How Does Nadh And Fadh2 Donate Electrons To The Electron Transport Chain
4 POGIL ™ Activities for AP* Biology 10. According to Model 1, glucose undergoes the following changes during cellular respiration. In each step NADH or FADH 2 is produced. Is glucose being oxidized or reduced during cellular respiration? Explain your reasoning. Glucose ⎯→ pyruvate ⎯→ acetyl-CoA ⎯→ carbon dioxide 11. Historically.
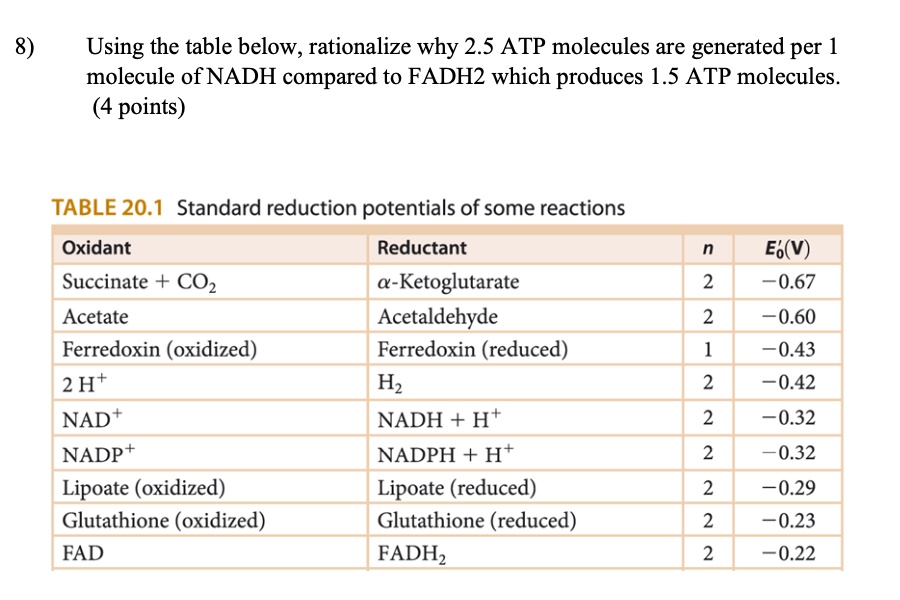
SOLVED Using the table below, rationalize why 2.5 ATP molecules are generated per 1 molecule of
2 NADH, 2 Acetyl-CoA, 2 Co2. Phase 3: Citric Acid Cycle Input. 2 Acetyl CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD, 2 ADP + 2 Pi. Phase 3: Citric Acid Cycle Output. 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2, 2 ATP. Electron Transport Chain Input. 10 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 O2, 34 ADP + 34 Pi. Electron Transport Chain Output. 10 NAD+, 2 FAD, 6 H20, 34 ATP. About us.
PPT Chapter 6 and 7 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4584730
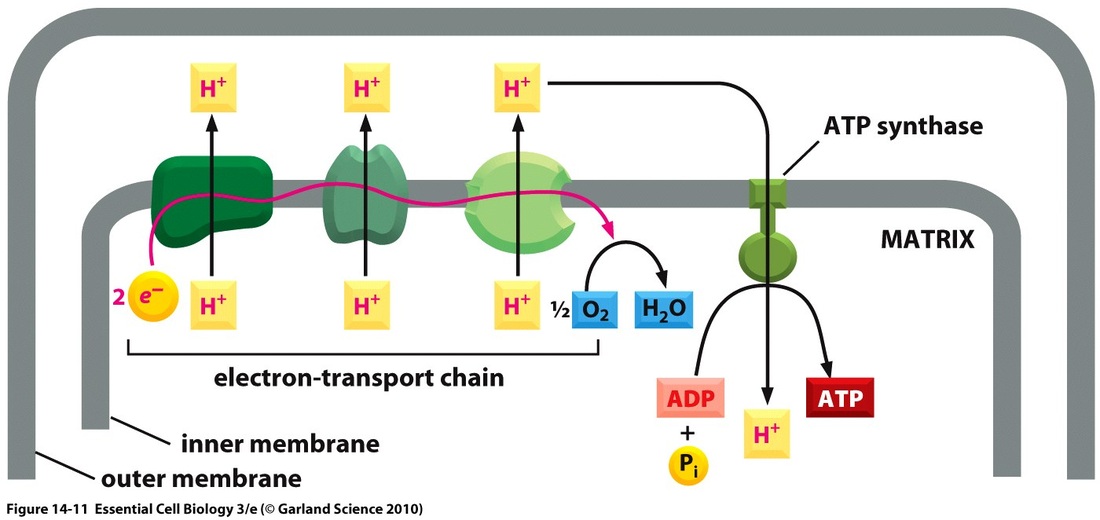
In the final step, the three NADH and one FADH2 amassed from the previous steps are used in oxidative phosphorylation, to make water and ATP.. 4 from complex III, and 2 from complex IV). ATP-synthase synthesizes 1 ATP for 4 H+ ions. Therefore, 1 NADH = 10 H+, and 10/4 H+ per ATP = 2.5 ATP per NADH (**some sources round up**). When NADH is.
