Myers briggs personality
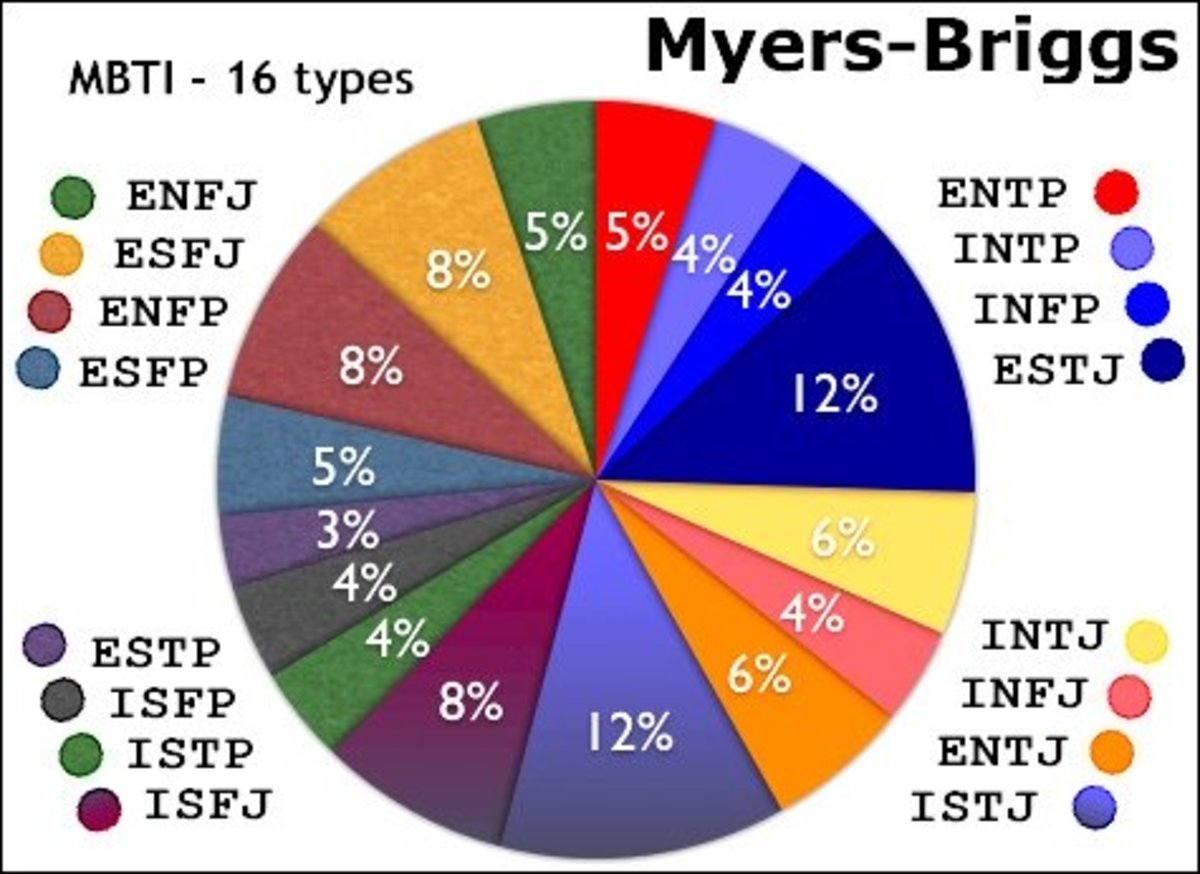
Sensing and Intuition are opposite preferences. A person's natural tendency toward one will be stronger than the other. There are by far more Sensing people in the population than Intuitives. Sensors make up almost three-fourths of all people with Intuitives at just over 26%. Females are on average slightly more Sensing than males.

N types Personality types, Personality psychology, Personality
The 'N' in Myers-Briggs theory stands for iNtuition. Those with a preference for intuition rely on hunches, future possibilities, implications, and abstract theories. They are often seen as imaginative and innovative, preferring to focus more on what could be rather than what is. People with an 'S' preference prefer Sensing.