Difference Between NADH and FADH2 Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
When electrons from NADH move through the transport chain, about 10 H + ions are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space, so each NADH yields about 2.5 ATP. Electrons from FADH 2 , which enter the chain at a later stage, drive pumping of only 6 H + , leading to production of about 1.5 ATP.

Ciencias de Joseleg NADH, FADH2 y la cadena de transporte de electrones
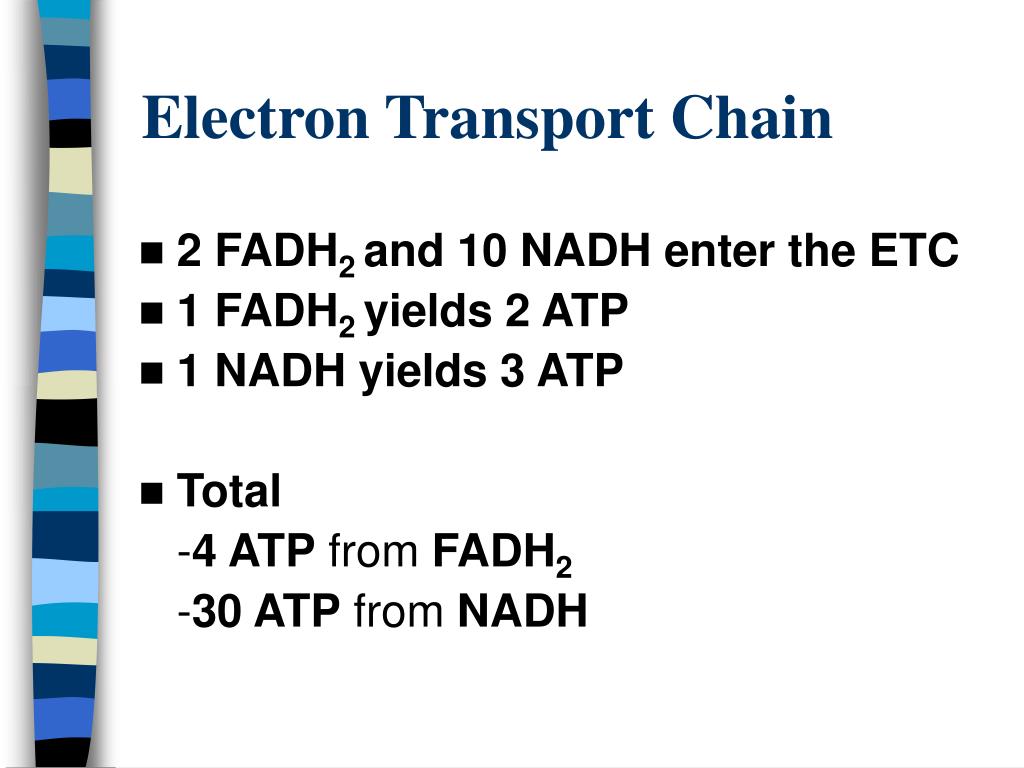
Total 10 NADH, 2 FADH2. Multiply that by the amount of ATP per NADH or FADH2 to yield: 10 NADH X 2.5 ATP/NADH = 25 ATP. 2 FADH2 X 1.5 ATP/FADH2 = 3 ATP. Total 28 ATP. The first video does a nice job of illustrating and reviewing the electron transport chain. Note that it uses 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2 so the totals from each cycle are.