Types Of Psychology, Personality Psychology, Infj Personality
The second letter of the MBTI test, Sensing (S) and Intuition (N) is how you process information. Someone who is strong in sensing lives in the now and enjoys facts. While being Intuitive means you try and find the deeper meaning in things. As always, the MBTI test is a very skin-deep test and does not tell you everything about a person.
16 MyersBriggs Personality Types Which MBTI Personality Are You
They provide either an S (for sensing) or N (for intuition) in the 4-character abbreviations for each Myers-Briggs personality type. In other words, you are either an XSXX or an XNXX where each X is also one of two letters (which we won't go into here). But what's the difference between these two traits? What makes you a sensor versus an intuitive?

How MyersBriggs Influences Communication in Relationships PairedLife
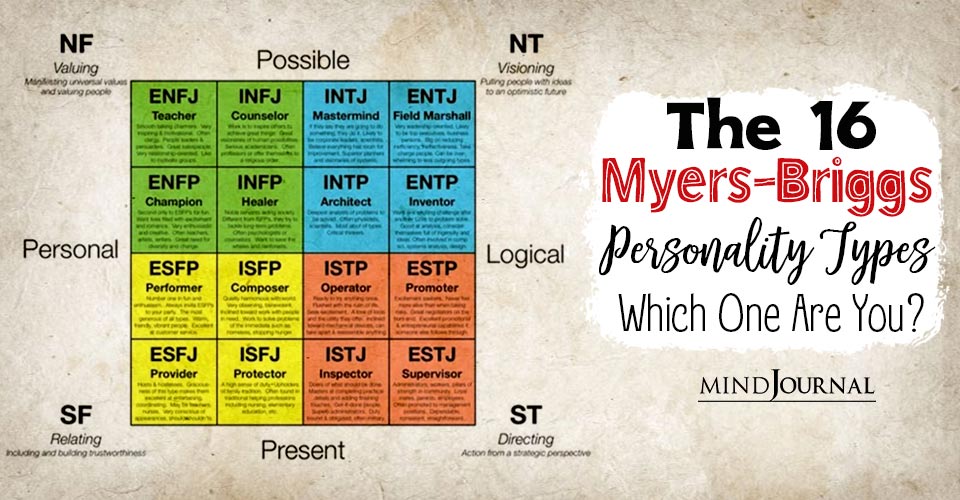
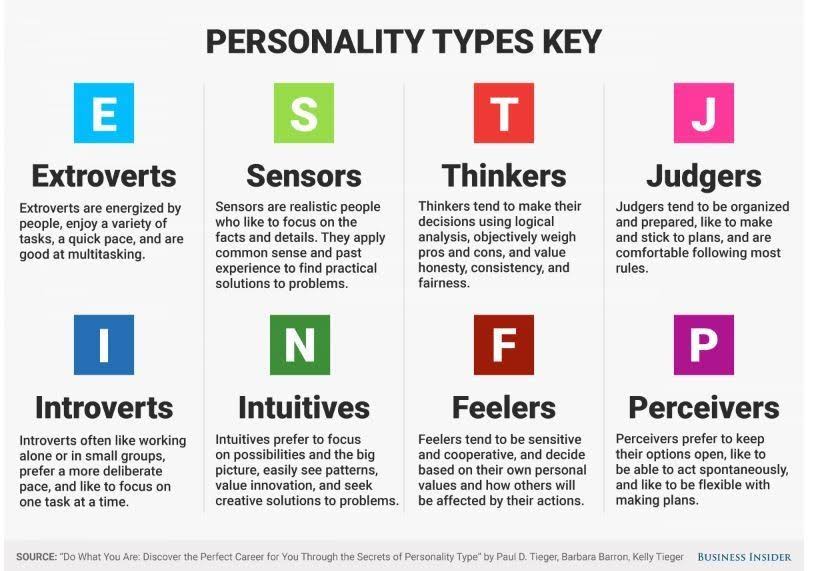
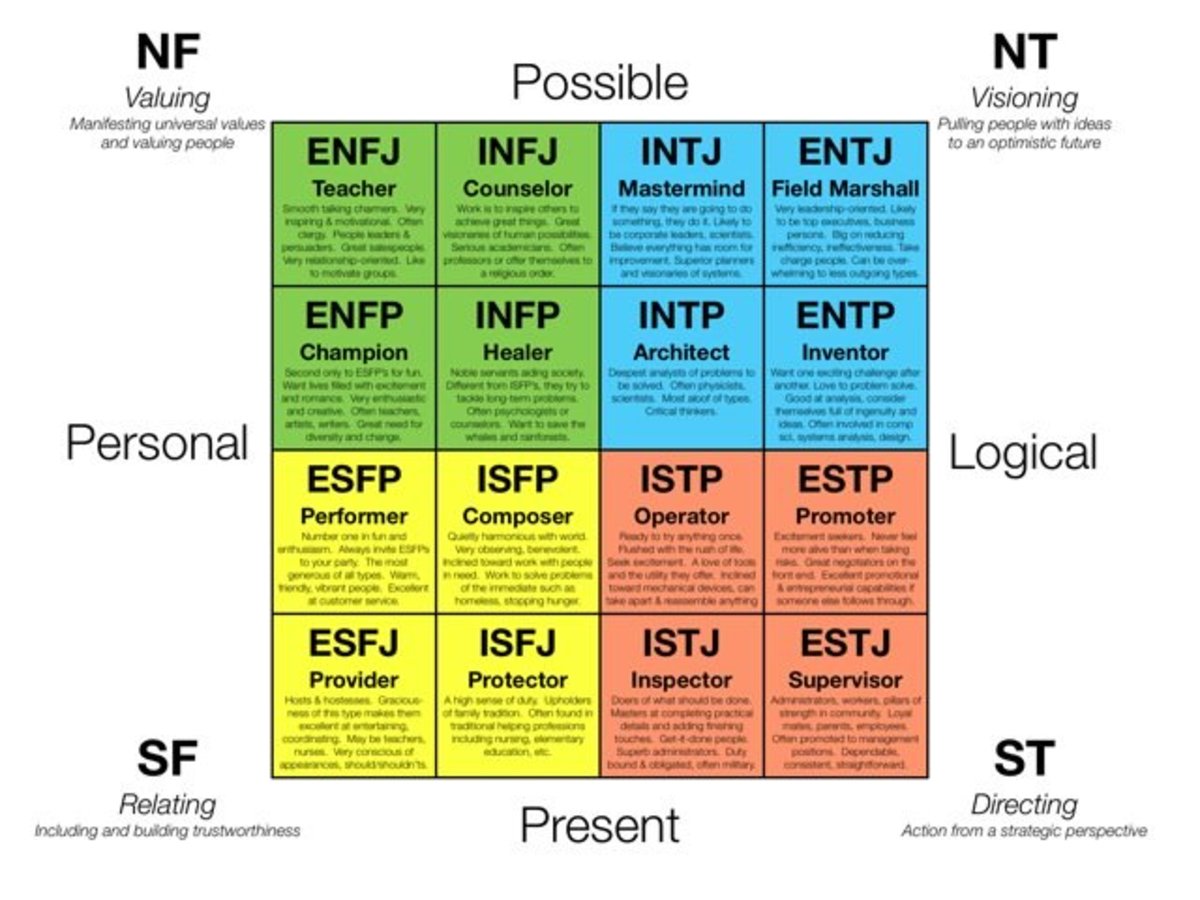
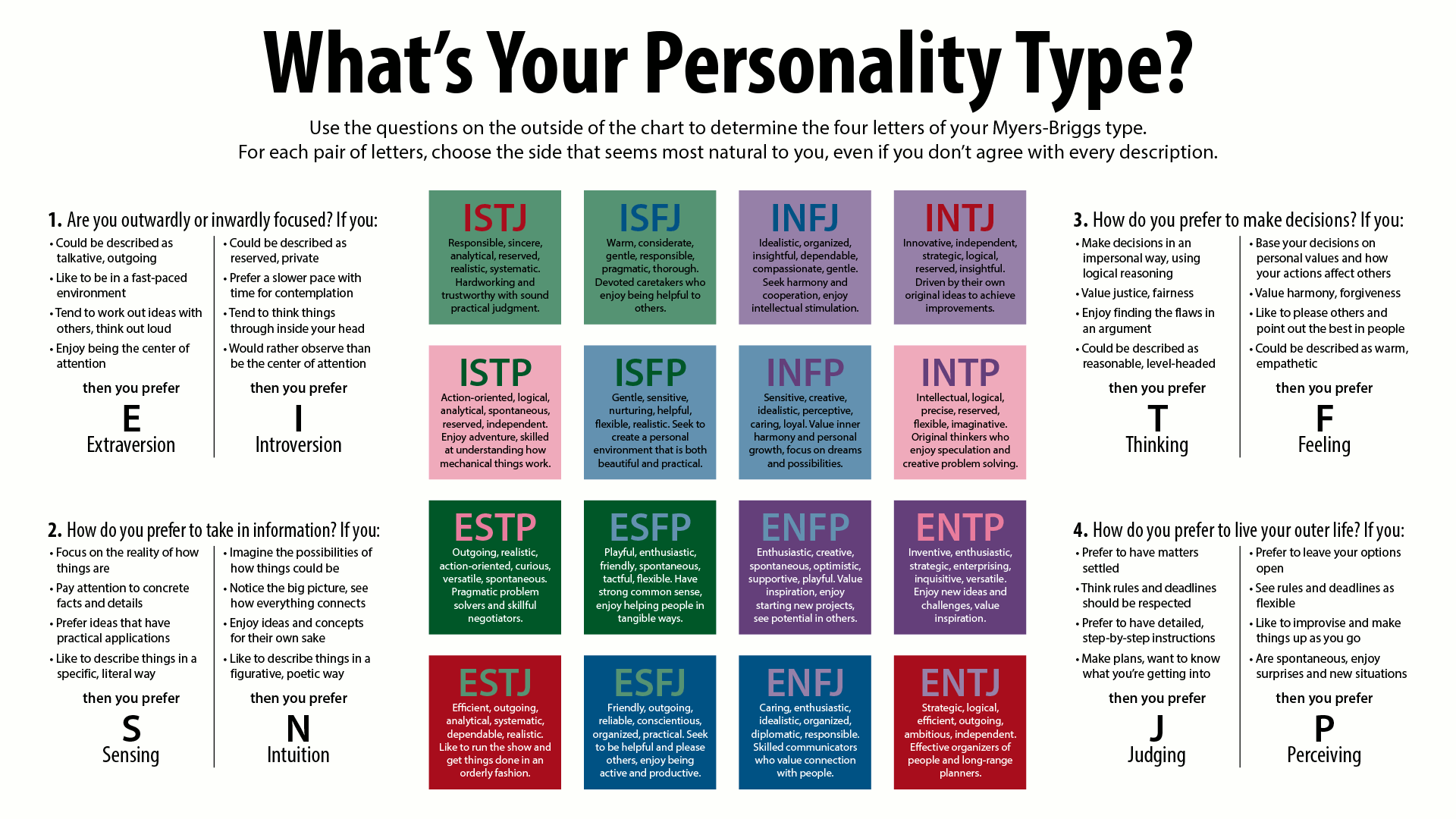
1. The 9 vs 16 type system To categorize and describe different personalities, both the Myers and Briggs system and Enneagram use 'types' or categories. Myers and Briggs has 16 possible personality types, resulting from four opposing personality functions, also called dichotomies, preferences or scales.

Absolute Truth. N vs. S MyersBrigg Mbti personality, Infp
Personality type is more complex and far richer than most people know. MBTI ® type is more than just the sum of four preferences; it is a dynamic, interrelated system of personality.. Myers's creation of the 16 MBTI personality types is ingenious. Within the four-letter MBTI type exists a code, a formula that is a shorthand way of telling you about the interaction of your four preferences.

Myers Briggs Personality Test Let’s Explore Your Personality Type!
IamBili. •. Usually, distinguish S from N is the hardest MBTI personality trait you can do, as the environments and the "friendship networks", where you know the person can skew from one trait or another, and it is possible that the "S/N balance" isn't so tipped for one than it is for another. If you can factor these things, then I guess one.