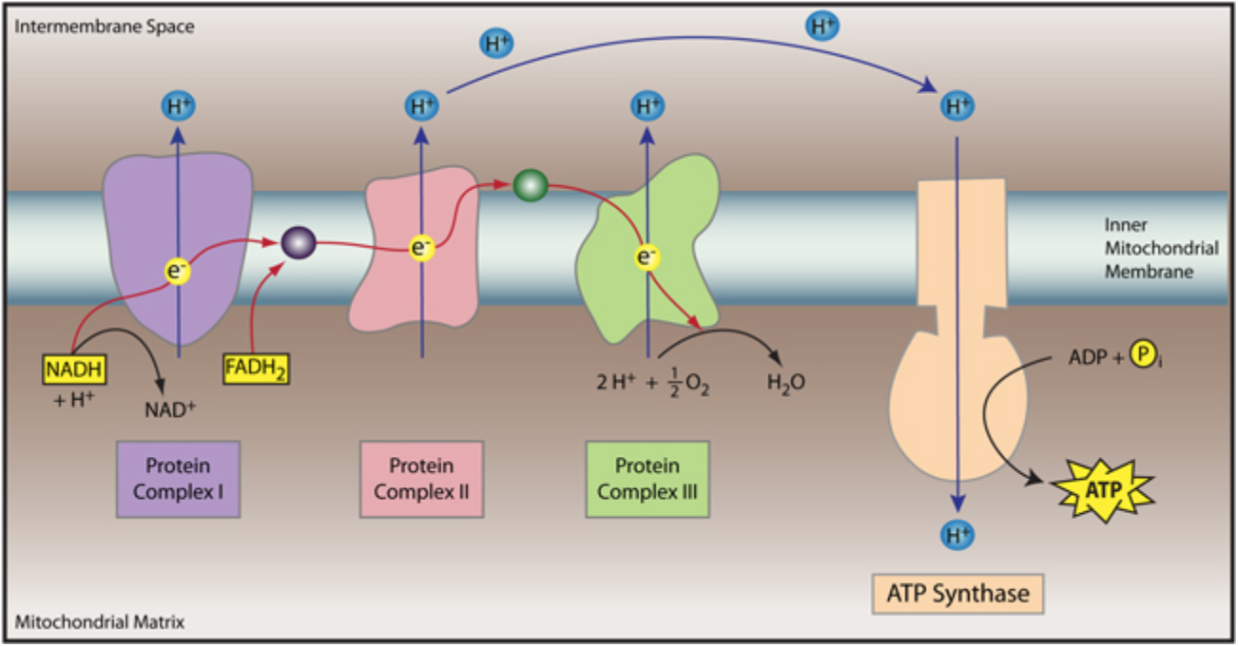
Complete the following paragraph to describe the role of nadh and fadh2 in cellular respiration.
The Electron Transport Chain. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons derived from NADH and FADH 2 combine with O 2, and the energy released from these oxidation/ reduction reactions is used to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADP.The transfer of electrons from NADH to O 2 is a very energy-yielding reaction, with ΔG°´ = -52.5 kcal/mol for each pair of electrons transferred.
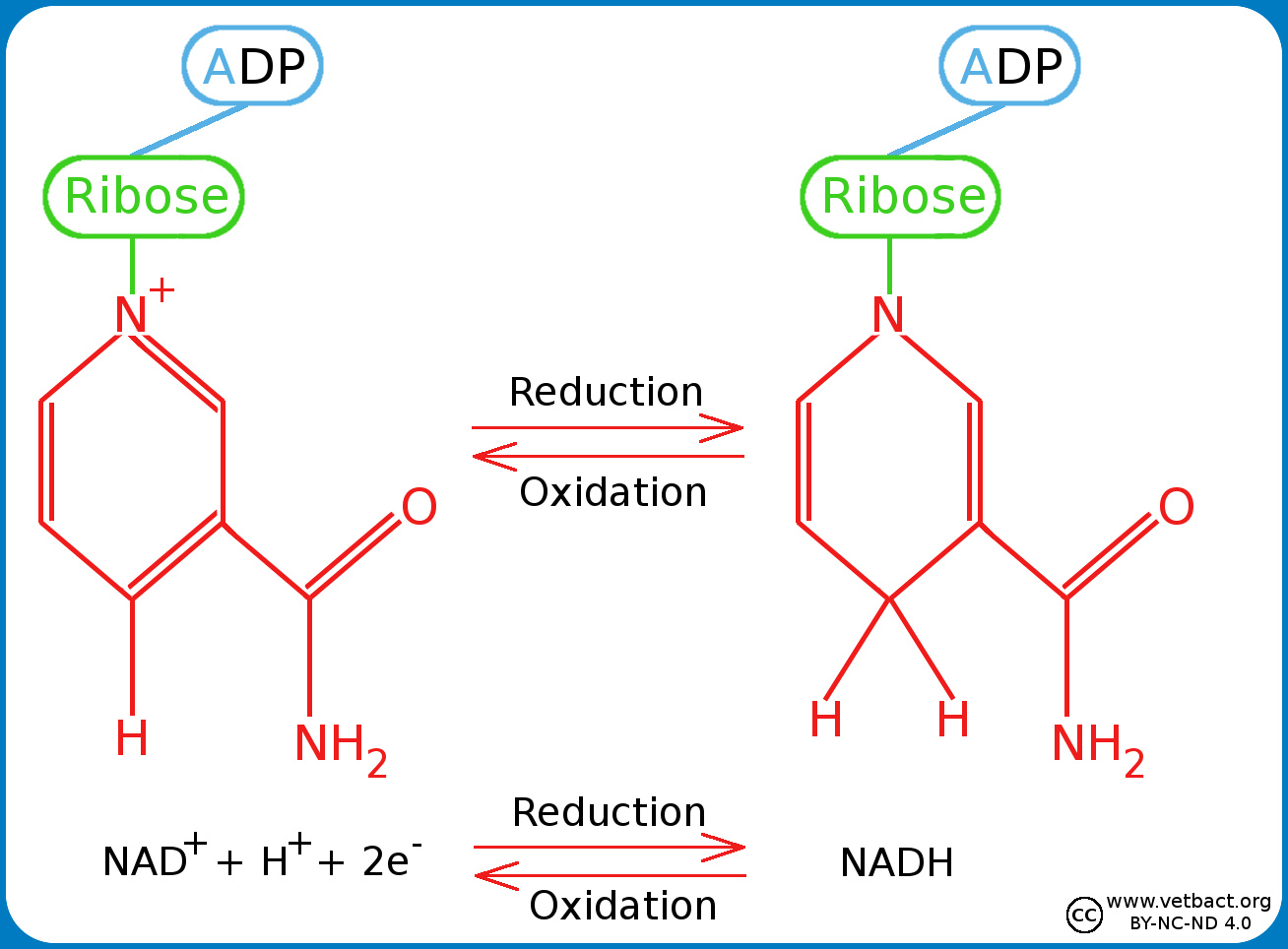
VetBact
Usually, that number varies in the oxidative phosphorylation step, depending on the amount of NADH and FADH2 available for the process. NADH produces 3 ATP while FADH2 produces 2 ATP via chemiosmosis. Glycolysis produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH, Krebs Cycle produces 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2. Then, you have a net total of 36 ATP.
Why are the two molecules of NADH and FADH2 generated in the TCA cycle not applicable with beta
10 NADH + 2 FADH 2 + O 2 ~ 32 ATP + H 2 O : Entire Cellular Respiration Process : Cytoplasm, mitochondria : 1 Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6), O 2 ~ 36 to 38 ATP, 6CO 2, 6H 2 O : Thus, the overall equation.

PPT Metabolisme Mikrobia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5362973
Consumed: 10 NADH, 2 FADH 2, 6 O 2, 32-34 ADP + 32-34 Pi; Produced: 10 NAD +, 2 FAD, 6 H 2 O, 32-34 ATP; Reaction: Electrons from NADH and FADH 2 are passed through protein complexes, pumping protons into the intermembrane space. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, forming water. The proton gradient drives ATP synthesis.

the differences between nadh versus fadh2
The reducing equivalents NADH and FADH 2 are essential products of the TCA that were used by the electron transport chain (ETC) to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation (Chandel 2020a). But an often-overlooked reducing equivalent is NADPH, which is not used for generating ATP but for biosynthesis of macromolecules. NADPH is the major.