MyersBriggs Type Indicators Overview
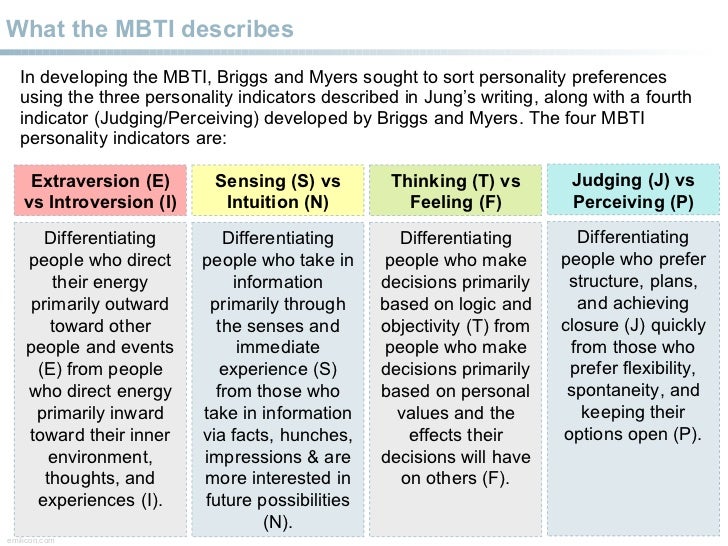
The Development of the Myers-Briggs Test. The MBTI tool was developed by Isabel Briggs Myers and her mother Katharine Cook Briggs in 1942 and is based on psychological conceptual theories proposed by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung in his work, Psychological Types.. Jung's theory of psychological types was based on the existence of four essential psychological functions - judging functions.
Myers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) Learning Styles by Tracy Atkinson
According to the Myers-Briggs, intuitives are inclined toward abstract processing and activities, whereas sensing (S) types are said to be oriented to the concrete. This distinction has been crudely summarized as being "book smart" (i.e., academic) vs. "street smart" (i.e., using common sense). One thing that's given me pause about.

How the MyersBriggs Type Indicator Works 16 Personality Types
In personality typology, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator ( MBTI) is an introspective self-report questionnaire indicating differing psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. It enjoys popularity despite being widely regarded as pseudoscience by the scientific community.
MyersBriggs Type Indicator (MBTI) LET'S THINK ABOUT IT
Myers-Briggs The 16 MBTI system and is the key to understanding type. Learn about process pairs and an overview of how type dynamics works. model is developmental. Discover the pathway for type development over the lifespan. assessment for helping you choose a career and manage career changes at every life stage.
The History and Significance of the MyersBriggs Personality Test
In the Myers-Briggs® system, Sensors have an "S" as the second letter of their type code (for example: ESFJ) while Intuitives have an "N" as the second letter of their type code (ENFJ). The Sensing/Intuitive preference is confusing for a lot of people, especially because Intuition is often defined in Western culture as a kind of emotional awareness of how people are feeling (which in.

Sensing vs. Intuition I usually test as an INTP but occasionally get
Core Theory Mind: Intuitive (N) vs. Observant (S) Thought at Every Scale Our second personality scale includes the Intuitive (N) and Observant (S) styles. These traits describe what people are more likely to do with the information gathered from the world around them.
History and Significance of the MyersBriggs Personality Test Owlcation
Do you prefer to focus on facts and details or patterns and possibilities? This is the question that the Sensing or Intuition preference pair of the MBTI personality type helps you answer. Learn more about how these two ways of perceiving the world affect your behavior and communication.

MeyersBriggs Classification Models by Alex S Analytics Vidhya Medium
If the second letter of your Myers-Briggs type is an "N," you would be considered intuitive rather than sensing. Where S types favor their senses and facts, N's are concerned with deeper meanings and patterns. They often have an abstract, roundabout way of thinking.
FileMyersBriggsTypes.png Wikipedia
One of the primary dichotomies in the Jungian personality taxonomy is intuition (N) vs. sensing (S). It is sometimes cast as a preference for the "big picture" (N) vs. details (S), theory (N) vs. practice (S), or abstract (N) vs. concrete (S) matters.