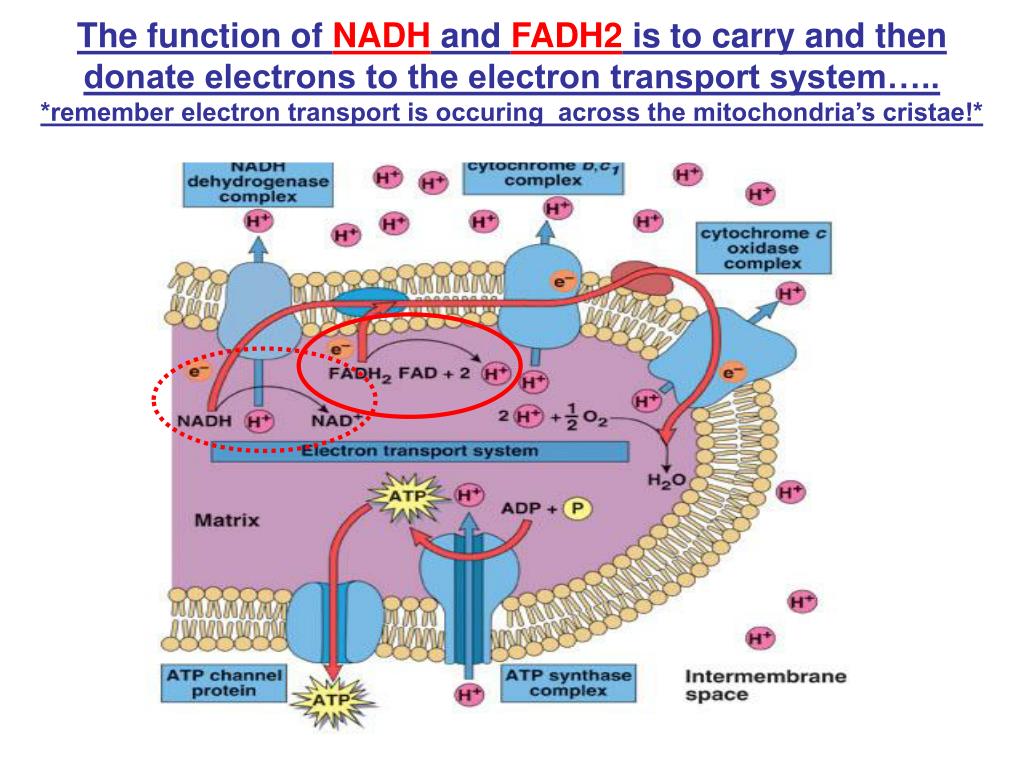
How Does Nadh And Fadh2 Donate Electrons To The Electron Transport Chain
Biology. Biology questions and answers. 1. A total of 10 NADH and 2 FADH2 molecules are formed during glycolysis and cellular respiration. List the stages where this occurs and the number of molecules produced at each location. 2. During what stages are most ATP molecules formed during cellular respiration (how much ATP is produced) 3.

PPT Cellular Respiration PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4875459
NAD: The full form of NAD is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. It is a cofactor that is found in living cells. It exists in two forms, that is oxidized form (NAD+) and reduced form (NADH). It carries electrons from one reaction to other. It has vital role in energy production via redox reaction. FAD+ is flavin adenine dinucleotide.
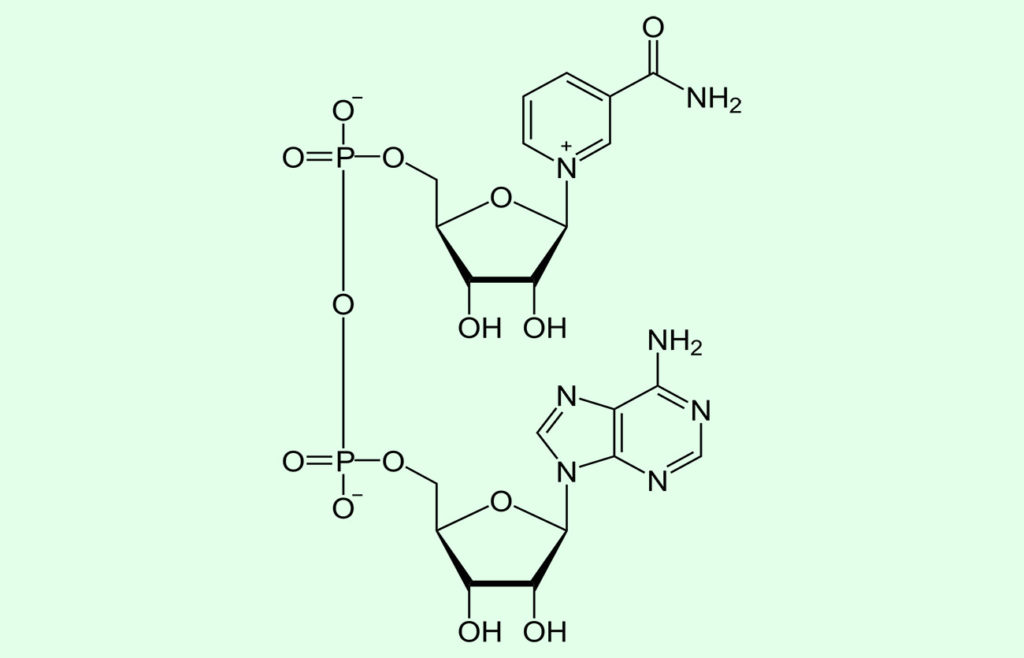
Diferencias entre NADH y FADH2 Sooluciona
Whatever you prefer to call it, the citric cycle is a central driver of cellular respiration. It takes acetyl CoA —produced by the oxidation of pyruvate and originally derived from glucose—as its starting material and, in a series of redox reactions, harvests much of its bond energy in the form of NADH , FADH 2 , and ATP.

Electron Transport Chain NADH and FADH2 YouTube
3 ATP per NADH. How many ATP are produced in the ETC per NADH produced in the transition reaction? Oxygen. What is the final electron acceptor in the ETC? Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 32-34 ATP, 10 NADH, 2 FADH2 and more.
UNIT 2 Metabolic Process Mind Map
Citric Acid Cycle: 6 NADH, 2 FADH2. Total 10 NADH, 2 FADH2. Multiply that by the amount of ATP per NADH or FADH2 to yield: 10 NADH X 2.5 ATP/NADH = 25 ATP 2 FADH2 X 1.5 ATP/FADH2 = 3 ATP. Total 28 ATP. The first video does a nice job of illustrating and reviewing the electron transport chain. Note that it uses 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2 so the.
nad+, fad Student Doctor Network
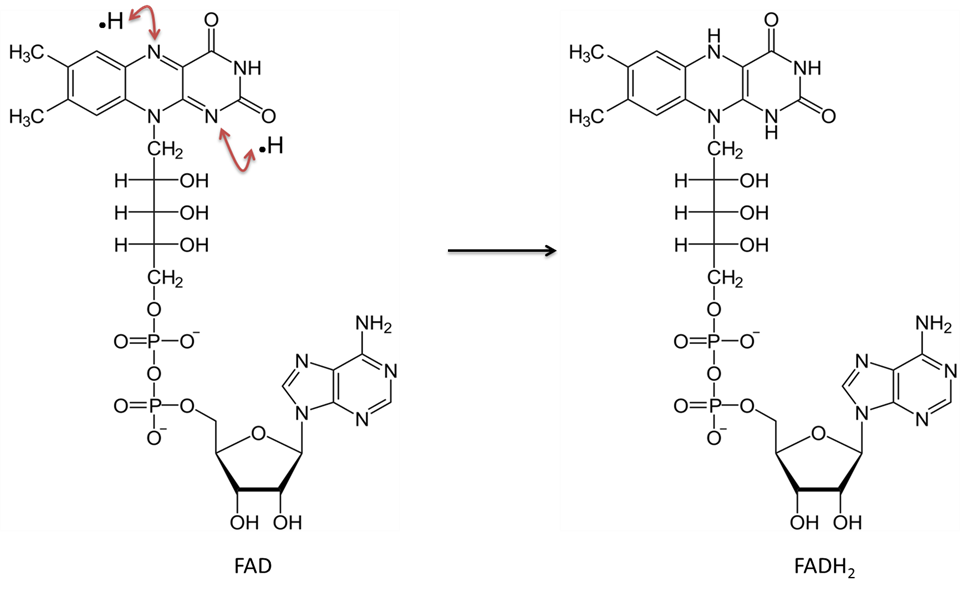
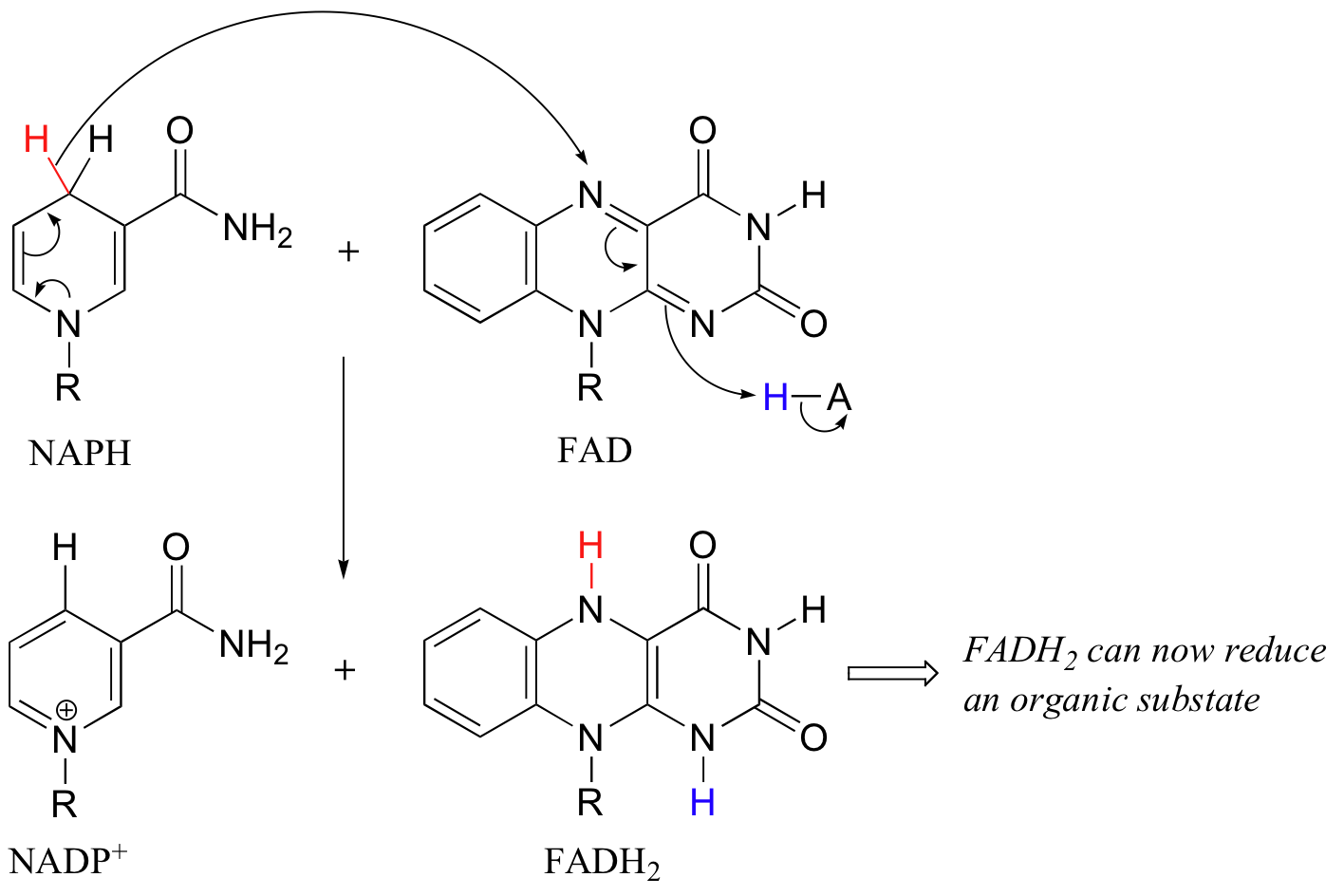
NAD + + 2 e − + 2 H + → NADH + H +. FAD + 2 e − + 2 H + → FADH 2. To see how a glucose molecule is converted into carbon dioxide and how its energy is harvested as ATP and NADH / FADH 2 in one of your body's cells, let's walk step by step through the four stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six.